A competitive inhibitor that reduces recruitment of androgen receptor to androgen-responsive genes
- PMID: 22589544
- PMCID: PMC3390614
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.344671
A competitive inhibitor that reduces recruitment of androgen receptor to androgen-responsive genes
Abstract
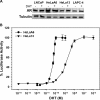
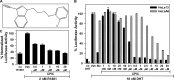
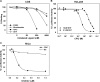
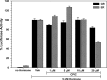
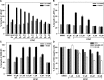
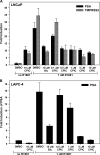
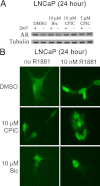
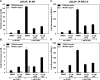
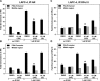
The androgen receptor (AR) has a critical role in the growth and progression of androgen-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancers. To identify novel inhibitors of AR transactivation that block growth of prostate cancer cells, a luciferase-based high-throughput screen of ~160,000 small molecules was performed in cells stably expressing AR and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA)-luciferase reporter. CPIC (1-(3-(2-chlorophenoxy) propyl)-1H-indole-3-carbonitrile) was identified as a small molecule that blocks AR transactivation to a greater extent than other steroid receptors. CPIC inhibited AR-mediated proliferation of androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cell lines, with minimal toxicity in AR-negative cell lines. CPIC treatment also reduced the anchorage-independent growth of LAPC-4 prostate cancer cells. CPIC functioned as a pure antagonist by inhibiting the expression of AR-regulated genes in LAPC-4 cells that express wild-type AR and exhibited weak agonist activity in LNCaP cells that express the mutant AR-T877A. CPIC treatment did not reduce AR levels or alter its nuclear localization. We used chromatin immunoprecipitation to identify the site of action of CPIC. CPIC inhibited recruitment of androgen-bound AR to the PSA promoter and enhancer sites to a greater extent than bicalutamide. CPIC is a new therapeutic inhibitor that targets AR-mediated gene activation with potential to arrest the growth of prostate cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel synthetic compound that interrupts androgen receptor signaling in human prostate cancer cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Jul;6(7):2057-64. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0735. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17620434
-
Prohibitin and the SWI/SNF ATPase subunit BRG1 are required for effective androgen antagonist-mediated transcriptional repression of androgen receptor-regulated genes.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Sep;29(9):1725-33. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn117. Epub 2008 May 16. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18487222 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged androgen receptor loading onto chromatin and the efficient recruitment of p160 coactivators contribute to androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells.Prostate. 2008 Dec 1;68(16):1816-26. doi: 10.1002/pros.20849. Prostate. 2008. PMID: 18780293
-
Experimental evidence of persistent androgen-receptor-dependency in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 26;14(8):15615-35. doi: 10.3390/ijms140815615. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23896594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Androgens as therapy for androgen receptor-positive castration-resistant prostate cancer.J Biomed Sci. 2011 Aug 23;18(1):63. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-18-63. J Biomed Sci. 2011. PMID: 21859492 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-137 regulates the constitutive androstane receptor and modulates doxorubicin sensitivity in parental and doxorubicin-resistant neuroblastoma cells.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 10;33(28):3717-29. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.330. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23934188 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput fluorescence anisotropy screen for inhibitors of the oncogenic mRNA binding protein, IMP-1.J Biomol Screen. 2014 Mar;19(3):427-36. doi: 10.1177/1087057113499633. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Biomol Screen. 2014. PMID: 24108120 Free PMC article.
-
The direct inhibitory effect of dutasteride or finasteride on androgen receptor activity is cell line specific.Prostate. 2013 Oct;73(14):1483-94. doi: 10.1002/pros.22696. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Prostate. 2013. PMID: 23813737 Free PMC article.
-
A 3-(4-nitronaphthen-1-yl) amino-benzoate analog as a bifunctional AKR1C3 inhibitor and AR antagonist: Head to head comparison with other advanced AKR1C3 targeted therapeutics.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Sep;192:105283. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30641225 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of (R)-2-(6-Methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)butanoic Acid as a Potent and Selective Aldo-keto Reductase 1C3 Inhibitor.J Med Chem. 2016 Aug 25;59(16):7431-44. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00160. Epub 2016 Aug 12. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27486833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He B., Kemppainen J. A., Voegel J. J., Gronemeyer H., Wilson E. M. (1999) Activation function 2 in the human androgen receptor ligand binding domain mediates interdomain communication with the NH2-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37219–37225 - PubMed
-
- He B., Kemppainen J. A., Wilson E. M. (2000) FXXLF and WXXLF sequences mediate the NH2-terminal interaction with the ligand binding domain of the androgen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 22986–22994 - PubMed
-
- He B., Minges J. T., Lee L. W., Wilson E. M. (2002) The FXXLF motif mediates androgen receptor-specific interactions with coregulators. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10226–10235 - PubMed
-
- Shang Y., Hu X., DiRenzo J., Lazar M. A., Brown M. (2000) Cofactor dynamics and sufficiency in estrogen receptor-regulated transcription. Cell 103, 843–852 - PubMed
-
- Kang Z., Pirskanen A., Jänne O. A., Palvimo J. J. (2002) Involvement of proteasome in the dynamic assembly of the androgen receptor transcription complex. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 48366–48371 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

