Orai1, STIM1, and their associating partners
- PMID: 22586216
- PMCID: PMC3473276
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.231522
Orai1, STIM1, and their associating partners
Abstract
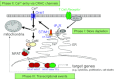
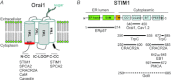
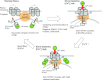
Store-operated Ca(2+) (SOC) entry is one of the major mechanisms to raise intracellular Ca(2+) concentration in non-excitable cells. Ca(2+)-release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channels are a subtype of SOC channels that are extensively characterized in immune cells. Identification of STIM1 as an endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) sensor and Orai1 as the pore subunit has dramatically advanced the molecular understanding of CRAC channels. Recent efforts have focused on understanding the physiological aspects of CRAC channels at an organism level using transgenic animal models and at a molecular level using electrophysiological and biochemical tools. In this review, we summarize our current understanding of the interacting partners of Orai and STIM proteins in the regulation of CRAC channel activity and other non-CRAC channel-related functions.
Figures
References
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:517–529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

