Efficacy of daptomycin-cloxacillin combination in experimental foreign-body infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 22585211
- PMCID: PMC3393403
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00127-12
Efficacy of daptomycin-cloxacillin combination in experimental foreign-body infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
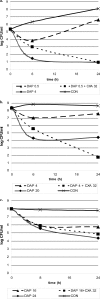
Despite the use of daptomycin alone at high doses (greater than 6 mg/kg of body weight/day) against difficult-to-treat infections, clinical failures and resistance appeared. Recently, the combination daptomycin-cloxacillin showed enhanced efficacy in clearing bacteremia caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of daptomycin at usual and high doses (equivalent to 6 and 10 mg/kg/day in humans, respectively) in combination with cloxacillin in a rat tissue cage infection model by MRSA and to compare its efficacy to that of daptomycin-rifampin. We used MRSA strain ATCC BAA-39. In the log- and stationary-phase kill curves, daptomycin-cloxacillin improved the bactericidal activity of daptomycin, especially in log phase. For in vivo studies, therapy was administered intraperitoneally for 7 days with daptomycin at 100 mg/kg/day and 45/mg/kg/day (daptomycin 100 and daptomycin 45), daptomycin 100-cloxacillin at 200 mg/kg/12 h, daptomycin 45-cloxacillin, and daptomycin 100-rifampin at 25 mg/kg/12 h. Daptomycin-rifampin was the best therapy (P < 0.05). Daptomycin 45 was the least effective treatment and did not protect against the emergence of resistant strains. There were no differences between the two dosages of daptomycin plus cloxacillin in any situation, and both protected against resistance. The overall effect of the addition of cloxacillin to daptomycin was a significantly greater cure rate (against adhered bacteria) than that for daptomycin alone. In conclusion, daptomycin-cloxacillin enhanced modestly the in vivo efficacy of daptomycin alone against foreign-body infection by MRSA and was less effective than daptomycin plus rifampin. The benefits of adding cloxacillin to daptomycin should be especially evaluated against infections by rifampin-resistant MRSA and for protection against the emergence of daptomycin nonsusceptibility.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of usual and high doses of daptomycin in combination with rifampin versus alternative therapies in experimental foreign-body infection by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Dec;54(12):5251-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00226-10. Epub 2010 Oct 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20921321 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacies of cloxacillin-daptomycin and the standard cloxacillin-rifampin therapies against an experimental foreign-body infection by methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Sep;58(9):5576-80. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02681-14. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24957833 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of high doses of daptomycin versus alternative therapies against experimental foreign-body infection by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Oct;53(10):4252-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00208-09. Epub 2009 Jul 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19635963 Free PMC article.
-
Fosfomycin-daptomycin and other fosfomycin combinations as alternative therapies in experimental foreign-body infection by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jan;57(1):606-10. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01570-12. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23089756 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteremia due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update on New Therapeutic Approaches.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2020 Dec;34(4):849-861. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 33011050 Review.
Cited by
-
Assembly of Complete Genome Sequences of Negative-Control and Experimental Strain Variants of Staphylococcus aureus ATCC BAA-39 Selected under the Effect of the Drug FS-1, Which Induces Antibiotic Resistance Reversion.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2019 Jul 25;8(30):e00579-19. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00579-19. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2019. PMID: 31346020 Free PMC article.
-
Caprine abscess model of tulathromycin concentrations in interstitial fluid from tissue chambers inoculated with Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis following subcutaneous or intrachamber administration.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Dec;57(12):6295-304. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00936-13. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 24100501 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Ceftobiprole and Daptomycin at Bone Concentrations Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm: Results of a Dynamic In Vitro PK/PD Model.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Apr 5;14(4):386. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14040386. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298551 Free PMC article.
-
CAMERA2 - combination antibiotic therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2016 Mar 31;17:170. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1295-3. Trials. 2016. PMID: 27029920 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of the combination of daptomycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole on clinical outcomes in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Apr;59(4):1969-76. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04141-14. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25605354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2009. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility test for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved standard, 8th ed, M7-A8 CLSI, Wayne, PA
-
- Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP. 1999. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322 - PubMed
-
- Craig WA. 1998. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters: rationale for antibacterial dosing of mice and men. Clin. Infect. Dis. 26:1–12 - PubMed
-
- Chapin-Robertson K, Edberg SC. 1991. Measurements of antibiotics in human body fluids: techniques and significance, p 295–366 In Lorian V. (ed), Antibiotics in laboratory medicine. Williams & Wilkins Co., New York, NY
-
- Chuard C, et al. 1991. Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus recovered from infected foreign body in vivo to killing by antimicrobials. J. Infect. Dis. 163:1369–1373 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical