Essential roles of EphB receptors and EphrinB ligands in endothelial cell function and angiogenesis
- PMID: 22588055
- PMCID: PMC3500853
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386503-8.00002-8
Essential roles of EphB receptors and EphrinB ligands in endothelial cell function and angiogenesis
Abstract
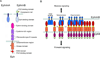
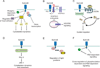
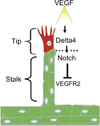
Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and their Ephrin ligands represent an important signaling system with widespread roles in cell physiology and disease. Receptors and ligands in this family are anchored to the cell surface; thus Eph/Ephrin interactions mainly occur at sites of cell-to-cell contact. EphB4 and EphrinB2 are the Eph/Ephrin molecules that play essential roles in vascular development and postnatal angiogenesis. Analysis of expression patterns and function has linked EphB4/EphrinB2 to endothelial cell growth, survival, migration, assembly, and angiogenesis. Signaling from these molecules is complex, with the potential for being bidirectional, emanating both from the Eph receptors (forward signaling) and from the Ephrin ligands (reverse signaling). In this review, we describe recent advances on the roles of EphB/EphrinB protein family in endothelial cell function and outline potential approaches to inhibit pathological angiogenesis based on this understanding.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Adams RH, Diella F, Hennig S, Helmbacher F, Deutsch U, Klein R. The cytoplasmic domain of the ligand ephrinB2 is required for vascular morphogenesis but not cranial neural crest migration. Cell. 2001;104:57–69. - PubMed
-
- Alon T, Hemo I, Itin A, Pe’er J, Stone J, Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat. Med. 1995;1:1024–1028. - PubMed
-
- Armulik A, Abramsson A, Betsholtz C. Endothelial/pericyte interactions. Circ. Res. 2005;97:512–523. - PubMed
-
- Armulik A, Genove G, Mae M, Nisancioglu MH, Wallgard E, Niaudet C, He L, Norlin J, Lindblom P, Strittmatter K, Johansson BR, Betsholtz C. Pericytes regulate the blood–brain barrier. Nature. 2010;468:557–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

