Effect of specific activation of γ-aminobutyric acid receptor in vivo on oxidative stress-induced damage after extended hepatectomy
- PMID: 22583816
- PMCID: PMC3438378
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01030.x
Effect of specific activation of γ-aminobutyric acid receptor in vivo on oxidative stress-induced damage after extended hepatectomy
Abstract
Aim: γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a multifunctional molecule with various physiological effects throughout the body. The regulation of GABA receptor (GABAR) plays a key role in reducing the damage mediated by oxidative stress (OS). Extended hepatectomy causes fatal OS-induced injury in the liver remnant. We aimed to investigate the effect of a GABAR agonist in extended hepatectomy.
Methods: Saline or a GABAR agonist (43.56 nmol/g bodyweight of muscimol) was administrated intravenously at 4 h preoperatively. C57BL/6 mice were divided into three groups: laparotomy only, 90% hepatectomy with saline and 90% hepatectomy with a GABAR agonist. Liver samples were obtained at 6 h after surgery.
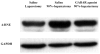
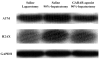
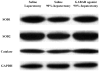
Results: Survival curves were prolonged by the GABAR agonist. Histopathological findings and biochemical profiles showed that the GABAR agonist reduced liver damage. Immunohistological assessment demonstrated that the GABAR agonist prevented apoptotic induction. As shown by 4-hydroxynonenal, which reflects OS-induced damage, 90% hepatectomy caused OS and the GABAR agonist reduced OS. We measured ataxia-telangiectasia mutated kinase (ATM), H2AX, Akt and free radical scavenging enzymes because they may be affected by GABAR regulation, and found that Akt was greatly decreased after 90% hepatectomy, but it recovered with the GABAR agonist.
Conclusion: GABAR is activated by a specific agonist in the liver in vivo. This activation reduces OS-mediated damage after extended hepatectomy in vivo, and the mechanism via an Akt-dependent pathway may be a key.
© 2012 The Japan Society of Hepatology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
















Similar articles
-
Pretreatment of liver grafts in vivo by γ-aminobutyric acid receptor regulation reduces cold ischemia/warm reperfusion injury in rat.Ann Transplant. 2013 Jun 17;18:299-313. doi: 10.12659/AOT.883955. Ann Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23792534 Free PMC article.
-
Liver graft pretreated in vivo or ex vivo by γ-aminobutyric acid receptor regulation.J Surg Res. 2013 Jun 1;182(1):166-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.08.055. Epub 2012 Sep 15. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23010512 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment of Small-for-Size Grafts In Vivo by γ -Aminobutyric Acid Receptor Regulation against Oxidative Stress-Induced Injury in Rat Split Orthotopic Liver Transplantation.Int J Hepatol. 2013;2013:149123. doi: 10.1155/2013/149123. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Int J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 24223309 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in mouse cultured spinal neurones.J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:243-86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016493. J Physiol. 1987. PMID: 2443667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Competitive Antagonists of Insect Ionotropic γ-Aminobutyric Acid Receptors as Insecticides.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Apr 29;68(17):4760-4768. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b08189. Epub 2020 Apr 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32243147 Review.
Cited by
-
Inactivation of GABAA receptor is related to heat shock stress response in organism model Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016 Sep;21(5):763-72. doi: 10.1007/s12192-016-0701-9. Epub 2016 May 27. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016. PMID: 27230213 Free PMC article.
-
GABA, γ-Aminobutyric Acid, Protects Against Severe Liver Injury.J Surg Res. 2019 Apr;236:172-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.11.047. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 30694753 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment of liver grafts in vivo by γ-aminobutyric acid receptor regulation reduces cold ischemia/warm reperfusion injury in rat.Ann Transplant. 2013 Jun 17;18:299-313. doi: 10.12659/AOT.883955. Ann Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23792534 Free PMC article.
-
γ-Aminobutyric Acid Effectively Modulate Growth Performance, Physiological Response of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus Salmoides) Under Combined Stress of Flow Velocity and Density.Aquac Nutr. 2024 Oct 24;2024:9180554. doi: 10.1155/2024/9180554. eCollection 2024. Aquac Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39555528 Free PMC article.
-
Diacylglycerol kinase alpha regulates post-hepatectomy liver regeneration.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84403-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acuna Castroviejo D, Lopez LC, Escames G, Lopez A, Garcia JA, Reiter RJ. Melatonin-mitochondria interplay in health and disease. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11:221–40. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh N, Ghosh R, Mandal SC. Antioxidant protection: A promising therapeutic intervention in neurodegenerative disease. Free Radic Res. 2011;45:888–905. - PubMed
-
- Turan B. Role of antioxidants in redox regulation of diabetic cardiovascular complications. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010;11:819–36. - PubMed
-
- Andang M, Hjerling-Leffler J, Moliner A, Lundgren TK, Castelo-Branco G, Nanou E, et al. Histone H2AX-dependent GABA(A) receptor regulation of stem cell proliferation. Nature. 2008;451:460–4. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

