[μ-1,6-Bis(diphenyphosphan-yl)hexane-1:2κ(2)P:P']deca-carbonyl-1κ(3)C,2κ(3)C,3κ(4)C-triangulo-triruthenium(0)
- PMID: 22590126
- PMCID: PMC3344360
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014614
[μ-1,6-Bis(diphenyphosphan-yl)hexane-1:2κ(2)P:P']deca-carbonyl-1κ(3)C,2κ(3)C,3κ(4)C-triangulo-triruthenium(0)
Abstract
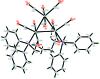
The title triangulo-triruthenium(0) compound, [Ru(3)(C(30)H(32)P(2))(CO)(10)], contains a triangle of singly bonded Ru atoms. The phosphane-bridged Ru-Ru distance [2.9531 (2) Å] is significantly longer than the non-bridged Ru-Ru distances [2.8842 (2) and 2.8876 (2) Å] . The bis-(diphenyl-phosphan-yl)hexane ligand bridges the Ru-Ru bond. Each phosphane-substituted Ru atom bears one equatorial and two axial terminal carbonyl ligands, whereas the unsubstituted Ru atom bears two equatorial and two axial terminal carbonyl ligands. The dihedral angles between the benzene rings attached to each P atom are 72.75 (7) and 82.02 (7)°. The mol-ecular structure is stabilized by an intra-molecular C-H⋯O hydrogen bond involving a methyl-ene group of the phosphane ligand and an axial carbonyl O atom, which generates an S(6) ring motif. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked via C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds into layers parallel to (100).
Figures
References
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruce, M. I., Hambley, T. W., Nicholson, B. K. & Snow, M. R. (1982). J. Organomet. Chem. 235, 83–91.
-
- Bruce, M. I., Matisons, J. G. & Nicholson, B. K. (1983). J. Organomet. Chem. 247, 321–343.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Churchill, M. R., Hollander, F. J. & Hutchinson, J. P. (1977). Inorg. Chem. 16, 2655–2659.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
