E2F1-dependent methyl cap formation requires RNA pol II phosphorylation
- PMID: 22592528
- PMCID: PMC3368866
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.20620
E2F1-dependent methyl cap formation requires RNA pol II phosphorylation
Abstract
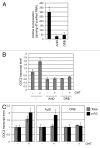
Gene expression is a process integral to cell proliferation. The E2F family of transcription factors upregulates expression of transcripts whose products are essential for cell cycle progression. Here, we report that E2F1 promotes gene expression by an additional mechanism, that is, formation of the methyl cap on RNA pol II transcripts. The methyl cap is required for mRNA maturation, expression and stability. We demonstrate that E2F1 increases RNA pol II phosphorylation, which promotes recruitment of the methyl cap synthetic enzymes. Upregulation of RNA pol II phosphorylation is required for E2F1-dependent methyl cap formation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
