ChREBP mediates glucose-stimulated pancreatic β-cell proliferation
- PMID: 22586588
- PMCID: PMC3402328
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0802
ChREBP mediates glucose-stimulated pancreatic β-cell proliferation
Abstract
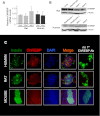
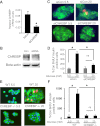
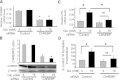
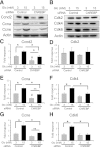
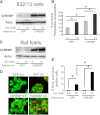
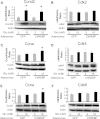
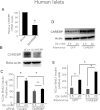
Glucose stimulates rodent and human β-cell replication, but the intracellular signaling mechanisms are poorly understood. Carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) is a lipogenic glucose-sensing transcription factor with unknown functions in pancreatic β-cells. We tested the hypothesis that ChREBP is required for glucose-stimulated β-cell proliferation. The relative expression of ChREBP was determined in liver and β-cells using quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR), immunoblotting, and immunohistochemistry. Loss- and gain-of-function studies were performed using small interfering RNA and genetic deletion of ChREBP and adenoviral overexpression of ChREBP in rodent and human β-cells. Proliferation was measured by 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine incorporation, [(3)H]thymidine incorporation, and fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis. In addition, the expression of cell cycle regulatory genes was measured by qRT-PCR and immunoblotting. ChREBP expression was comparable with liver in mouse pancreata and in rat and human islets. Depletion of ChREBP decreased glucose-stimulated proliferation in β-cells isolated from ChREBP(-/-) mice, in INS-1-derived 832/13 cells, and in primary rat and human β-cells. Furthermore, depletion of ChREBP decreased the glucose-stimulated expression of cell cycle accelerators. Overexpression of ChREBP amplified glucose-stimulated proliferation in rat and human β-cells, with concomitant increases in cyclin gene expression. In conclusion, ChREBP mediates glucose-stimulated proliferation in pancreatic β-cells.
Figures

References
-
- Muoio DM, Newgard CB. Mechanisms of disease: molecular and metabolic mechanisms of insulin resistance and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008;9:193–205 - PubMed
-
- Cozar-Castellano I, Fiaschi-Taesch N, Bigatel TA, et al. . Molecular control of cell cycle progression in the pancreatic beta-cell. Endocr Rev 2006;27:356–370 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

