Regulation of integrin adhesions by varying the density of substrate-bound epidermal growth factor
- PMID: 22589066
- PMCID: PMC3939687
- DOI: 10.1007/s13758-012-0023-0
Regulation of integrin adhesions by varying the density of substrate-bound epidermal growth factor
Abstract
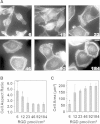
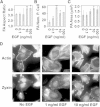
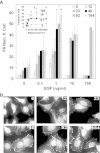
Substrates coated with specific bioactive ligands are important for tissue engineering, enabling the local presentation of extracellular stimulants at controlled positions and densities. In this study, we examined the cross-talk between integrin and epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors following their interaction with surface-immobilized Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) and EGF ligands, respectively. Surfaces of glass coverslips, modified with biotinylated silane-polyethylene glycol, were functionalized by either biotinylated RGD or EGF (or both) via the biotin-NeutrAvidin interaction. Fluorescent labeling of the adhering A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells for zyxin or actin indicated that EGF had a dual effect on focal adhesions (FA) and stress fibers: at low concentrations (0.1; 1 ng/ml), it stimulated their growth; whereas at higher concentrations, on surfaces with low to intermediate RGD densities, it induced their disassembly, leading to cell detachment. The EGF-dependent dissociation of FAs was, however, attenuated on higher RGD density surfaces. Simultaneous stimulation by both immobilized RGD and EGF suggest a strong synergy between integrin and EGFR signaling, in FA induction and cell spreading. A critical threshold level of EGF was required to induce significant variation in cell adhesion; beyond this critical density, the immobilized molecule had a considerably stronger effect on cell adhesion than did soluble EGF. The mechanisms underlying this synergy between the adhesion ligand and EGF are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of focal adhesion constituents and their down-stream events by EGF: On the cross-talk of integrins and growth factor receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1853(10 Pt A):2183-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26079101
-
Signaling by epidermal growth factor differentially affects integrin-mediated adhesion of tumor cells to extracellular matrix proteins.J Mol Med (Berl). 1996 Oct;74(10):609-16. doi: 10.1007/s001090050064. J Mol Med (Berl). 1996. PMID: 8912181
-
Adhesion, actin cytoskeleton organisation and the spreading of colon adenocarcinoma cells induced by EGF are mediated by alpha2beta1 integrin low clustering through focal adhesion kinase.Histochem Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;116(4):337-48. doi: 10.1007/s004180100324. Histochem Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11702192
-
Integrin regulation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and of EGF-dependent responses.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Jun;32(Pt3):438-42. doi: 10.1042/BST0320438. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15157155 Review.
-
Integrins in cell adhesion and signaling.Hum Cell. 1996 Sep;9(3):181-6. Hum Cell. 1996. PMID: 9183647 Review.
Cited by
-
Immobilization of Growth Factors for Cell Therapy Manufacturing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 19;8:620. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00620. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32637403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface-Patterned DNA Origami Rulers Reveal Nanoscale Distance Dependency of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Activation.Nano Lett. 2024 Feb 7;24(5):1611-1619. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c04272. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Nano Lett. 2024. PMID: 38267020 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

