Green tea halts progression of cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis: an observational report
- PMID: 22584381
- PMCID: PMC3445797
- DOI: 10.1007/s00392-012-0463-z
Green tea halts progression of cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis: an observational report
Abstract
Background: Treatment options in patients with amyloidotic transthyretin (ATTR) cardiomyopathy are limited. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), the most abundant catechin in green tea (GT), inhibits fibril formation from several amyloidogenic proteins in vitro. Thus, it might also halt progression of TTR amyloidosis. This is a single-center observational report on the effects of GT consumption in patients with ATTR cardiomopathy.
Methods: 19 patients with ATTR cardiomyopathy were evaluated by standard blood tests, echocardiography, and cardiac MRI (n = 9) before and after consumption of GT and/or green tea extracts (GTE) for 12 months.
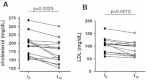
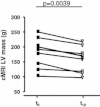
Results: Five patients were not followed up for reasons of death (n = 2), discontinuation of GT/GTE consumption (n = 2), and heart transplantation (n = 1). After 12 months no increase of left ventricular (LV) wall thickness and LV myocardial mass was observed by echocardiography. In the subgroup of patients evaluated by cardiac MRI a mean decrease of LV myocardial mass (-12.5 %) was detected in all patients. This was accompanied by an increase of mean mitral annular systolic velocity of 9 % in all 14 patients. Total cholesterol (191.9 ± 8.9 vs. 172.7 ± 9.4 mg/dL; p < 0.01) and LDL cholesterol (105.8 ± 7.6 vs. 89.5 ± 8.0 mg/dL; p < 0.01) decreased significantly during the observational period. No serious adverse effects were reported by any of the participants.
Conclusions: Our observation suggests an inhibitory effect of GT and/or GTE on the progression of cardiac amyloidosis. We propose a randomized placebo-controlled investigation to confirm our observation.
Figures


References
-
- Puille M, Altland K, Linke RP, Klett R, Bauer R (2002) Tc99 m-DPD scintigraphy in transthyretin-type amyloidosis. Presented at the 5th Internat. Symposium on Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy and Other Related Disorders, Sept 25–27, 2002 Matsumoto, Japan
-
- Cibeira MT, Sanchorawala V, Seldin DC, Quillen K, Berk JL, Dember LM, Segal A, Ruberg F, Meier-Ewert H, Andrea NT, Sloan JM, Finn KT, Doros G, Blade J, Skinner M. Outcome of AL amyloidosis after high-dose melphalan and autologous stem cell transplantation: long-term results in a series of 421 patients. Blood. 2011;118:4346–4352. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-330738. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

