A20 ubiquitin ligase-mediated polyubiquitination of RIP1 inhibits caspase-8 cleavage and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioblastoma
- PMID: 22585859
- PMCID: PMC3354650
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0172
A20 ubiquitin ligase-mediated polyubiquitination of RIP1 inhibits caspase-8 cleavage and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioblastoma
Abstract
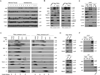
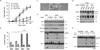
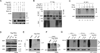
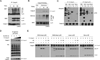
The TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) apoptotic pathway has emerged as a therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer. However, clinical trials have proven that the vast majority of human cancers are resistant to TRAIL apoptotic pathway-targeted therapies. We show that A20-mediated ubiquitination inhibits caspase-8 cleavage and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioblastoma through 2 signaling complexes. A20 is highly expressed in glioblastomas and, together with the death receptor 5 and receptor-interacting protein 1, forms a plasma membrane-bound preligand assembly complex under physiologic conditions. Treatment with TRAIL leads to the recruitment of caspase-8 to the plasma membrane-bound preligand assembly complex for the assembly of a death-inducing signaling complex. In the death-inducing signaling complex, the C-terminal zinc finger (Znf) domain of the A20 ubiquitin ligase mediates receptor-interacting protein 1 polyubiquitination through lysine-63-linked polyubiquitin chains, which bind to the caspase-8 protease domain and inhibit caspase-8 dimerization, cleavage, and the initiation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioblastoma-derived cell lines and tumor-initiating cells.
Significance: These results identify A20 E3 ligase as a therapeutic target whose inhibition can overcome TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in glioblastoma and thus have an impact on ongoing clinical trials of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-targeted combination cancer therapies.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

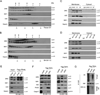
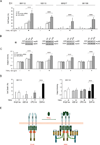
Comment in
-
Regulating the TRAIL of destruction: how A20 protects glioblastomas from TRAIL-mediated death.Cancer Discov. 2012 Feb;2(2):112-4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0350. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22585854
Similar articles
-
E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases as modulators of TRAIL-mediated extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway.BMB Rep. 2019 Feb;52(2):119-126. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.2.011. BMB Rep. 2019. PMID: 30638181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulating the TRAIL of destruction: how A20 protects glioblastomas from TRAIL-mediated death.Cancer Discov. 2012 Feb;2(2):112-4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0350. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22585854
-
miR-200a enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by targeting A20.Cell Biol Int. 2018 May;42(5):506-514. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10924. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Cell Biol Int. 2018. PMID: 29274253
-
Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Sensitizes TRAIL-Induced Hepatocyte Apoptosis by Inhibiting the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase A20.PLoS One. 2015 May 20;10(5):e0127329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127329. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25993287 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of apoptosis.Trends Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;19(3):130-40. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.01.004. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Trends Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19217783 Review.
Cited by
-
E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases as modulators of TRAIL-mediated extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway.BMB Rep. 2019 Feb;52(2):119-126. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.2.011. BMB Rep. 2019. PMID: 30638181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting CAND1 promotes caspase-8/RIP1-dependent apoptosis in liver cancer cells.Am J Transl Res. 2018 May 15;10(5):1357-1372. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29887951 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogen-induced ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 bifunctionally shuts off NF-κB and caspase-8-dependent apoptotic cell death.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Sep;24(9):1621-1631. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.89. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28574503 Free PMC article.
-
The API2-MALT1 fusion exploits TNFR pathway-associated RIP1 ubiquitination to promote oncogenic NF-κB signaling.Oncogene. 2014 May 8;33(19):2520-30. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.195. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23770847 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications as key regulators of TNF-induced necroptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jul 7;7(7):e2293. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.197. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27383048 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–682. - PubMed
-
- Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:12687–12690. - PubMed
-
- Vesely MD, Kershaw MH, Schreiber RD, Smyth MJ. Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu Rev Immunol. 2011;29:235–271. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone RW, Frew AJ, Smyth MJ. The TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:782–798. - PubMed
-
- Bellail AC, Qi L, Mulligan P, Chhabra V, Hao C. TRAIL agonists on clinical trials for cancer therapy: the promises and the challenges. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2009;4:34–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

