Interactions between vascular endothelial growth factor and neuroglobin
- PMID: 22583764
- PMCID: PMC3371093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.05.018
Interactions between vascular endothelial growth factor and neuroglobin
Abstract
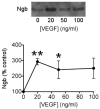
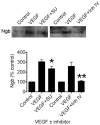
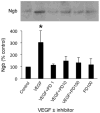
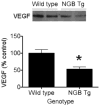
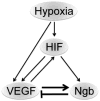
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and neuroglobin (Ngb) participate in neuronal responses to hypoxia and ischemia, but the relationship between their effects, if any, is unknown. To address this issue, we measured Ngb levels in VEGF-treated mouse cerebrocortical cultures and VEGF levels in cerebrocortical cultures from Ngb-overexpressing transgenic mice. VEGF stimulated Ngb expression in a VEGFR2/Flk1 receptor-dependent manner, whereas Ngb overexpression suppressed expression of VEGF. These findings provide further insight into hypoxia-stimulated neuronal signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroglobin-overexpression alters hypoxic response gene expression in primary neuron culture following oxygen glucose deprivation.Neuroscience. 2009 Aug 18;162(2):396-403. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.04.055. Epub 2009 May 3. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19401220 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial distribution of neuroglobin and its response to oxygen-glucose deprivation in primary-cultured mouse cortical neurons.Neuroscience. 2012 Aug 30;218:235-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.05.054. Epub 2012 May 29. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22659017 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroglobin-overexpressing transgenic mice are resistant to cerebral and myocardial ischemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 21;103(47):17944-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607497103. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17098866 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroglobin and neuronal cell survival.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Sep;1834(9):1744-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.01.015. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23357651 Review.
-
Neuroglobin: an endogenous neuroprotectant.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008 Feb;8(1):20-4. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2007.09.003. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17942367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroglobin, a Factor Playing for Nerve Cell Survival.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 31;17(11):1817. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111817. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27809238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroglobin mediates neuroprotection of hypoxic postconditioning against transient global cerebral ischemia in rats through preserving the activity of Na+/K+ ATPases.Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 25;9(6):635. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0656-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29802248 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from the post-genomic era: Globin diversity beyond oxygen binding and transport.Redox Biol. 2020 Oct;37:101687. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101687. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32863222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protection by Neuroglobin Expression in Brain Pathologies.Front Neurol. 2016 Sep 12;7:146. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00146. eCollection 2016. Front Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27672379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Neuroglobin Is Necessary for Protection Induced by Conditioned Medium from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Astrocytic Cells Subjected to Scratch and Metabolic Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jul;56(7):5167-5187. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1442-9. Epub 2018 Dec 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30536184
References
-
- Croll SD, Wiegand SJ. Vascular growth factors in cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol. 2001;23:121–135. - PubMed
-
- De Marinis E, Ascenzi P, Pellegrini M, Galluzzo P, Bulzomi P, Arevalo MA, Garcia-Segura LM, Marino M. 17β-Estradiol--a new modulator of neuroglobin levels in neurons: role in neuroprotection against H2O2-induced toxicity. Neurosignals. 2010;18:223–235. - PubMed
-
- Deudero JJ, Caramelo C, Castellanos MC, Neria F, Fernandez-Sanchez R, Calabia O, Penate S, Gonzalez-Pacheco FR. Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α gene expression by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:11435–11444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

