Preexisting MEK1 exon 3 mutations in V600E/KBRAF melanomas do not confer resistance to BRAF inhibitors
- PMID: 22588879
- PMCID: PMC3594852
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0022
Preexisting MEK1 exon 3 mutations in V600E/KBRAF melanomas do not confer resistance to BRAF inhibitors
Abstract
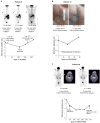
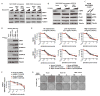
BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) induce antitumor responses in nearly 60% of patients with advanced V600E/KBRAF melanomas. Somatic activating MEK1 mutations are thought to be rare in melanomas, but their potential concurrence with V600E/KBRAF may be selected for by BRAFi. We sequenced MEK1/2 exon 3 in melanomas at baseline and upon disease progression. Of 31 baseline V600E/KBRAF melanomas, 5 (16%) carried concurrent somatic BRAF/MEK1 activating mutations. Three of 5 patients with BRAF/MEK1 double-mutant baseline melanomas showed objective tumor responses, consistent with the overall 60% frequency. No MEK1 mutation was found in disease progression melanomas, except when it was already identified at baseline. MEK1-mutant expression in V600E/KBRAF melanoma cell lines resulted in no significant alterations in p-ERK1/2 levels or growth-inhibitory sensitivities to BRAFi, MEK1/2 inhibitor (MEKi), or their combination. Thus, activating MEK1 exon 3 mutations identified herein and concurrent with V600E/KBRAF do not cause BRAFi resistance in melanoma.
Significance: As BRAF inhibitors gain widespread use for treatment of advanced melanoma, biomarkers for drug sensitivity or resistance are urgently needed. We identify here concurrent activating mutations in BRAF and MEK1 in melanomas and show that the presence of a downstream mutation in MEK1 does not necessarily make BRAF–mutant melanomas resistant to BRAF inhibitors.
© 2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Ribas and R.S. Lo declare patent application under PCT application serial no. PCT/US11/061552 (Compositions and Methods for Detection and Treatment of BRAF Inhibitor-Resistant Melanomas). K.B. Dahlman, B. Chmielowski, J.A. Sosman, R.F. Kefford, G.V. Long, and A. Ribas have received honoraria from or served as consultants to pharmaceutical firms (Roche-Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Illumina). No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures

Comment in
-
Making sense of MEK1 mutations in intrinsic and acquired BRAF inhibitor resistance.Cancer Discov. 2012 May;2(5):390-2. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0128. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22588873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Long GV, Menzies AM, Nagrial AM, Haydu LE, Hamilton AL, Mann GJ, et al. Prognostic and clinicopathologic associations of oncogenic BRAF in metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1239–46. - PubMed
-
- Kefford R, Arkenau H, Brown MP, Millward M, Infante JR, Long GV, et al. Phase I/II study of GSK2118436, a selective inhibitor of oncogenic mutant BRAF kinase, in patients with metastatic melanoma and other solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(15s) suppl;abstr 8503.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

