Baicalin improves survival in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis via suppressing inflammatory response and lymphocyte apoptosis
- PMID: 22590504
- PMCID: PMC3348138
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035523
Baicalin improves survival in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis via suppressing inflammatory response and lymphocyte apoptosis
Abstract
Background: An imbalance between overwhelming inflammation and lymphocyte apoptosis is the main cause of high mortality in patients with sepsis. Baicalin, the main active ingredient of the Scutellaria root, exerts anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and even antibacterial properties in inflammatory and infectious diseases. However, the therapeutic effect of baicalin on polymicrobial sepsis remains unknown.
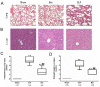
Methodology/principal findings: Polymicrobial sepsis was induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) in C57BL/6 mice. Mice were infused with baicalin intraperitoneally at 1 h, 6 h and 12 h after CLP. Survival rates were assessed over the subsequent 8 days. Bacterial burdens in blood and peritoneal cavity were calculated to assess the bacterial clearance. Neutrophil count in peritoneal lavage fluid was also calculated. Injuries to the lung and liver were detected by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Levels of cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10 and IL-17, in blood and peritoneum were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Adaptive immune function was assessed by apoptosis of lymphocytes in the thymus and counts of different cell types in the spleen. Baicalin significantly enhanced bacterial clearance and improved survival of septic mice. The number of neutrophils in peritoneal lavage fluid was reduced by baicalin. Less neutrophil infiltration of the lung and liver in baicalin-treated mice was associated with attenuated injuries to these organs. Baicalin significantly reduced the levels of proinflammatory cytokines but increased the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine in blood and peritoneum. Apoptosis of CD3(+) T cell was inhibited in the thymus. The numbers of CD4(+), CD8(+) T lymphocytes and dendritic cells (DCs) were higher, while the number of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells was lower in the baicalin group compared with the CLP group.
Conclusions/significance: Baicalin improves survival of mice with polymicrobial sepsis, and this may be attributed to its antibacterial property as well as its anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

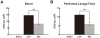


Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 improves survival in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis by suppressing the inflammatory response and apoptosis of lymphocytes.J Surg Res. 2013 Aug;183(2):760-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.01.068. Epub 2013 Feb 26. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23478085
-
The immunoprotective activity of baicalin in mouse model of cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Mar;71(2):543-7. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0232-x. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25534487
-
Adoptive transfer of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells decreases inhibitory and regulatory T-cell differentiation and improves survival in murine polymicrobial sepsis.Immunology. 2015 May;145(1):50-9. doi: 10.1111/imm.12423. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25382110 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of T cell response in sepsis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jun 1;19(8):1370-6. doi: 10.2741/4287. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24896356 Review.
-
Pharmacological properties of baicalin on liver diseases: a narrative review.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Oct;73(5):1230-1239. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00227-1. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33595821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibition of cytokine secretion and lymphocyte infiltration.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Aug;380(1-2):203-10. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1674-y. Epub 2013 May 11. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23666740
-
The role of anesthetic drugs in liver apoptosis.Hepat Mon. 2013 Aug 25;13(8):e13162. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.13162. Hepat Mon. 2013. PMID: 24069040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalin protects the cardiomyocytes from ER stress-induced apoptosis: inhibition of CHOP through induction of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 10;9(2):e88389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088389. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24520378 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin Inhibits Renal Cell Apoptosis and Protects Against Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Sepsis.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Dec 25;22:5109-5115. doi: 10.12659/msm.899061. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 28013315 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin alleviates benign prostate hyperplasia through androgen-dependent apoptosis.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Feb 4;12(3):2142-2155. doi: 10.18632/aging.102731. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32018227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–54. - PubMed
-
- Cheng B, Xie G, Yao S, Wu X, Guo Q, et al. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in critically ill surgical patients in ten university hospitals in China. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2538–46. - PubMed
-
- de Jong HK, van der Poll T, Wiersinga WJ. The systemic pro-inflammatory response in sepsis. J Innate Immun. 2010;2:422–30. - PubMed
-
- Bone RC. Sir Isaac Newton, sepsis, SIRS, and CARS. Crit. Care Med. 24, 1996;1125–1128 - PubMed
-
- Iwata A, Stevenson VM, Minard A, Tasch M, Tupper J, et al. Over-expression of Bcl-2 provides protection in septic mice by a trans effect. J. Immunol. 2003;171:3136–3141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

