Lung transplant infection
- PMID: 22591266
- PMCID: PMC7192226
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2012.02196.x
Lung transplant infection
Abstract
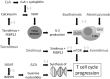
Lung transplantation has become an accepted therapeutic procedure for the treatment of end-stage pulmonary parenchymal and vascular disease. Despite improved survival rates over the decades, lung transplant recipients have lower survival rates than other solid organ transplant recipients. The morbidity and mortality following lung transplantation is largely due to infection- and rejection-related complications. This article will review the common infections that develop in the lung transplant recipient, including the general risk factors for infection in this population, and the most frequent bacterial, viral, fungal and other less frequent opportunistic infections. The epidemiology, diagnosis, prophylaxis, treatment and outcomes for the different microbial pathogens will be reviewed. The effects of infection on lung transplant rejection will also be discussed.
© 2012 The Authors. Respirology © 2012 Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Figures

References
-
- Chmiel C, Speich R, Hofer M et al Ganciclovir/valganciclovir prophylaxis decreases cytomegalovirus‐related events and bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008; 46: 831–9. - PubMed
-
- Speich R, van der Bij W. Epidemiology and management of infections after lung transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001; 33(Suppl. 1): S58–65. - PubMed
-
- Parada MT, Alba A, Sepulveda C. Early and late infections in lung transplantation patients. Transplant. Proc. 2010; 42: 333–5. - PubMed
-
- Levine SM. ACCP Pulm Crit Care Update. 1999; 13:lesson 16.
-
- Christie JD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY et al The registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: twenty‐eighth adult lung and heart‐lung transplant report–2011. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2011; 30: 1104–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

