Evaluation of the behavioral and pharmacokinetic profile of SYA013, a homopiperazine analog of haloperidol in rats
- PMID: 22588199
- PMCID: PMC3383382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.05.003
Evaluation of the behavioral and pharmacokinetic profile of SYA013, a homopiperazine analog of haloperidol in rats
Abstract
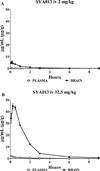
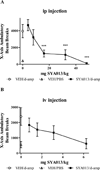
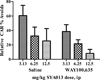
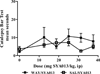
SYA013, a homopiperazine analog of haloperidol, was further evaluated for antipsychotic potential using additional animal models. Previously, SYA013 was tested in mice with an antipsychotic screening model in which it inhibited apomorphine induced climbing behavior, indicating antagonism of the dopaminergic system and the potential for use in the treatment of schizophrenia. In this study, SYA013 was shown to inhibit both d-amphetamine-induced locomotor activity in rats and conditioned avoidance response (CAR) in rats in a dose dependent manner and in the case of CAR, without producing any escape failure responses (EFRs), two tests predictive of antipsychotic action. The selective 5HT(1A) antagonist WAY100,635 was used to determine if binding of SYA013 to the 5HT(1A) receptor contributed to suppression of CAR. The results indicated that 0.63mg/kg WAY100,635 did not have a significant effect on the inhibition of CAR by SYA013. Pharmacokinetic parameters in brain and plasma were determined for SYA013. A log brain/plasma concentration ratio at a t(max) of 1.48 suggests that SYA013 readily crosses the blood brain barrier (BBB). The hypothesis that binding of SYA013 to the 5HT(1A) receptor contributed to the lack of significant catalepsy was investigated using the 5HT(1A) antagonist WAY100,635. The results of acute and semi-chronic tests suggest that binding to the 5HT(1A) receptor alone did not significantly account for the lack of catalepsy. Lack of catalepsy was preserved after the semi-chronic challenge with SYA013. These tests further indicate that SYA013 has a pharmacological profile with the potential for use in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases. In addition, the 5HT(1A) receptor does not appear to play a significant role in the pharmacological profile of SYA013.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Ahlenius S, Hillegaart V. Involvement of extrapyramidal motor mechanisms in the suppression of locomotor activity by antipsychotic drugs: a comparison between the effects produced by pre- and postsynaptic inhibition of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1986;24:1409–1415. - PubMed
-
- Arnt J. Pharmacological specificity of conditioned avoidance response inhibition in rats. Inhibition by neuroleptics and correlation to dopamine receptor blockade. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;51:321–329. - PubMed
-
- Arterburn D, Rukstalis M, Wood C, Westbrook E, Theis K, Daar Z, Still C, Gerhard G. C-a3-02: identification of extreme weight gain among users of atypical antipsychotic medications. Clin Med Res. 2011;9(3–4):160.
-
- Assie M-B, Koek W. Effects of 5-HT1A receptor antagonists on hippocampal 5-hydroxytryptamine levels: (S)-WAY100135, but not WAY100635, has partial agonist properties. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996;304:15–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

