Infant outcomes after maternal antiretroviral exposure in resource-limited settings
- PMID: 22585772
- PMCID: PMC3362906
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2011-2340
Infant outcomes after maternal antiretroviral exposure in resource-limited settings
Abstract
Background and objective: The impact of maternal antiretrovirals (ARVs) during pregnancy, labor, and postpartum on infant outcomes is unclear.
Methods: Infants born to HIV-infected mothers in ARV studies were followed for 18 months.
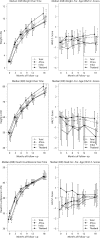
Results: Between June 2006 and December 2008, 236 infants enrolled from Africa (n = 36), India (n = 47), Thailand (n = 152), and Brazil (n = 1). Exposure to ARVs in pregnancy included ≥ 3 ARVs (10%), zidovudine/intrapartum ARV (81%), and intrapartum ARV (9%). There were 4 infant infections (1 in utero, 3 late postpartum) and 4 deaths with 1.8% mortality (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.1%-3.5%) and 96.4% HIV-1-free survival (95% CI, 94.0%-98.9%). Birth weight was ≥ 2.5 kg in 86%. In the first 6 months, Indian infants (nonbreastfed) had lowest median weights and lengths and smallest increases in growth. After 6 months, African infants had the lowest median weight and weight-for-age z scores. Infants exposed to highest maternal viral load had the lowest height and height-for-age z scores. Serious adverse events occurred in 38% of infants, did not differ by country, and correlated with less maternal ARV exposure. Clinical diagnoses were seen in 84% of Thai, 31% of African, and 9% of Indian infants. Congenital defects/inborn errors of metabolism were seen in 18 (7.6%) infants, of which 17 were Thai (11%: 95% CI, 6.7%-17.0%); none had first trimester ARV exposure.
Conclusions: Infant follow-up in large international cohorts is feasible and provides important safety and HIV transmission data following maternal ARV exposure. Increased surveillance increases identification of congenital/inborn errors.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00084136.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Rapid advice: use of antiretroviral drugs for treating pregnant women and preventing HIV infection in infants. November, 2009. Available at: www.who.int/hiv/pub/mtct/advice/en/ Accessed May 29, 2011
-
- Dorenbaum A, Cunningham CK, Gelber RD, et al. International PACTG 316 Team Two-dose intrapartum/newborn nevirapine and standard antiretroviral therapy to reduce perinatal HIV transmission: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2002;288(2):189–198 - PubMed
-
- Lallemant M, Jourdain G, Le Coeur S, et al. Perinatal HIV Prevention Trial (Thailand) Investigators Single-dose perinatal nevirapine plus standard zidovudine to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Thailand. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(3):217–228 - PubMed
-
- Marazzi MC, Nielsen-Saines K, Buonomo E, et al. Increased infant human immunodeficiency virus-type one free survival at one year of age in sub-Saharan Africa with maternal use of highly active antiretroviral therapy during breastfeeding. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28(6):483–487 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- AI68634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U01 AI069463-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI069512/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800001G/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069429/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI046749/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U01 AI069450/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI041110/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069518/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068616/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069399/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U01 AI069399-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HD-3-3345/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069512/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI047986/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U01 AI069436-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068616/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069450/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800001C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U01 AI069518/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U01 AI068616/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U01 AI41110/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069436/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical