Nutritional support for liver disease
- PMID: 22592729
- PMCID: PMC6823271
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008344.pub2
Nutritional support for liver disease
Abstract
Background: Weight loss and muscle wasting are commonly found in patients with end-stage liver disease. Since there is an association between malnutrition and poor clinical outcome, such patients (or those at risk of becoming malnourished) are often given parenteral nutrition, enteral nutrition, or oral nutritional supplements. These interventions have costs and adverse effects, so it is important to prove that their use results in improved morbidity or mortality, or both.
Objectives: To assess the beneficial and harmful effects of parenteral nutrition, enteral nutrition, and oral nutritional supplements on the mortality and morbidity of patients with underlying liver disease.
Search methods: The following computerised databases were searched: the Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library), MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Science Citation Index Expanded (January 2012). In addition, reference lists of identified trials and review articles and Clinicaltrials.gov were searched. Trials identified in a previous systematic handsearch of Index Medicus were also considered. Handsearches of a number of medical journals, including abstracts from annual meetings, were done. Experts in the field and manufacturers of nutrient formulations were contacted for potential references.
Selection criteria: Randomised clinical trials (parallel or cross-over design) comparing groups of patients with any underlying liver disease who received, or did not receive, enteral or parenteral nutrition or oral nutritional supplements were identified without restriction on date, language, or publication status. Six categories of trials were separately considered: medical or surgical patients receiving parenteral nutrition, enteral nutrition, or supplements.
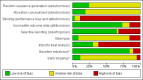
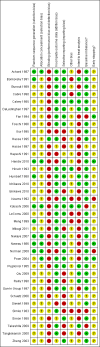
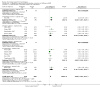
Data collection and analysis: The following data were sought in each report: date of publication; geographical location; inclusion and exclusion criteria; the type of nutritional support and constitution of the nutrient formulation; duration of treatment; any nutrition provided to the controls; other interventions provided to the patients; number, sex, age of the study participants; hospital or outpatient status; underlying liver disease; risks of bias (sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding, incomplete outcome reporting, intention-to-treat analysis, selective outcome reporting, others (vested interests, baseline imbalance, early stopping)); mortality; hepatic morbidity (development or resolution of ascites or hepatic encephalopathy, occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding); quality of life scores; adverse events; infections; lengths of stay in the hospital or intensive care unit; costs; serum bilirubin; postoperative complications (surgical trials only); and nutritional outcomes (nitrogen balance, anthropometric measurements, body weight). The primary outcomes of this review were mortality, hepatic morbidity, quality of life, and adverse events. Data were extracted in duplicate; differences were resolved by consensus.Data for each outcome were combined in a meta-analysis (RevMan 5.1). Estimates were reported using risk ratios or mean differences, along with the 95% confidence intervals (CI). Both fixed-effect and random-effects models were employed; fixed-effect models were reported unless one model, but not the other, found a significant difference (in which case both were reported). Heterogeneity was assessed by the Chi(2) test and I(2) statistic. Subgroup analyses were planned to assess specific liver diseases (alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma), acute or chronic liver diseases, and trials employing standard or branched-chain amino acid formulations (for the hepatic encephalopathy outcomes). Sensitivity analyses were planned to compare trials at low and high risk of bias and trials reported as full papers. The following exploratory analyses were undertaken: 1) medical and surgical trials were combined for each nutritional intervention; 2) intention-to-treat analyses in which missing dichotomous data were imputed as best- and worst-case scenarios; 3) all trials were combined to assess mortality; 4) effects were estimated by absolute risk reductions.
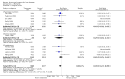
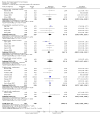
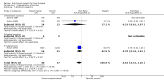
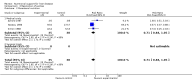
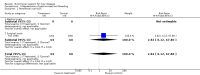
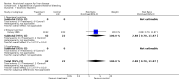
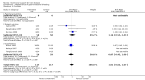
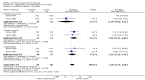
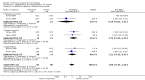
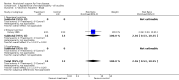
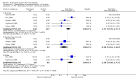
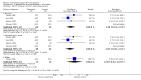
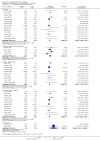
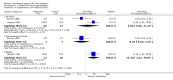
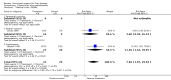
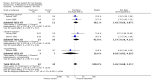
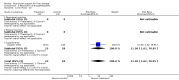
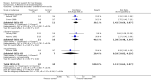
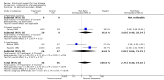
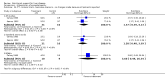
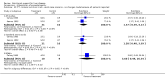
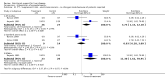
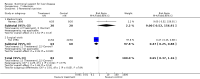
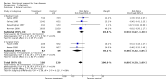
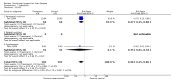
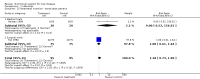
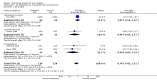
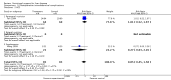
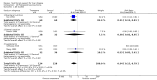
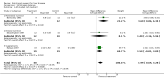
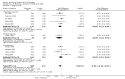
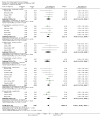
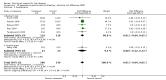
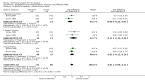
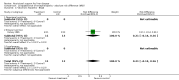
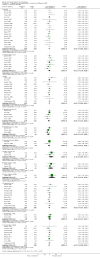
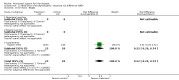
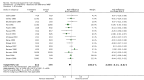
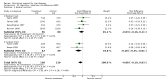
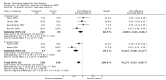
Main results: Thirty-seven trials were identified; only one was at low risk of bias. Most of the analyses failed to find any significant differences. The significant findings that were found were the following: 1) icteric medical patients receiving parenteral nutrition had a reduced serum bilirubin (mean difference (MD) -2.86 mg%, 95% CI -3.82 mg% to -1.89 mg%, 3 trials) and better nitrogen balance (MD 3.60 g/day, 95% CI 0.86 g/day to 6.34 g/day, 1 trial); 2) surgical patients receiving parenteral nutrition had a reduced incidence of postoperative ascites only in the fixed-effect model (RR 0.65, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.87, 2 trials, I(2) = 70%) and one trial demonstrated a reduction in postoperative complications, especially infections (pneumonia in particular); 3) enteral nutrition may have improved nitrogen balance in medical patients (although a combination of the three trials was not possible); 4) one surgical trial of enteral nutrition found a reduction in postoperative complications; and 5) oral nutritional supplements had several effects in medical patients (reduced occurrence of ascites (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.37 to 0.88, 3 trials), possibly (significant differences only seen in the fixed-effect model) reduced rates of infection (RR 0.49, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.99, 3 trials, I(2) = 14%), and improved resolution of hepatic encephalopathy (RR 3.75, 95% CI 1.15 to 12.18, 2 trials, I(2) = 79%). While there was no overall effect of the supplements on mortality in medical patients, the one low risk of bias trial found an increased risk of death in the recipients of the supplements. Three trials of supplements in surgical patients failed to show any significant differences. No new information was derived from the various subgroup or sensitivity analyses. The exploratory analyses were also unrevealing except for a logical conundrum. There was no difference in mortality when all of the trials were combined, but the trials of parenteral nutrition found that those recipients had better survival (RR 0.53, 95% CI 0.29 to 0.98, 10 trials). Either the former observation represents a type II error or the latter one a type I error.
Authors' conclusions: The data do not compellingly justify the routine use of parenteral nutrition, enteral nutrition, or oral nutritional supplements in patients with liver disease. The fact that all but one of these trials were at high risks of bias even casts doubt on the few benefits that were demonstrated. Data from well-designed and executed randomised trials that include an untreated control group are needed before any such recommendation can be made. Future trials have to be powered adequately to see small, but clinically important, differences.
Conflict of interest statement
Neither RK, AA, or TL have any real or potential conflict of interest with any party (commercial or third party payers). There was no external or internal funding source that sponsored this review.
Figures





























































































































































































































Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008344
References
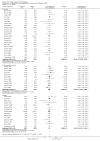
References to studies included in this review
Achord 1987 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Achord JL. A prospective randomized clinical trial of peripheral amino acid‐glucose supplementation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1987;82(9):871‐5. - PubMed
Bonkovsky 1991 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Bonkovsky H, Fiellin D, Smith G, Slaker D, Simon D, Galambos J. Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis with parenteral nutrition and oxandrolone: a randomized controlled trial I short‐term effects on liver function [AASLD abstract]. Hepatology 1990;12(4):870. - PubMed
-
- Bonkovsky H, Jafri I, Singh R, Cotsonis G, Slaker D. Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis with parenteral nutrition and oxandrolone: a randomized controlled trial II Effects on nitrogen metabolism [AASLD abstract]. Hepatology 1990;12(4):978. - PubMed
-
- Bonkovsky HL, Fiellin DA, Smith GS, Slaker DP, Simon D, Galambos JT. A randomized, controlled trial of treatment of alcoholic hepatitis with parenteral nutrition and oxandrolone I Short‐term effects on liver function. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1991;86(9):1200‐8. - PubMed
-
- Bonkovsky HL, Singh RH, Jafri IH, Fiellin DA, Smith GS, Simon D, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of treatment of alcoholic hepatitis with parenteral nutrition and oxandrolone II Short‐term effects on nitrogen metabolism, metabolic balance, and nutrition. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1991;86(9):1209‐18. - PubMed
Bunout 1989 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Bunout D, Aicardi V, Hirsch S, Petermann M, Kelly M, Silva G, et al. Nutritional support in hospitalized patients with alcoholic liver disease. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1989;43(9):615‐21. - PubMed
Cabre 1990 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Abad‐Lacruz A, Cabre E, Gonzalez‐Huix F, Esteve M, Xiol X, Acero D, et al. Total enteral nutrition (TEN) as a new approach influencing the clinical outcome and mortality in liver cirrhosis (LC) [AASLD abstract]. Hepatology 1988;8(5):1413.
-
- Cabre E, Abad A, Glez‐Huix F, Esteve M, Xiol X, Acero D, et al. Total enteral nutrition as a new approach influencing the clinical outcome and mortality in liver cirrhosis [abstract]. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1989;13 Suppl(1):10.
-
- Cabre E, Gonzales‐Huix F, Abad‐Lacruz A, Esteve M, Xiol X, Acero D, et al. Effect of total enteral nutrition (TEN) on the clinical outcome of hospitalized cirrhotics with severe protein‐energy malnutrition (PEM) [abstract]. Clinical Nephrology 1988;7 Special Suppl:34.
-
- Cabre E, Gonzalez Huix F, Abad Lacruz A, Esteve M, Acero D, Fernandez Banares F, et al. Effect of total enteral nutrition on the short‐term outcome of severely malnourished cirrhotics A randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 1990;98(3):715‐20. - PubMed
Calvey 1985 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation, with and without branched chain amino acid enrichment, in treatment of acute alcoholic hepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 1985;1(2):141‐51. - PubMed
-
- Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Prospective study of nasogastric feeding via East Grinstead (Reg.trademark) or Viomedex (Reg.trademark) tubes compared with oral dietary supplementation in patients with cirrhosis. Clinical Nutrition 1984;3(2):63‐6. - PubMed
-
- Williams R, Calvey H, Davis M. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and nutrition in liver disease. Lancaster, England: MTP Press, Ltd., 1985:361‐8.
DeLedinghen 1997 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ledinghen V, Mannant PR, Beau P, Borderie C, Oui B, Silvain C, et al. Effects of early enteral nutrition in cirrhotics patients after bleeding from esophageal varices: a randomized controlled study (Abstract). Gastroenterology 1996;110(4):A13.
-
- Ledinghen V, Beau P, Mannant PR, Borderie C, Ripault MP, Silvain C, et al. Early feeding or enteral nutrition in patients with cirrhosis after bleeding from esophageal varices? A randomized controlled study. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1997;42(3):536‐41. - PubMed
-
- Ledinghen V, Mannant PR, Beau P, Borderie C, Ripault MP, Silvain C, et al. Effect of enteral nutrition immediately after digestive hemorrhage in cirrhotics: A randomised controlled study (abstract) [Effets de la nutrition enterale au decours immediat de l`hemorragie digestive du cirrhotique: Etude controlee randomisee (abstract)]. Gastroenterologie Clinique et Biologique 1996;20 Suppl:A120.
Fan 1994 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Fan ST, Lo CM, Lai EC, Chu KM, Liu CL, Wong J. Perioperative nutritional support in patients undergoing hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;331(23):1547‐52. - PubMed
Foschi 1986 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Foschi D, Cavagna G, Callioni F, Morandi E, Rovati V. Hyperalimentation of jaundiced patients on percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage. British Journal of Surgery 1986;73(9):716‐9. - PubMed
Guy 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Guy S, Tanzer‐Torres G, Palese M, Sheiner P, Mor E, Emre S, et al. Does nasoenteral nutritional support reduce mortality after liver transplant? (Abstract). Hepatology 1995;22:144A.
Hasse 1995 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Hasse JM, Blue LS, Liepa GU, Goldstein RM, Jennings LW, Mor E, et al. Early enteral nutrition support in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1995;19(6):437‐43. - PubMed
Hasse 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hasse J, Crippin J, Blue L, Huang K, DiCecco S, Francisco‐Ziller N, et al. Does nutrition supplementation benefit liver transplant candidates with a history of encephalopathy? (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1997;21(1):S16.
Hayashi 1991 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hayashi S, Aoyagi Y, Fujiwara K, Oka H, Oda T. A randomized controlled trial of branched‐chain amino acid (BCAA)‐enriched elemental diet (ED‐H) for hepatic encephalopathy [abstract]. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1991;6(2):191.
-
- Hayashi S, Aoyagi Y, Oka H, Oda T. A randomized controlled study of an elementary diet (ED‐H) in cirrhotics with hepatic encephalopathy. Unpublished data.
Hendry 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hendry PO, Dam RM, Bukkems SFFW, McKeovm DW, Parks RW, Preston T, et al. Randomized clinical trial of laxatives and oral nutritional supplements within an enhanced recovery after surgery protocol following liver resection. British Journal of Surgery 2010;97(8):1198‐206. - PubMed
Hirsch 1993 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Hirsch S, Bunout D, Maza P, Iturriaga H, Petermann M, Icazar G, et al. Controlled trial on nutrition supplementation in outpatients with symptomatic alcoholic cirrhosis. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1993;17(2):119‐24. - PubMed
Humbert 1988 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Humbert P, Pintó A, Johnston S, Fábrega C, Planas R, Boix J, et al. Effect of oral administration of branched‐chain amino acids for the treatment of nutrition disturbances and for the prophylaxis of encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [Efecto de la administración oral de aminoácidos ramificados en el tratamiento de los trastornos nutricionales y en la prevención de la encefalopatía de pacientes cirróticos.]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 1989;12(1):9‐13.
Ichikawa 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ichikawa T, Naota T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Isomoto H, Takeshima F, et al. Effect of an oral branched chain amino acid‐enriched snack in cirrhotic patients with sleep disturbance. Hepatology Research 2010;40(10 (Oct)):971‐8. - PubMed
Ishikawa 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ishikawa Y, Yoshida H, Mamada Y, Taniai N, Matsumoto S, Bando K, et al. Prospective randomized controlled study of short‐term perioperative oral nutrition with branched chain amino acids in patients undergoing liver surgery. Hepatogastroenterology 2010;57:583‐90. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa Y, Yoshida H, Weiner J, Tajiri T. Prospective randomized controlled study of short‐term perioperative enteral nutrition support with branched chain amino acids in liver surgery (Abstract). Gastroenterology 2009;136 Suppl 1:176. - PubMed
Kearns 1992 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Kearns PJ, Young H, Garcia G, Blaschke T, O'Hanlon G, Rinki M, et al. Accelerated improvement of alcoholic liver disease with enteral nutrition. Gastroenterology 1992;102(1):200‐5. - PubMed
Kobashi 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kobashi H, Morimoto Y, Ito T, Shimoe T, Makino Y, Araki Y, et al. Effects of supplementation with a branched‐chain amino acid‐enriched preparation on event‐free survival and quality of life in cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. A multicenter, randomized controlled trial (Abstract) . Gastroenterology 2006;130:A497.
LeCornu 2000 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- LeCornu KA, McKiernan FJ, Kapadia SA, Neuberger JM. A prospective randomized study of preoperative nutritional supplementation in patients awaiting elective orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation 2000;69(7):1364‐9. - PubMed
Meng 1999 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Meng WC, Leung KL, Ho RL, Leung TW, Lau WY. Prospective randomized control study on the effect of branched‐chain amino acids in patients with liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Surgery 1999;69(11):811‐5. - PubMed
Mikagi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mikagi K, Kawahara R, Kinoshita H, Aoyagi S. Effect of preoperative immunonutrition in patients undergoing hepatectomy; a randomized controlled trial. Kurume Medical Journal 2011;58(1):1‐8. - PubMed
Nakaya 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Nakaya Y, Ikita K, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H, Kato A, Miwa Y, et al. BCAA‐enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. . Nutrition 2007;23:113‐20. - PubMed
-
- Nakaya Y, Okita K, Kato A, Miwa Y, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H. Randomized trial of branched chain amino acid rich supplement against carbohydrate‐rich snacks as a late evening snack in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2005;42 Suppl 1(4):699A‐700A.
Naveau 1986 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Naveau S, Pelletier G, Poynard T, Attali P, Poitrine A. Buffet C, et al. A randomised Clinical trial of supplementary parenteral nutrition in jaundiced alcoholic cirrhotic patients. Hepatology 1986;6(2):270‐4. - PubMed
Norman 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Norman K, Kirchner H, Friedrich U, Lochs H, Ockenga J, Pirlich M. Enteral nutrition improves functional parameters in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis (Abstract) [Enterale Ernahrung verbessert funktionale Parameter in Patienten mit fortgeschrittener Leberzirrhose]. Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie 2005;43(8):913.
-
- Norman K, Smoliner C, Stobacus N, Schuetz T, Lochs H, Ockenga, et al. Early enteral nutrition improves functional parameters in liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Gastroenterology 2008;134 Suppl 1:A563.
-
- Pirlich M, Norman K, Lochs H. Malnutrition in liver cirrhosis: impact of protein rich oral diet. Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie 2006;44(4):344‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Poon 2004 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Poon RT, Yu WC, Fan ST, Wong J. Long‐term oral branched chain amino acids in patients undergoing chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized trial. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2004;19(7):779‐88. - PubMed
Puglionisi 1985 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ceriati F, Cavicchioni C, Marino IR, Luca G, Puglionisi A. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients after derivative surgery [Trattamento dell'encefalopatia epatica nei pazienti cirrotici sottoposti ad intervento chirurgico derivativo]. Acta Medica Romana 1985;23(1):69‐76.
-
- Puglionisi A, Ceriati F, Marino IR, Cavicchioni C, Luca G, Roncone A, et al . Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after porta‐caval anastomosis using branched chain amino acid mixtures. In: Capacaccio L, Fischer JE, Rossi‐Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:345‐50.
Qiu 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Qiu Y, Zhu X, Wang W, Xu Q, Ding Y. Nutrition support with glutamine dipeptide in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplantation Proceedings 2009;41:4232‐7. - PubMed
Reilly 1990 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Reilly J, Mehta R, Teperman L, Cemaj S, Tzakis A, Yanaga K, et al. Nutritional support after liver transplantation: a randomized prospective study. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1990;14(4):386‐91. - PubMed
-
- Reilly J, Yanaga K, Tzakis A, Teperman L, Mehta R, Rezak A, et al. A randomized prospective study of nutritional support after liver transplant (Abstract). Journal Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1989;13:8S. - PubMed
San‐In Group 1997 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Heys SD. Long‐term oral administration of branched chain amino acids after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial (Letter). British Journal of Surgery 1998;85(3):423. - PubMed
-
- Mann DV. Long‐term oral administration of branched chain amino acids after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial (Letter). British Journal of Surgery 1998;85(6):875. - PubMed
-
- Nagasue N. Long‐term oral administration of branched chain amino acids after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial ‐ reply. British Journal of Surgery 1998;85(3):423‐4. - PubMed
-
- San‐in Group of Liver Surgery. Long‐term oral administration of branched chain amino acids after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial. British Journal of Surgery 1997;84(11):1525‐31. - PubMed
Schuetz 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Schuetz T, Norman K, Friedrich‐Pagels U, Ockenga J, Luu TN, Lochs H, et al. Tube feeding does not affect subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract) . Gastroenterology 2006;130:A326.
Sievert 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Stevert W, Gibson PR, Colman JC, Kronborg I, Crawford DH, Keogh J, et al. Energy and amino acid supplements in malnourished patients with cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial (Abstract) . Hepatology 1999;30:434A.
Simko 1983 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Simko V. Long‐term tolerance of a special amino acid oral formula in patients with advanced liver disease. Nutrition Reports International 1983;27(4):765‐73.
Simon 1988 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Galambos JT, Simon D. Peripheral hyperalimentation (Ppn) in moderate and severe alcoholic hepatitis (Ah) ‐ a randomized controlled‐study (abstract). Alcohol and Alcoholism 1988;23(3):A25. - PubMed
-
- Simon D, Galambos JT. A randomized controlled study of peripheral parenteral nutrition in moderate and severe alcoholic hepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 1988;7(2):200‐7. - PubMed
-
- Simon D, Galambos JT. Peripheral hyperalimentation (Ppn) in moderate and severe alcoholic hepatitis (Ah): a randomized controlled study (Abstract). Hepatology 1986;6(5):1163. - PubMed
-
- Simon D, Galambos JT. Peripheral hyperalimentation (Ppn) in severe alcoholic hepatitis (Ah) ‐ a blinded randomized controlled study ‐ preliminary data (abstract). Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1986;31(10):S216.
-
- Simon DM, Galambos JT. Peripheral hyperalimentation (Ppn) in moderate and severe alcoholic hepatitis (Ah) a randomized controlled study (abstract). American Journal of Gastroenterology 1987;82(9):979.
Takeshita 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Takeshita S, Ichikawa T, Nakao K, Miyaaki H, Shibata H, Matsuzaki T, et al. A snack enriched with oral branched‐chain amino acids prevents a fall in albumin in patients with liver cirrhosis undergoing chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nutrition Research 2009;29:89‐93. - PubMed
Tangkijvanich 2000 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Tangkijvanich P, Mahachai V, Wittayalertpanya S, Ariyawongsopon V, Isarasena S. Short‐term effects of branched‐chain amino acids on liver function tests in cirrhotic patients. The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2000;31(1):152‐7. - PubMed
Zheng 2003 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Zheng Q, Hu Q. The influence of enteral nutrition on gut barrier in the post‐operative patients with damaged hepatic function. Journal of Tongji Medical University 2001;21(4):323‐5. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abad Lacruz 1990 {published data only}
-
- Abad Lacruz A, Gonzalez Huix F, Esteve M, Fernandez Banares F, Cabre E, Boix J, et al. Liver function tests (LFT) derangement in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) on either ten or TPN A prospective, randomized study (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1988;7 Special Suppl:60.
-
- Abad Lacruz A, Gonzalez Huix F, Esteve M, Fernandez Banares F, Cabre E, Boix J, et al. Liver function tests abnormalities in patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving artificial nutrition: a prospective randomized study of total enteral nutrition vs total parenteral nutrition. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1990;14(6):618‐21. - PubMed
Adams 2011 {published data only}
-
- Adams L, Zhu K, Kerr D, Devine A, Solah V.A, Binns C, et al. The effect of whey protein supplementation on hepatic steatosis: Results from a randomized placebo controlled trial in postmenopausal women (abstract). Hepatology 2011;54 Suppl 1:1146A.
Akoglu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Akoglu B, Schrott M, Bolouri H, Jaffari A, Kutschera E, Caspary WF, et al. The folic acid metabolite L‐5‐methyltetrahydrofolate effectively reduces total serum homocysteine level in orthotopic liver transplant recipients: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;62(6):796‐801. - PubMed
Al Mardini 2006 {published data only}
-
- Al Mardini H, Douglass A, Record CA. Amino acid challenge in patients with cirrhosis and control subjects: ammonia, plasma amino acid and EEG changes. Metabolic Brain Disease 2006;21(1):1‐10. - PubMed
Alvarez 2004 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez MA, Cabre E, Lorenzo‐Zuniga V, Montoliu S, Planas R, Gassull MA. Combining steroids with enteral nutrition: a better therapeutic strategy for severe alcoholic hepatitis? Results of a pilot study. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2004;16(12):1375‐80. - PubMed
Andreone 2001 {published data only}
-
- Andreone P, Fiorino S, Cursaro C, Gramenzi A, Margotti M, Giammarino L, et al. Vitamin E as treatment for chronic hepatitis B: Results of a randomized controlled pilot trial. Antiviral Research 2001;49(2):75‐81. - PubMed
Awad 2010 {published data only}
-
- Awad S, Constantin‐Teodosiu D, Constantin D, Rowlands BJ, Fearon KCH, Macdonald IA, et al. Cellular mechanisms underlying the protective effects of preoperative feeding. Annals of Surgery 2010;252:247‐53. - PubMed
Badalamenti 1995 {published data only}
-
- Badalamenti S, Salerno F, Lorenzano E, Paone G, Como G, Finazzi S, et al. Renal effects of dietary supplementation with fish oil in cyclosporine‐ treated liver transplant recipients. Hepatology 1995;22(6):1695‐701. - PubMed
Baldermann 1988 {published data only}
-
- Baldermann H, Wicklmayr M, Rett K, Banholzer P, Dietze G, Mehnert H. Changes in ultrasonic findings in the liver in relation to parenteral nutrition with long chain triglyceride and medium chain triglyceride/long chain triglyceride lipid solutions [Untersuchungen zur Veranderung des Sonographiebefundes der Leber unter parenteraler Ernahrung mit LCT‐bzw MCT/LCT Lipidlosungen ]. Infusionstherapie 1988;15(4):140‐3. - PubMed
-
- Baldermann H, Wicklmayr M, Rett K, Banholzer P, Dietze G, Mehnert H. Changes of hepatic morphology during parenteral nutrition with lipid emulsions containing LCT or MCT/LCT quantified by ultrasound. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1991;15(6):601‐3. - PubMed
Barle 1997 {published data only}
-
- Barle H, Nyberg B, Andersson K, Essen P, McNurlan MA, Wernerman J, et al. The effects of short‐term parenteral nutrition on human liver protein and amino acid metabolism during laparoscopic surgery. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1997;21(6):330‐5. - PubMed
Bartels 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bartels M, Biesalski HK, Engelhart K, Sendlhofer G, Rehak P, Nagel E. Pilot study on the effect of parenteral vitamin E on ischemia and reperfusion induced liver injury: a double blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition 2004;23(6):1360‐70. - PubMed
Bernardi 1981 {published data only}
-
- Bernardi R. Liver, protein metabolism, branched chain amino acids [Fegato, metabolismo proteico, aminoacidi a catena ramificata]. La Clinica Terapeutica 1981;99:653‐75. - PubMed
Bianchi 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bianchi G.P, Marchesini G, Fabbri A, Rondelli A, Bugianesi E, Zoli M, et al. Vegetable versus animal protein diet in cirrhotic patients with chronic encephalopathy. A randomized cross‐over comparison. Journal of Internal Medicine 1993;233(5):385‐92. - PubMed
Bories 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bories PN, Campillo B. One‐month regular oral nutrition in alcoholic cirrhotic‐patients ‐ changes of nutritional‐status, hepatic‐function and serum‐lipid pattern. British Journal of Nutrition 1994;72(6):937‐46. - PubMed
Brans 1987 {published data only}
Bresci 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bresci G, Parisi G, Banti S. Management of hepatic encephalopathy with oral zinc supplementation: A long‐term treatment. European Journal of Medicine 1993;2(7):414‐6. - PubMed
Buchmiller 1993 {published data only}
-
- Buchmiller CE, Kleiman‐Wexler RL, Ephgrave KS, Booth B, Hensley CE. Liver dysfunction and energy source: results of a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1993;17(4):301‐6. - PubMed
Cabre 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cabre E. Outcome of severe alcoholic hepatitis (SAH) treated with steroids (STE) or total enteral nutrition (TEN) (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 2000;32(2):32.
-
- Cabre E. Short and long‐term outcome in severe alcoholic hepatitis (SAH) treated with steroids or total enteral nutrition (TEN) (Abstract). Hepatology 1999;30(4):405A.
-
- Cabre E. Short and long‐term outcome in severe alcoholic hepatitis (SAH) treated with steroids or total enteral nutrition (TEN). A multicentric randomized controlled trial (Abstract). Hepatology 1999;30(4):979.
-
- Cabre E. Treatment of severe alcoholic hepatitis with steroids or total enteral nutrition: Interim results of a prospective, randomized, multicentric trial. Gastroenterology 1998;114(4):G3562.
-
- Cabre E. Treatment of severe alcoholic hepatitis with steroids or total enteral nutrition: interim results of a prospective, randomized, multicentric trial (Abstract). Clinical Nephrology 1998;17 Suppl 1:18.
Campo 1997 {published data only}
-
- Campo G, Amodio P, Caregaro L, Sacerdoti D, Bolognesi M, Burlina A, et al. Effect of a dietary integration with BCAA or casein on nutritional state and lower limb amino acid exchange in cirrhosis. Advances in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Metabolism in Liver Disease. Great Britain: Ipswich Book Company Ltd., 1997:149‐55.
Cao 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cao J, Luo SM, Liang L, Lai J. Effects of parenteral nutrition without and with growth hormone on growth hormone/insulin‐like growth factor‐1 axis after hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma with liver cirrhosis. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2007;31(6):496‐501. - PubMed
Cerra 1983 {published data only}
-
- Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. A multicenter trial of branched chain enriched amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy (HE) (Abstract). Hepatology 1982;2(5):699.
-
- Cerra FB, McMillen M, Angelico R, Cline B, Lyons J, Faulkenbach L, et al. Cirrhosis, encephalopathy, and improved results with metabolic support. Surgery 1983;94(4):612‐9. - PubMed
Cerra 1985 {published data only}
-
- Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. Disease‐specific amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective, randomized, double‐blind, controlled trial. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1985;9(3):288‐95. - PubMed
-
- Cowan GS Jr. Disease‐specific amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective, randomized, double‐blind, controlled trial (Letter). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1986;10:247. - PubMed
Cerwenka 1998 {published data only}
-
- Cerwenka H, Bacher H, Werkgartner G, El‐Shabrawi A, Quehenberger F, Hauser H, et al. Antioxidant treatment during liver resection for alleviation of ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 1998;45(21):777‐82. - PubMed
Chelarescu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chelarescu O, Chelarescu D, Rusu M, Stratan I. Parenteral vs enteral nutrition in acute liver failure (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 2003;38 Suppl 2:192.
Chin 1992 {published data only}
-
- Chin SE, Shepherd RW, Thomas BJ, Cleghorn GJ, Patrick MK, Wilcox JA, et al. Nutritional support in children with end‐stage liver disease: a randomized crossover trial of a branched‐chain amino acid supplement. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1992;56(1):158‐63. - PubMed
Christie 1985 {published data only}
-
- Christie ML, Sack DM, Horst D, Lenger S, Pomposelli J. Enriched branched‐chain amino acid formula versus a casein based supplement in the treatment of cirrhosis (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1984;8:91. - PubMed
-
- Christie ML, Sack DM, Pomposelli J, Horst D. Enriched branched‐chain amino acid formula versus a casein‐based supplement in the treatment of cirrhosis. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1985;9(6):671‐8. - PubMed
Clarke 2004 {published data only}
-
- Clarke S, Bernal W, Rees G, Wendon J. Immunonutrition in critically ill patients with liver disease: a prospective randomised double‐blind controlled trial. Hepatology 2004;40 Suppl 1:500A.
Conti 1971 {published data only}
-
- Conti F, Natangelo R, Cattani F, Mandelli V. Controlled clinical trial of liver‐protective agents [La sperimentazione clinica controllata degli epatoprotettori]. La Clinica Terapeutica 1971;59(2):155‐65. - PubMed
Córdoba {unpublished data only}
-
- Córdobo J. Effects of proteins in patients with cirrhosis and prior hepatic encephalopathy. ClinicalTrials.gov 2009. [Other (ClinicalTrials.gov): NCT00955500]
Córdoba 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cordoba J, Sanpedro F, Lopez‐Hellin Sabin P, Planas M, Esteban R, Guardia J. A low‐protein diet does not improve the outcome of acute hepatic encephalopathy. Results of a pilot study using enteral nutrition (Abstract). Hepatology 2001;34(4):187A.
-
- Córdoba J, López‐Hellín J, Planas M, Sabín P, Sanpedro F, Castro F, et al. Normal protein diet for episodic hepatic encephalopathy: results of a randomized study. Journal of Hepatology 2004;41(1):38‐43. - PubMed
Cortez Pinto 1990 {published data only}
-
- Cortez Pinto H, Cravo M, Saraiva A, Camilo ME, Moura MC. Parenteral nutrition in cirrhosis (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 1990;10 Suppl 1:19.
Cunha 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cunha L, Nono MH, Guibert AL, Nidegger D, Beau P, Beauchant M. Effects of prolonged oral nutritional support in malnourished cirrhotic patients: Results of a pilot study. Gastroenterologie Clinique Et Biologique 2004;28(1):36‐9. - PubMed
De Antoni 1984 {published data only}
-
- Antoni E, Grilli P, Orsi E. . Efficacy of TPN in cirrhotic patients with bleeding esophageal varices. Italian Journal of Surgical Sciences 1984;14(3):253‐5. - PubMed
De‐Fang 2011 {published data only}
-
- De‐Fang Z, Ke Z, Ren L, Li‐Jun Z. Clinical observation of enteral immunonutrition in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 2011;15(31):5873‐8.
de la Maza 1995 {published data only}
-
- Maza MP, Petermann M, Bunout D, Hirsch S. Effects of long‐term vitamin E supplementation in alcoholic cirrhotics. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 1995;14(2):192‐6. - PubMed
de Luis 2010 {published data only}
-
- Luis DA, Aller R, Izaola O, Gonzalez Sagrado M, Conde RTI. Effect of two different hypocaloric diets in transaminases and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients. Nutricion Hospitalaria 2010;25(5):730‐5. - PubMed
Di Cecco 1997 {published data only}
-
- Cecco SR, Francisco‐Ziller NM, Porayko MK, Crippin JS, Blue LS, Huang KS, et al. Does pretransplant oral nutrition supplementation affect post‐transplant clinical outcomes? (Abstract). Hepatology 1997;26(4 (Pt 2)):500A.
Diehl 1985 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Diehl AM, Boitnott JK, Herlong HF, Potter JJ, Duyn MA, Chandler E, et al. Effect of parenteral amino acid supplementation in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 1985;5(1):57‐63. - PubMed
Dionigi 1984 {published data only}
-
- Dionigi P, Holdsworth JD, Clague MB, James OF, Wright PD. Body protein synthesis and breakdown in chronic liver disease. The effect of different amino acid solutions (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1984;2 Special Suppl:O.81.
Egberts 1981 {published data only}
-
- Egberts E‐H, Hamster W, Jurgens P, Schumacher H, Fondalinski G, Reinhard U, et al. Effect of branched chain amino acids on latent portal‐systemic encephalopathy. In: Walser M, Williamson JR editor(s). Metabolism and Clinical Implications of Branched Chain Amino and Ketoacids. Amsterdam: Elsevier North Holland, 1981:453‐63.
-
- Hamster W, Egberts EH, Hamster H. Treatment with branched‐chain amino acids and effect on psycho‐physical capacity functions in latent porto‐systemic encephalopathy [Behandlung mit verzweigtkettigen aminosauren und ihre auswirkung auf psychophysische leistungsfunktionen bel latenter portosystemischer enzephalopathie]. Arzneimittelforschung 1982;32:901‐2.
Egberts 1985 {published data only}
-
- Egberts EH, Hamster W, Schomerus H, Jürgens P. Effect of branched chain amino acids on latent porto‐systemic‐encephalopathy (PSE) (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:354.
-
- Egberts EH, Schomeerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Effective treatment of latens porto‐systemic encephalopathy with oral branched chain amino acids. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi‐Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. Plenum Press, New York, 1984:351‐7.
-
- Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jurgens P. Branched chain amino acids in the treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy A double‐blind placebo‐controlled crossover study. Gastroenterology 1985;88(4):887‐95. - PubMed
-
- Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jurgens P. Branched‐chain amino acids in the treatment of latent porto‐systemic encephalopathy A placebo‐controlled double‐blind cross‐over study [Verzweigtkettige Aminosauren bei der Behandlung der latenten portosystemischen Enzephalopathie Eine placebokontrollierte Doppelblind‐Cross‐over‐Studie ]. Zeitschrift für Ernährungswissenschaft 1986;25(1):9‐28. - PubMed
Egberts 1988 {published data only}
-
- Egberts E‐H, Plauth M, Hamster W, Torok M, Brand O, Furst P. Long‐term double‐blind crossover study on the treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) with branched chain amino acids (BCAA) (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1988;76 Suppl:31.
Eriksson 1982 {published data only}
-
- Eriksson LS, Persson A, Wahren J. Failure of oral branched‐chain amino acids to improve chronic hepatic encephalopathy (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:355.
Ferenci 1981 {published data only}
-
- Ferenci P, Dragosics B, Wewalka F. Oral administration of branched chain amino acids (BCAA) and keto acids (BCKA) in patients with liver cirrhosis (LC). In: Walser M, Williamson JR editor(s). Metabolism and Clinical Implications of Branched Chain Amino and Ketoacids. Amsterdam: Elsevier North Holland, 1981:507‐12.
Fiaccadori 1984 {published data only}
-
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Zeneroli ML, et al. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi‐Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver failure. Plenum Press, New York, 1984:323‐33.
-
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Zeneroli ML, et al. Branched‐chain enriched amino acid solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: A controlled trial (Abstract). Italian Journal of Gastroenterology 1985;17:5‐10.
-
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Vaona GL, Zeneroli ML, et al. Selective amino acid solutions in hepatic encephalopathy (a preliminary report). La Ricerca in Clinica e in Laboratorio 1980;10:411‐22. - PubMed
Fiaccadori 1988 {published data only}
-
- Fiaccadori F, Elia GF, Lehndorff H, Merli M, Pedretti G, Riggio O, et al. The Effect of dietary supplementation with branched‐chain amino acids (BCAAs)vs casein in patients with chronic recurrent portal systemic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Soeters PB, Wilson JHP, Meijer AJ, Holm E editor(s). Advances in Ammonia Metabolism and Hepatic Encephalopathy. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., 1988:489‐97.
-
- Fiaccadori F, Lehndorff H, Merli M, Pedretti G, Perinotto P, Riggio O, et al. BCAA oral dietary supplementation vs casein in chronic recurrent HE A controlled trial (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 1987;4 Suppl 1:16.
Freeman 1983 {published data only}
-
- Freeman JG, Bassendine M, Heath P, James OFW, Record CO. Double blind trial of branched chain amino acid infusions in cases of hepatic encephalopathy (Abstract). Gut 1983;24(5):A503.
Fukushima 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fukushima H, Miwa Y, Ida E, Kuriyama S, Toda K, Shimomura Y, et al. Nocturnal branched‐chain amino acid administration improves protein metabolism in patients with liver cirrhosis: comparison with daytime administration. Journal Parenteral Enteral Nutrition 2003;27(5):315‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Galloway 1987 {published data only}
-
- Galloway JR, Hooks MA, Millikan WJ, HendersonJM, Towns M, Kutner MH, et al. The nutritional effects of F080 versus standard intravenous hyperalimentation in malnourished cirrhotics with subclinical encephalopathy (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1987;13 Suppl 1:8.
Gavazzl 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gavazzl C, Bozzetti F, Crippa F, Mariani L, Antonini R. Impact of different energy substrates on liver metastases metabolism (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1999;18 Suppl 1:50.
Glynn 1988 {published data only}
-
- Glynn MJ, Powell Tuck J, Reaveley DA, Murray Lyon IM. High lipid parenteral nutrition improves portosystemic encephalopathy. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1988;12(5):457‐61. - PubMed
-
- Glynn MJ, Powell‐Tuck J, Reaveley D, Murray‐Lyon IM. High lipid parenteral feeds raise plasma branched chain amino acid concentrations ‐ a possible therapeutic approach to portasystemic encephalopathy? (Abstract). Gut 1985;26(5):A569. - PubMed
-
- Glynn MJ, Powell‐Tuck J, Reaveley DA, Murray‐Lyon IM. High lipid parenteral feeds raise plasma branched chain amino acid concentrations ‐ a possible therapeutic approach to portasystemic encephalopathy?. Clinical Nephrology 1986;5:109‐12. - PubMed
Grungreiff 1993 {published data only}
-
- Grungreiff K, Kleine FD, Musil HE, Diete U, Franke D, Klauck S, et al. Valine enriched branched‐chain amino acids in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy [Valin und Verzweigtkettige Aminosauren in der Behandlung der Hepatischen Enzephalopathie]. Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie 1993;31(4):235‐41. - PubMed
Grungreiff 2001 {published data only}
-
- Grungreiff K, Lambert‐Baumann J. Efficacy of L‐ornithin‐L‐aspartate‐granules in chronic liver diseases [Wirksamkeit von L‐ornithin‐L‐aspartat‐granulat bei chronischen lebererkrankungen]. Medizinische Welt 2001;52(7‐8):219‐26.
Guarnieri 1982 {published data only}
-
- Guarnieri GF, Toigo G, Pozzato G, Faccini L, Giuntini D, Situlin R, et al. Long‐term oral supplementation of chronic liver disease patients with branched‐chain amino acids and/or energy (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1982;1 Special Suppl:54.
-
- Guarnieri GF, Toigo G, Situlin R, Pozzato G, Faccini L, et al. Muscle biopsy studies on malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi‐Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:193‐208.
Guarnieri 1984 {published data only}
-
- Guarnieri GF, Chiesa L, Toigo G, Pozzato G, Lucchesi A, Sasso F, et al. Short‐term treatment of chronic recurrent hepatic encephalopathy with enteral administration of a mixture rich in branched‐chain amino acids and energy [Trattamento a breve termine dell'encefalopatia epatica cronica ricorrente con somministrazione enterale di una miscela ricca in aminoacidi ramificati ed energia]. Giornale di Clinica Medica 1984;65(2):79‐85. - PubMed
Habu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Habu D, Nishiguchi S. Effect of oral supplementation with branched‐chain amino acid granules on serum albumin level in the early stage of cirrhosis (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2003;27(1):37‐8.
-
- Habu D, Nishiguchi S, Nakatani S, Kawamura E, Lee C, Enomoto M, et al. Effect of oral supplementation with branched‐chain amino acid granules on serum albumin level in the early stage of cirrhosis: a randomized pilot trial. Hepatology Research 2003;25(3):312‐8. - PubMed
Habu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Habu D, Nishiguchi S, Nakatani S, Lee C, Enomoto M, Tamori A, et al. Comparison of the effect of BCAA granules on between decompensated and compensated cirrhosis. Hepato‐gastroenterology 2009;56(96):1719‐23. - PubMed
Haji 2008 {published data only}
-
- Haji S, Shinzaki W, Satoi S, Ohlyanagi H. Immunonutrition with high‐dose EPA and arginine induces immunological preconditioning on TH1/TH2 balance in major hepatic resection for liver malignancy (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 2008;Suppl 1:64.
Hayaishi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hayaishi S, Chung H, Kudo M, Ishikawa G, Takita M, Ueda T, et al. Oral Branched‐Chain Amino Acid Granules Reduce the Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Improve Event‐Free Survival in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis. Digestive Diseases 2011;29(3):326‐32. - PubMed
Hayashi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hayashi M, Ikezawa K, Ono A, Okabayashi S, Hayashi Y, Shimizu S, et al. Evaluation of the effects of combination therapy with branched‐chain amino acid and zinc supplements on nitrogen metabolism in liver cirrhosis. Hepatology Research 2007;37(8):615‐9. - PubMed
Herlong 1980 {published data only}
-
- Herlong HF, Maddrey WC, Walser M. The use of ornithine salts of branched‐chain ketoacids in portal‐systemic encephalopathy. Annals of Internal Medicine 1980;93(4):545‐50. - PubMed
Hernandez‐Guerra 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hernandez‐Guerra M, Garcia‐Pagan JC, Turnes J, Bellot P, Deulofeu R, Abraldes JG, et al. Ascorbic acid improves the intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction of patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Hepatology 2006;43(3):485‐91. - PubMed
Holdsworth 1984 {published data only}
-
- Holdsworth JD, Dionigi P, Clague MB, James OFW, Wright PD. Body protein metabolism and plasma amino acids in cirrhosis of the liver The effect of varying the branched chain amino acid content of intravenous amino acid solutions. Clinical Nutrition 1984;3:153‐62. - PubMed
Holm 1981 {published data only}
-
- Holm E, Langhans W, Meisinger E, Hiltmann W‐D, Gastreiger P. BCAA‐enriched diets for oral treatment of patients with liver cirrhosis: a controlled study of biochemical variables, psychometric performance, and the EEG (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:354.
Holm 1984 {published data only}
-
- Holm E, Tschepe A, Staedt U, Leweling H, Striebel JP. Concentrations of energy yielding substrates and metabolites in the postabsorptive state and during parenteral nutrition (lipid systems) in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1984;2(Spec Suppl):O.66.
Holm 2000 {published data only}
-
- Holm E, Hess Y, Leweling H, Barth H‐O, Hagmüller E. Ornithine aspartate (OA) promotes amino acid (AA) retention in the peripheral tissues of patients with liver cirrhosis A double‐blind randomized crossover study (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2000;15(1):368.
Horst 1984 {published data only}
-
- Horst D, Grace N, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. A double‐blind randomized comparison of dietary protein and an oral branched chain amino acid (BCAA) solution in cirrhotic patients with chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy (PSE) (Abstract). Hepatology 1982;2(1):184. - PubMed
-
- Horst D, Grace N, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. A double‐blind randomized comparison of dietary protein and oral branched chain amino acid (BCAA) supplement in cirrhotic patients with chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy (PSE) (Abstract). Hepatology 1981;1:518. - PubMed
-
- Horst D, Grace ND, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. Comparison of dietary protein with an oral, branched chain‐enriched amino acid supplement in chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 1984;4(2):279‐87. - PubMed
Huisman 2011 {published data only}
-
- Huisman E, Hoek B, Soest H, Nieuwkerk KC, Arends J, Siersema PD, et al. Preventive versus "on‐Demand" nutritional support to maintain nutritional state and quality of life during antiviral therapy for hepatitis C: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 2011;54 Suppl 1:851A.
Hwang 1988 {published data only}
-
- Hwang SJ, Chan CY, Wu JC, Lee SD, Huan YS, Tsai YT. A randomized controlled trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of branched chain amino acid‐enriched amino acid solution in the treatment of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 1988;5:185‐92.
Ichida 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ichida T, Shibasaki K, Muto Y, Satoh S, Watanabe A, Ichida F. Clinical‐study of an enteral branched‐chain amino‐acid solution in decompensated liver‐cirrhosis with hepatic‐encephalopathy. Nutrition 1995;11(2):238‐44. - PubMed
Ikegami 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ikegami T, Shirabe K, Yoshiya S, Yoshizumi T, Ninomiya M, Uchiyama H, et al. Bacterial sepsis after living donor liver transplantation: the impact of early enteral nutrition. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 2012;214:288‐95. - PubMed
Ilan 2000 {published data only}
-
- Ilan Y, Sobol T, Sasson O, Ashur Y, Berry EM. A balanced 5:1 carbohydrate:protein diet: a new method for supplementing protein to patients with chronic liver disease. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2000;15(12):1436‐41. - PubMed
Itou 2009 {published data only}
-
- Itou M, Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Shiraishi S, Ibi R, Mutou M, et al. Heating improves poor compliance with branched chain amino acid‐rich supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis: a before‐after pilot study. Molecular Medicine Reports 2009;2(6):983‐7. - PubMed
Itou 2011 {published data only}
-
- Itou M, Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Oriishi T, Suetsugu T, Hano R, et al. Supplementation before endoscopic therapy for esophageal varices reduces mental stress in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 2011;58(107‐108):814‐8. - PubMed
Jentschura 1996 {published data only}
-
- Jentschura D, Storz LW, Rumstadt B, Winkler M. Hepatic encephalopathy following porto‐systemic shunt. Langenbecks Archiv Fur Chirurgie 1996;381(5):283‐8. - PubMed
Jiang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jiang ZM, Gu ZY, Chen FL, Wang XR, Li ZJ, Xu Y, et al. The role of immune enhanced enteral nutrition on plasma amino acid, gut permeability and clinical outcome (a randomized, double blind, controlled, multi‐center clinical trail with 120 cases). Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae 2001;23(5):515‐8. - PubMed
Jiang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jiang H, Li B, Yan L‐N, Lu S‐C, Wen T‐F, Zhao J‐C, et al. Effect of intravenous glutamine‐dipeptide fortified enteral nutrition on clinical outcomes in patients after liver transplantation: a prospective randomized controlled study. Chinese Jouirnal of Clinical Nutrition 2007;15(1):21‐5.
Jonung 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jonung T, Jeppsson B, Aslund U, Nair BM. A comparison between meat and vegan protein diet in patients with mild chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Clinical Nutrition 1987;6(3):169‐74.
Kaido 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kaido T, Mori A, Ogura Y, Hata K, Yoshizawa A, Iida T, et al. Impact of enteral nutrition using a new immuno‐modulating diet after liver transplantation. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 2010;57(104):1522‐5. - PubMed
Kakumitsu 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kakumitsu S, Shijo H, Yokoyama M, Kim T, Akiyoshi N, Ota K, et al. Effects of L‐arginine on the systemic, mesenteric, and hepatic circulation in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1998;27(2):377‐82. - PubMed
Kanematsu 1988 {published data only}
-
- Kanematsu T, Koyanagi N, Matsumata T, Kitano S, Takenaka K, Sugimachi K. Lack of preventive effect of branched‐chain amino acid solution on postoperative hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a randomized, prospective trial. Surgery 1988;104(3):482‐8. - PubMed
-
- Kanematsu Takashi, et al. Is branched chain amino acid infusion effective in prevention of postoperative hepatic failure in patients with hepatic cirrhosis?: a prospective, randomized study [Kankohen Shorei no Jutsugo Kanfuzen Yobo ni Bunkisa Aminosan (BCAA) Yueki wa Yuko ka?: Prostective, Randomized Study]. Rinsho to Kenkyu (The Japanese Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine) 1988;65(3):897.
Katsumi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Katsumi N, Kawamura N, Yamaguchi Y, Sato Y, Morozumi K, Nakajima H, et al. Effect of oral branched chain amino acid‐rich nutrient administered during endoscopic injection sclerotherapy of cirrhotic patients. Hepatology Research 2005;32(3):158‐62. - PubMed
Kawaguchi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Itou M, Mutou M, Ibi R, Shiraishi S, et al. Supplement improves nutrition and stresses caused by examination‐associated fasting in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology Research 2008;38(12):1178‐85. - PubMed
Kawamura 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kawamura E, Habu D, Iwai S, Morikawa H, Enomoto M, Tamori A, et al. A randomized pilot trial of oral branched‐chain amino acids in early liver cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology 2008;48 Suppl 2:116‐7.
-
- Kawamura E, Habu D, Morikawa H, Enomoto EM, Kawabe J, Tammori A, et al. A randomized pilot trial of oral branched‐chain amino acids in early cirrhosis: validation using prognostic markers for pre‐liver transplant status. Liver Transplantation 2009;15(7):790‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Keshavarzian 1984 {published data only}
-
- Keshavarzian A, Meek J, Sutton C, Emery VM, Hughes EA, Hodgson HJ. Dietary protein supplementation from vegetable sources in the management of chronic portal systemic encephalopathy. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1984;79(12):945‐9. - PubMed
Kircheis 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kircheis G, Nilius R, Held C, Berndt H, Buchner M, Gortelmeyer R, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of L‐ornithine‐L‐aspartate infusions in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a placebo‐controlled, double‐blind study. Hepatology 1997;25(6):1351‐60. - PubMed
-
- Stauch S, Kircheis G, Adler G, Beckh K, Ditschuneit H, Gortelmeyer R, et al. Oral L‐ornithine‐L‐aspartate therapy of chronic hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a placebo‐controlled double‐blind study. Journal of Hepatology 1998;28(5):856‐64. - PubMed
Kobayashi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kobayashi M, Ikeda K, Arase Y, Suzuki Y, Suzuki F, Akuta N, et al. Inhibitory effect of branched‐chain amino acid granules on progression of compensated liver cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus. Journal of Gastroenterology 2008;43(1):63‐70. - PubMed
Krasnoff 2006 {published data only}
-
- Krasnoff JB, Vintro AQ, Ascher NL, Bass NM, Paul SM, Dodd MJ, et al. A randomized trial of exercise and dietary counselling after liver transplantation. American Journal of Transplantation 2006;6(8):1896‐905. - PubMed
Kuroda 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kuroda H, Ushio A, Miyamoto Y, Sawara K, Iokawa K, Kasai K, et al. Effects of branched‐chain amino acid‐enriched nutrient for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma following radiofrequency ablation: a one‐year prospective trial. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2010;25:1550‐5. - PubMed
Kuse 1990 {published data only}
-
- Kuse ER, Kemnitz J, Kotzerke J, Wassmann R, Gubernatis G, Ringe B, et al. Fat emulsions in parenteral nutrition after liver transplantation: The recovery of the allografts RES function and histological observations. Clinical Nutrition 1990;9(6):331‐6. - PubMed
-
- Kuse ER, Kotzerke J, Ringe B, Wassmann R, Gubernatis G, Pichlmayr I. Fat emulsions in parenteral feeding following liver transplantation I Effect on the recovery of RES function in the transplant [Fettemulsionen in der parenteralen Ernahrung nach Lebertransplantation I Einfluss auf die Erholung der RES‐Funktion im Transplantat]. Annales Chirurgiae et Gynaecologiae 1990;25(6):428‐31. - PubMed
-
- Kuse ER, Nordmann S, Kemnitz J, Gubernatis G, Kotzerke J. MCT/LCT‐fat emulsions in the parenteral nutrition of patients after liver transplantation. Influence on the recovery of the RES function and the level of liver cell fatty degeneration [MCT/LCT‐Fettemulsionen in der parenteralen Ernahrung des lebertransplantierten Patienten. Einfluss auf die Erholung der RES‐Funktion und den Grad der Leberzellverfettung.]. Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie 1989;27(1):40.
Kuse 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kuse ER, Kotzerke J, Muller S, Nashan B, Luck R, Jaeger K. Hepatic reticuloendotherlial function during parenteral nutrition including an MCT/LCT or LCT emulsion after liver transplantation ? a double‐blind study. Transplantation International 2002;15:272‐7. - PubMed
-
- Müller S, Kotzerke J, Behrend M, Liebau P, Wu A, Kuse ER. Double‐blind study on hepatic RES‐function after hepatic transplantation under parenteral nutrition with an MCT‐ or LCT‐lipid‐emulsion [Doppelblind‐Studie zur hepatischen RES‐Funktion nach Lebertransplantation unter parenteraler Ernährung mit einer MCT‐ oder LCT‐Fettemulsion]. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 1995;107 Suppl 198:13‐4.
Labadie 1994 {published data only}
-
- Labadie M, Arnaud J, Enkaoua W, Zarski JP, Tricot F, Vaysse J, et al. Effect of zinc supplementation in alcoholic cirrhosis. A double blind, randomized study. Trace Elements in Medicine 1994;11(1):23‐8.
LaTerre 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Laterre P‐F, Fleury Y. Safety and tolerance on lipids of parenteral and enteral nutrition in critically ill patients with liver failure. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00522730.
Leon 2009 {published data only}
-
- Leon CDG. Nocturnal nutritional supplementation improves total body protein status of patients with liver cirrhosis: A randomized 12‐month trial. Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2009;24(1):104‐6. - PubMed
Les 2011 {published data only}
-
- Les I, Doval E, Garcia‐Martinez R, Planas M, Cardenas G, Gomez P, et al. Effects of branched‐chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized study. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;106:1081‐8. - PubMed
-
- Les I, Planas M, Cardenas G, Flavia M, Vergara M, Soriano G, et al. Effects of the proteins of the diet in patients with cirrhosis and a prior episode of hepatic encephalopathy. A long‐term randomized study. Hepatology 2009;50 Suppl(4):313A.
Luntz 2005 {published data only}
-
- Luntz SP, Unnebrink K, Seibert‐Grafe M, Bunzendahl H, Kraus TW, Buchler MW, et al. HEGPOL: Randomized, placebo controlled, multicenter, double‐blind clinical trial to investigate hepatoprotective effects of glycine in the postoperative phase of liver transplantation [ISRCTN69350312]. BMC Surgery 2005;5:18. - PMC - PubMed
Mager 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mager DR, Wykes LJ, Roberts EA, Ball RO, Pencharz PB. Branched‐chain amino acid needs in children with mild‐to‐moderate chronic cholestatic liver disease. Journal of Nutrition 2006;136(1):133‐9. - PubMed
-
- Mager DR, Wykes LJ, Roberts EA, Ball RO, Pencharz PB. Effect of orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) on branched‐chain amino acid requirement. Pediatric Research 2006;59(6):829‐34. - PubMed
Makay 2007 {published data only}
-
- Makay B, Duman N, Ozer E, Kumral A, Yesilirmak D, Ozkan H. Randomized, controlled trial of early intravenous nutrition for prevention of neonatal jaundice in term and near‐term neonates. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2007;44(3):354‐8. - PubMed
Malaguarnera 2009 {published data only}
-
- Malaguarnera M, Risino C, Cammalleri L, Malaguanera L, Astuto M, Vecchio I, et al. Branched chain amino acids supplemented with l‐acetylcarnitine versus BCAA treatment in hepatic coma: a randomized and controlled double blind study. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2009;21(7):762‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mangiante 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mangiante G, Rossi L, Carluccio S, Marchiori L, Colucci G, Ciola M, et al. Influence of enteral nutrition on cytokine response in resective liver surgery [Influenza della nutrizione enterale sulla risposta citochinica in chirurgia resettiva epatica]. Chirurgia Italiana 2002;54(5):613‐9. - PubMed
-
- Mangiante GL. Influence of enteral nutrition on cytokines response in resective liver surgery for HCC. International Journal of Cancer 2002;Suppl 13:235.
Manguso 2005 {published data only}
-
- Manguso F, D'Ambra G, Menchise A, Sollazzo R, D'Agostino L. Effects of an appropriate oral diet on the nutritional status of patients with HCV‐related liver cirrhosis: a prospective study. Clinical Nutrition 2005;24(5):751‐9. - PubMed
Marchesini 1980 {published data only}
-
- Marchesini G, Zoll M, Dondi C, Cecchini L, Angiolini A, Bianchi F, et al. Prevalence of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics and relationship to plasma amino acid imbalance. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1980;25(10):763‐8. - PubMed
Marchesini 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bianchi GP, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Abbiati R, Ferrario E, Fabbri A, et al. Oral BCAA supplementation in cirrhosis with chronic encephalopathy: effects on prolactin and estradiol levels. Hepatogastroenterology 1992;39(5):443‐6. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi GP, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Bellati G, Colombo A, Ideol G, et al. Oral BCAA supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis Preliminary results of a randomized double multicentre study (Abstract). Italian Journal of Gastroenterology 1987;19:120.
-
- Marchesini G, Bianchi GP, Zoli M, Bellati G, Colombo A, Ideo G, et al. A randomized double‐blind study of oral BCAA in patients with cirrhosis (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 1987;5 Suppl 1:43.
-
- Marchesini G, Dioguardi F.S, Bianchi G.P, Zoli M, Bellati G, Roffi L, et al. Long‐term oral branched‐chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A randomized double‐blind casein‐controlled trial. Journal of Hepatology 1990;11(1):92‐101. - PubMed
-
- Marchesini G, Dioguardi FS, Bianchi GP, Zoli M, Bellati G, Roffi L, et al. A randomized double‐blind study of oral BCAA in patients with cirrhosis (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 1990;10 Suppl 1:15. - PubMed
Marchesini 2003 {published data only}
-
- Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Merli M, Amodio P, Panella C, Loguercio C, et al. Nutritional supplementation with branched‐chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: a double‐blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology 2003;124(7):1792‐801. - PubMed
Marchini 1983 {published data only}
-
- Marchini JS, Vannucchi H, Dutra de Oliveira JE. Effect of two carbohydrate :lipid ratios of diets enterally fed to chronic alcoholics. Human Nutrition: Clinical Nutrition 1983;37C:329‐37. - PubMed
Marra 1998 {published data only}
-
- Marra F, Riccardi D, Melani L, Spadoni S, Galli C, Fabrizio P, et al. Effects of supplementation with unsaturated fatty acids on plasma and membrane lipid composition and platelet function in patients with cirrhosis and defective aggregation. Journal of Hepatology 1998;28(4):654‐61. - PubMed
McGhee 1983 {published data only}
Mendenhall 1985 {published data only}
-
- Mendenhall C, Bongiovanni G, Goldberg S, et al. VA cooperative study on alcoholic hepatitis III: Changes in protein‐calorie malnutrition associated with 30 days of hospitalization with and without enteral nutritional therapy. Journal of Parenteral & Enteral Nutrition 1985;9(5):590‐6. - PubMed
Mendenhall 1993 {published data only}
-
- Mendenhall CL, Moritz TE, Roselle GA, Morgan TR, Nemchausky BA, Tamburro CH, et al. A study of oral nutritional support with oxandrolone in malnourished patients with alcoholic hepatitis: results of a Department of Veterans Affairs cooperative study. Hepatology 1993;17(4):564‐76. - PubMed
-
- Mendenhall CL, Moritz TE, Roselle GA, Morgan TR, Nemchausky BA, Tamburro CH, et al. Protein‐energy malnutrition in severe alcoholic hepatitis ‐ diagnosis and response to treatment. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1995;19(4):258‐65. - PubMed
-
- Morgan TR, Moritz TE, Mendenhall CL, Haas R. Protein consumption and hepatic encephalopathy in alcoholic hepatitis VA Cooperative Study Group #275. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 1995;14(2):152‐8. - PubMed
Mezey 1991 {published data only}
-
- Mezey E, Caballeria J, Mitchell MC, Pares A, Herlong HF, Rodes J. Effect of parenteral amino‐acid supplementation on short‐term and long‐term outcomes in severe alcoholic hepatitis ‐ a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 1991;14(6):1090‐6. - PubMed
Michel 1985 {published data only}
-
- Michel H, Bories P, Aubin JP, Pomier‐Layrargues G, Bauret P, Bellet‐Herman H. Treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics with a branched‐chain amino acids enriched versus a conventional amino acids mixture. A controlled study of 70 patients. Liver 1985;5(5):282‐9. - PubMed
-
- Michel H, Bories P, Nalet B, Mourrut C, Pierrugues R. Exclusive parenteral nutrition (EPN) in denutritive alcoholic cirrhotics (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 1985;1 Suppl 2:290.
-
- Michel H, Pomier‐Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleet G, Bellet‐Hermann H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino‐acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy (controlled study, 30 patients) (AASLDabstract). Gastroenterology 1980;79:1038.
-
- Michel H, Pomier‐Layrargues G, Qubin JP, Bories P, Mirouze D, Bellet‐Herman H. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by infusion of a modified amino acid solution: results of a controlled study in 47 cirrhotic patients. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi‐Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:301‐10.
-
- Pomier‐Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet H, Michel H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino‐acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Liver 1981;1:140.
Mochizuki 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mochizuki H, Togo S, Tanaka K, Endo I, Shimada H. Early enteral nutrition after hepatectomy to prevent postoperative infection. Hepatogastroenterology 2000;47:1407‐10. - PubMed
Moreno 2010 {published data only}
-
- Moreno C, Langlet P, Hittelet A, Evrard S, Lasser L, Colle I, et al. Enteral nutrition with or without n‐acetylcysteine in the treatment of severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a randomized, multicenter, controlled trial (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 2009;50 Suppl 1:366. - PubMed
-
- Moreno C, Langlet P, Hittelet A, Lasser L, Degre D, Evrard S, et al. Enteral nutrition with or without N‐acetylcysteine in the treatment of severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a randomized multicenter controlled trial. Journal of Hepatology 2010;53:1117‐22. - PubMed
Morioka 1983 {published data only}
-
- Morioka S, Kanai K, Kako M, Nakajima T, Yoshimi T, Masaka M, et al. Effects of branched chain amino acid infusion on glucose metabolism in cirrhotic patients with encephalopathy. Gastroenterologia Japonica 1983;18(6):553‐9. - PubMed
Muto 1984 {published data only}
-
- Muto Y, Yoshida T. Effect of oral supplementation with branched‐chain amino acid granules on improvement of protein nutrition in decompensated liver cirrhosis: a cross‐over controlled study. In: Ogoshi S, Ikada A editor(s). Parenteral and Enteral Hyperalimentation. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1984:280‐92.
Muto 1991 {published data only}
-
- Muto Y, Yoshida T, Sato SI, Watanabe A, Okabe K. Effect of branched‐chain amino acid granule (BSAA‐G) on improvement in protein malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis: a multicentre double‐blind trial (Abstract). Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1991;6(3):312.
Muto 2005 {published data only}
-
- Moriwaki H, Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Oral supplementation with branched chain amino acids reduces the incidence of liver failure in lean cirrhotic patients and prevents liver cancer in overweight/obese cirrhotics (Abstract). Hepatology 2006;44 Suppl 1(4):216A.
-
- Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Effects of oral branched‐chain amino acid granules on event‐free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2005;3(7):705‐13. - PubMed
-
- Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Long‐term survival study (LOTUS) of branched‐chain amino acid (BCAA) granules improves event‐free survival in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2004;40 Suppl 4(4):511A.
-
- Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Overweight and obesity increase the risk for liver cancer in patients with liver cirrhosis and long‐term oral supplementation with branched‐chain amino acid granules inhibits liver carcinogenesis in heavier patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology Research 2006;35(3):204‐14. - PubMed
Nagayama 1989 {published data only}
-
- Nagayama M, Takai T, Okuno M, Umeyama K. Fat emulsion in surgical patients with liver disorders. The Journal of Surgical Research 1989;47(1):59‐64. - PubMed
Nasrallah 1980 {published data only}
-
- Nasrallah SM, Galambos JT. Aminoacid therapy of alcoholic hepatitis. Lancet 1980;2(8207):1276‐7. - PubMed
Ndraha 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ndraha S, Hasan I, Simadibrata M. The effect of L‐ornithine L‐aspartate and branch chain amino acids on encephalopathy and nutritional status in liver cirrhosis with malnutrition. Acta Medica Indonesiana 2011;43(1):18‐22. - PubMed
Nickkholgh 2007 {published data only}
Nielsen 1995 {published data only}
-
- Nielsen K, Kondrup J, Martinsen L, Dossing H, Larsson B, Stilling B, et al. Long‐term oral refeeding of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. British Journal of Nutrition 1995;74(4):557‐67. - PubMed
Nishiguchi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nishiguchi S, Habu D. Effect of oral supplementation with branched‐chain amino acid granules in the early stage of cirrhosis. Hepatology Research 2004;30 Suppl:36‐41. - PubMed
Nishizaki 1996 {published data only}
-
- Nishizaki T, Takenaka K, Yanaga K, Shimada M, Shirabe K, Matsumata T, et al. Nutritional support after hepatic resection: a randomized prospective study. Hepatogastroenterology 1996;43(9):608‐13. - PubMed
Nordenstrom 1995 {published data only}
-
- Nordenstrom J, Johansson U, Thorne A, Hagenfeldt L. Metabolism of long‐chain triglycerides (LCT) vs structured triglycerides (STG) in chronic liver failure (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1995;14 Suppl 2:59.
O'Keefe 1987 {published data only}
-
- O'Keefe SJ, Ogden J, Dicker J. Enteral and parenteral branched chain amino acid‐supplemented nutritional support in patients with encephalopathy due to alcoholic liver disease. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1987;11(5):447‐53. - PubMed
Okabayashi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Okabayashi T, Nishimori I, Sugimoto T, Iwasaki S, Akisawa N, Maeda H, et al. The benefit of the supplementation of perioperative branched‐chain amino acids in patients with surgical management for hepatocellular carcinoma: a preliminary study. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2008;53(1):204‐9. - PubMed
-
- Okabayashi T, Nishimori I, Sugimoto T, Maeda H, Dabanaka K, Onishi S, et al. Effects of branched‐chain amino acids‐enriched nutrient support for patients undergoing liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2008;23(12):1869‐73. - PubMed
Okabayashi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Okabayashi T, Iyoki M, Sugimoto T, Kobayashi M, Hanazaki K. Oral supplementation with carbohydrate‐ and branched‐chain amino acid‐enriched nutrients improves postoperative quality of life in patients undergoing hepatic resection. Amino Acids 2011;40:1213‐20. - PubMed
-
- Okabayashi T, Nishimori I, Yamashita K, Sugimoto T, Namikawa T, Maeda H, et al. Preoperative oral supplementation with carbohydrate and branched‐chain amino acid‐enriched nutrient improves insulin resistance in patients undergoing a hepatectomy: a randomized clinical trial using an artificial pancreas. Amino Acids 2010;38:901‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Okita 1985 {published data only}
-
- Okita M, Watanabe A, Nagashima H. A branched‐chain amino acid‐supplemented diet in the treatment of liver cirrhosis. Current Therapeutic Research 1984;35(1):83‐92.
-
- Okita M, Watanabe A, Nagashima H. Nutritional treatment of liver cirrhosis by branched‐chain amino acid‐enriched nutrient mixture. Journal of Nutrition Science and Vitaminology 1985;31(3):291‐303. - PubMed
Okuno 1985 {published data only}
-
- Okuno M, Nagayama M, Takai T, Rai A, Nakao S, Kamino K, et al. Postoperative total parenteral nutrition in patients with liver disorders. Journal of Surgical Research 1985;39(2):93‐102. - PubMed
Olde Damink 2007 {published data only}
-
- Olde Damink SWM, Jalan R, Deutz NEP, Dejong CHC, Redhead DN, Hynd P, et al. Isoleucine infusion during "simulated" upper gastrointestinal bleeding improves liver and muscle protein synthesis in cirrhotic patients. Hepatology 2007;45(3):560‐8. - PubMed
Panella 1987 {published data only}
-
- Panella C, Guglielmi FW, Laddaga L, Rocco VP, Marcone I, Polimeno L, et al. Improvement of nitrogen balance in cirrhotic patients after oral BCAA (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 1987;5 Suppl 1:50.
Pierrugus {published data only}
-
- Pierrugues R, Bauret P, Michel H. Continous enteral nutrition (CEN) in denutritive alcoholic cirrhotics (randomized trial) (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 1985;1 Suppl 2:308.
Plank 2005 {published data only}
-
- Plank LD, McCall JL, Gane EJ, Rafique M, Gillanders LK, McIlroy K, Munn SR. Pre‐ and postoperative immunonutrition in patients undergoing liver transplantation: a pilot study of safety and efficacy. Clinical Nutrition 2005;24(2):288‐96. - PubMed
Plank 2008 {published data only}
-
- Plank LD, Gane EJ, Peng S, Muthu C, Mathur S, Gillanders L, et al. Nocturnal nutritional supplementation improves total body protein status of patients with liver cirrhosis: a randomized 12‐month trial. Hepatology 2008;48(2):557‐66. - PubMed
Plauth 1993 {published data only}
-
- Plauth M, Egberts EH, Hamster W, Török M, Müller P, Brand O, et al. Long‐term treatment with branched‐chain amino acids (BCA) improves the portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) in ambulant patients Results of a double blind, placebo controlled crossover study (Abstract) [Langzeitbehandlung mit verzweigtkettingen aminosauren verbessert die portosystemische enzephalopathie (PSE) ambulanter patienten Ergebnisse einer dobbelt‐blinden plazebo‐kontrollerten crossover studie]. Klinische Wochenschrift 1992;69 Suppl 28:126.
-
- Plauth M, Egberts EH, Hamster W, Török M, Müller PH, Brand O, et al. Long‐term treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy with branched‐chain amino acids. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled crossover study. Journal of Hepatology 1993;17(3):308‐14. - PubMed
Protheroe 1996 {published data only}
-
- Protheroe S, Jones R, Kelly DA. Evaluation of the role of branched chain amino acids in the treatment of protein malnutrition in infants with liver disease (Abstract). Gut 1995;37 Suppl 2:A30.
-
- Protheroe S, McNurlan M, Garlick P, Golden M, Booth I, Kelly D. Faillure to suppress protein breakdown contributes towards malnutrition in infants with liver disease (Abstract). Hepatology 1996;24(4 (Pt 2)):141A.
Puglionisi 1984 {published data only}
-
- Puglionisi A, Ceriati F, Marino IR, Cavicchioni C, Luca G, Roncone A, et al. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after porta‐caval anastomosis using branched chain amino acid mixtures. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi‐Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:345‐50.
Rakette 1981 {published data only}
-
- Rakette S, Fischer M, Reimann H‐J, Sommoggy S. Effects of special amino acid solutions in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy. In: Walser M, Williamson JR editor(s). Metabolism and Clinical Implications of Branched Chain Amino and Ketoacids. Amsterdam: Elsevier North Holland, 1981:419‐25.
Rayes 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rayes N, Hansen S, Boucsein K, Seehofer D, Muller AR, Bengmark S, et al. Enteral nutrition containing lactobacillus versus selective gut decontamination after liver transplantation [Laktobazillenhaltige enterale Ernahrung versus SDD nach Lebertransplantation]. Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie 2002;40(2):119.
-
- Rayes N, Hansen S, Muller AR, Staffa G, Bechstein WO, Neuhaus P. SBD versus fibre containing enteral nutrition plus Lactobacillus or placebo to prevent bacterial infections after liver transplantation. Transplantation 1999;67(7):747.
-
- Rayes N, Seehofer D, Hansen S, Boucsein K, Muller AR, Serke S, et al. Early enteral supply of lactobacillus and fiber versus selective bowel decontamination: a controlled trial in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation 2002;74(1):123‐7. - PubMed
-
- Rayes N, Seehofer D, Theruvath T, Langrehr JM, Muller AR, Bengmark S, et al. Impact of early enteral nutrition with a combination of pre‐ and probiotics in patients following liver transplantation on the incidence of postoperative bacterial infections ‐ a randomised, double‐blind trial. Liver Transplantation 2003;9(6):305.
-
- Rayes N, Seehofer D, Theruvath T, Schiller RA, Langrehr JM, Jonas S, et al. Supply of pre‐ and probiotics reduces bacterial infection rates after liver transplantation‐‐a randomized, double‐blind trial. American Journal of Transplantation 2005;5(1):125‐30. - PubMed
Riederer 1980 {published data only}
-
- Riederer P, Jellinger K, Kleinberger G, Weiser M. Oral and parenteral nutrition with L‐valine: mode of action. Nutrition and Metabolism 1980;24:209‐17. - PubMed
Rifai 2006 {published data only}
-
- Rifai K, Ockenga J, Manns MP, Bischoff SC. Repreated administration of a vitamin preparation containing glycocholic acid in patients with hepatobiliary disease. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2006;23(9):`337‐45. - PubMed
Riggio 1984 {published data only}
-
- Riggio O, Canbgiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Stortoni M, Rossi Fanelli F, et al. Long term dietary supplement with branched chain amino acids: a new approach in the prevention of hepatic encephalopathy: results of a controlled study in cirrhotics with porto‐caval anastomosis. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi‐Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:183‐92.
Rocchi 1985 {published data only}
-
- Rocchi E, Cassanelli M, Gibertini P, Pietrangelo A, Casalgrandi G, Ventura E. Standard or branched‐chain amino acid infusions as short‐term nutritional support in liver cirrhosis?. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1985;9(4):447‐51. - PubMed
-
- Rocchi E, Cassanelli M, Gibertini P, Pietrangelo A, Trenti T, Ventura E. Nutritional effects of branched chain amino acid alone and enriched parenteral solutions in liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1984;2 Special Suppl:O.65.
-
- Rocchi E, Gibertini P, Casanelli M, Pietrangelo A, Ventura E. Plasma amino acids and nitrogen balance in response to short term branched amino acid parenteral nutrition in liver cirrhosis. Medecine and Chirurgie Digestives 1984;13:185‐92.
Rossi Fanelli 1986 {published data only}
-
- Rossi Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Riggio O, Stortoni M, et al. Branched‐chain amino acids in the treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi‐Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:335‐44.
-
- Rossi Fanelli F, Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, DeConciliis D, Merli M, et al. Branched‐chain amino acids vs lactulose in the treatment of hepatic coma: a controlled study. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1982;27:929‐35. - PubMed
Sakaida 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sakaida I, Tsuchiya M, Okamoto M, Terai S, Okita K. The effect of a late evening snack in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2004;40:632A. - PubMed
Sato 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sato S, Watanabe A, Muto Y, Suzuki K, Kato A, Moriwaki H, et al. Clinical comparison of branched‐chain amino acid (l‐Leucine, l‐Isoleucine, l‐Valine) granules and oral nutrition for hepatic insufficiency in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis (LIV‐EN study). Hepatology Research 2005;31(4):232‐40. - PubMed
Schafer 1981 {published data only}
-
- Schafer VK, Winther MB, Ukida M, Leweling H, Reiter HJ, Bode JC. Influence of an orally administered protein mixture enriched in branched chain amino acids on the chronic hepatic encephalopathy (CHE) of patients with liver cirrhosis. Zeitschrift Gastroenterologie 1981;19:356‐62. - PubMed
Shirabe 1997 {published data only}
-
- Shirabe K, Matsumata T, Shimada M, Takenaka K, Kawahara N, Yamamoto K, et al. A comparison of parenteral hyperalimentation and early enteral feeding regarding systemic immunity after major hepatic resection‐‐ the results of a randomized prospective study. Hepatogastroenterology 1997;44(13):205‐9. - PubMed
Shirabe 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shirabe K, Yoshimatsu M, Motomura T, Takeishi K, Toshima T, Muto J, et al. Beneficial effects of supplementation with branched‐chain amino acids on postoperative bacteremia in living donor liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplantation 2011;17(9):1073‐80. - PubMed
Sieg 1983 {published data only}
-
- Sieg A, Walker S, Czygan P, Gärtner U, Lanzinger‐Rossnagel G, Stiehl A, et al. Branched‐chain amino acid‐enriched elemental diet in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. A double blind crossover trial. Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie 1983;21(11):644‐50. - PubMed
Soriano {unpublished data only}
-
- Soriano G. Study of the benefit of exercise and aminoacid supplements in cirrhotic patients. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01060813.
Strauss 1986 {published data only}
-
- Strauss E, Dos Santos WR, Silva EC, Lacet CM, Capacci Mde LL, Bernardini AP. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized clinical trial comparing a branched chain enriched amino acid solution to oral neomycin. Nutritional Support Services 1986;6(7):18‐21.
-
- Strauss E, Santos WR, Cartapatti da Silva E, Lacet CM, Capacci MLL, Bernardini AP. A randomized controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of a enriched branched‐chain amino‐acid solution compared to neomycin in hepatic encephalopathy (Abstract). Hepatology 1983;3(5):862.
Striebel 1979 {published data only}
-
- Striebel JP, Holm E, Lutz H, Storz LW. Parenteral nutrition and coma therapy with amino acids in hepatic failure. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1979;3(4):240‐6. - PubMed
Sugawara 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sugawara G, Ebata T, Yokoyama Y, Igami T, Takahashi Y, Nagino M. Perioperative nutritional support for biliary cancer surgery. HPB 2011;13 Suppl 3:226.
Suzuki 2004 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki K, Kato A, Iwai M. Branched‐chain amino acid treatment in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology Research 2004;30 Suppl:25‐9. - PubMed
Swart 1981 {published data only}
-
- Swart GR, Frenkel M, Berg JWO. Minimum protein requirements in advanced liver disease: a metabolic ward study of the effects of oral branched chain amino acids . In: Walser M, Williamson JR editor(s). Metabolism and Clinical Implications of Branched Chain Amino and Ketoacids. Amsterdam: Elsevier North Holland, 1981:427‐32.
Swart 1989 {published data only}
Tai 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tai M‐LS, Razlan H, Goh K‐L, Taib SHM, Huzaini ATM, Rampal S, et al. Short‐term nasogastric feeding for hospitalised Asian patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology International 2011;5(1):356.
-
- Tai MLS, Mahadeva S. Short term feeding for Asian patients with liver cirrhosis. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT 01165073.
-
- Tai MLS, Razlan H, Goh K‐L, Mohd Taib SH, Huzaini AHM, Rampal S, et al. Short term nasogastric versus oral feeding in hospitalised patients with advanced cirrhosis: A randomised trial. e‐SPEN 2011;6(6):e242‐e247.
Tang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Tang Z‐F, Ling Y‐B, Hao Z, Lin N, Xu R‐Y. Effects of glutamine and recombinant human growth hormone on intestinal mucosal barrier in postoperative portal hypertension patients. Chinese Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;14(5):296‐9.
Tayek {unpublished data only}
-
- Tayek JA. Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis with arginine. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00200746.
Togo 2005 {published data only}
-
- Togo S, Tanaka K, Morioka D, Sugita M, Ueda M, Miura Y, et al. Usefulness of granular BCAA after hepatectomy for liver cancer complicated with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2005;21(4):480‐6. - PubMed
Tomiya 2002 {published data only}
-
- Tomiya T, Inoue Y, Yamaoka M, Hayashi S, Yanase M, Arai M, et al. Branched‐chain amino acids may stimulate protein production by hepatocytes through the induction of hepatocyte growth factor synthesis by hepatic stellate cells (Abstract). Hepatology 2002;36(4 (Pt 2)):320A.
Tschepe 1985 {published data only}
-
- Tschepe A, Holm E, Leweling H, Staedt U, Weber K. Oral administration of branched chain amino acids (BCAA) in patients with liver cirrhosis. A double‐blind, randomized crossover study (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1985;4 Special Suppl:40.
Tsuchiya 2007 {published data only}
-
- Tsuchiya K, Asahina Y, Hirayama I, Sato M, Tanaka T, Komatsu N, et al. Oral supplementation with branched‐chain amino acids improves survival and recurrence‐free survival after successful treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: A prospective study. Hepatology 2007;46 Suppl 1(4):401A‐2A.
Uribe 1982 {published data only}
-
- Uribe M, Márquez MA, Garcia Ramos G, Ramos‐Uribe MH, Vargas F, Villalobos A, et al. Treatment of chronic portal‐‐systemic encephalopathy with vegetable and animal protein diets. A controlled crossover study. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1982;27(12):1109‐16. - PubMed
Valdivieso 1989 {published data only}
-
- Valdivieso A, Morales H, Maiz A, Vial S. Effect of intravenous branched chain‐enriched amino acids (BCAA)on renal function in patients with chronic liver disease (CLD). Kidney International 1989;35:475.
Vilar‐Gomez 2009 {published data only}
-
- Vilar Gomez E, Rodriguez De Miranda A, Gra Oramas B, Arus Soler E, Llanio Navarro R, Calzadilla Bertot L, et al. Clinical trial: A nutritional supplement Viusid, in combination with diet and exercise, in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2009;30(10):999‐1009. - PubMed
Vilstrup 1990 {published data only}
-
- Gluud C, Dejgaard A, Hardt F, Kristensen, Kohler O, Melgaard B, et al. Preliminary treatment results with balanced amino acid infusion to patients with hepatic encephalopathy (Abstract). Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1983;18 Suppl 86:19.
-
- Hardt F, Dejgard A, Gluud C, Kristensen M, Kohler O, Melgaard B, et al. The effect of branched chain enriched amino acid nutrition on the outcome of acute hepatic coma in cirrhosis. The Copenhagen Coma Group (Abstract). Clinical Nutrition 1985;4 Special Suppl:43.
-
- Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid versus glucose treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. A double‐blind study of 65 patients with cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology 1990;10(3):291‐6. - PubMed
-
- Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Melgaard B, Køhler O, et al. Branced chain enriched amino acid nutrition does not change the outcome of hepatic coma in patients with cirrhosis of the liver (Abstract). Journal of Hepatology 1985;1 Suppl 2:347.
Wahren 1983 {published data only}
-
- Wahren J, Denis J, Desurmont P, Eriksson LS, Escoffier JM, GauthierAP, et al. Is intravenous administration of branched chain amino acids effective in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy? A multicenter study. Hepatology 1983;3(4):475‐80. - PubMed
-
- Wahren JH, Gauthier H, Michel P, Opolon H. Influence of branched‐chain amino acid administration on hepatic encephalopathy‐ A multicenter study (Abstract). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:355.
Walker 1982 {published data only}
-
- Walker S, Gotz R, Czygan P, Stiehl A, Lanzinger G, Sieg A, et al. Oral keto analogs of branched‐chain amino acids in hyperammonemia in patients with cirrhosis of the liver A double‐blind crossover study. Digestion 1982;24(2):105‐11. - PubMed
Wang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wang Y‐L, Cao J‐Y, Wu L‐Q, Liu J‐X. Effects of ‐3 fatty acids on inflammatory reaction and immunologic function of patients after hepatectomy. Chinese Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2011;19(3):162‐6.
Watanabe 1983 {published data only}
-
- Watanabe A, Shiota T, Okita M, Nagashima H. Effect of a branched chain amino acid‐enriched nutritional product on the pathophysiology of the liver and nutritional state of patients with liver cirrhosis. Acta Medica Okayama 1983;37(4):321‐33. - PubMed
Watanabe 1995 {published data only}
-
- Watanabe A, Kuwabara Y, Hioki O, Yago K, Kugu K, Akira M. Tentative diet for liver failure containing well‐polished rice. Nutrition 1995;11(4):355‐9. - PubMed
Weber 1990 {published data only}
-
- Weber FL, Bagby BS, Licate L, Kelsen SG. Effects of branched‐chain amino acids on nitrogen metabolism in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1990;11(6):942‐50. - PubMed
Wicks 1994 {published data only}
-
- Wicks C, Somasundaram S, Bjarnason I, Menzies IS, Routley D, Potter D, et al. Comparison of enteral feeding and total parenteral nutrition after liver transplantation. Lancet 1994;344(8926):837‐40. - PubMed
Yamamoto 2005 {published data only}
Yamana‐Okumuru 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yamanaka‐Okumura H, Nakamura T, Miyake H, Takeuchi H, Katayama T, Morine Y, et al. Effect of long‐term late‐evening snack on health‐related quality of life in cirrhotic patients. Hepatology Research 2010;40(5):470‐6. - PubMed
Yang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yang J, Zhang J‐X, Zheng Q‐C. Olive oil‐based lipid emulsion for parenteral nutrition in patients after hepatectomy. Chinese Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2011;19(2):79‐83.
Yoshiji 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yoshiji H, Noguchi R, Ikenaka Y, Kaji K, Aihara Y, Yamazaki M, et al. Combination of branched‐chain amino acids and angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor suppresses the cumulative recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized control trial. Oncology Reports 2011;26(6):1547‐53. - PubMed
Yu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yu L‐X, Liu Y‐H, Shen Z‐Y, Kang M‐N. Prospective study of effect of recombinant human growth hormone on nutritional status and immune function in early postoperative stage of liver transplantation. Chinese Critical Care Medicine 2007;19(7):390‐3. - PubMed
Zhang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhang T, Jia JD, Zhang FK, Wang BE. The effect of oral branched amino acid for cirrhotic patient with low serum protein. Chinese Journal of Clinical Hepatology 2003;19(2):84‐5.
Zhang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zhang K, Sun WB, Wang HF, Li ZW, Zhang XD, Wang HB, et al. Early enteral and parenteral nutritional support in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension after pericardial devascularization. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International 2005;4(1):55‐9. - PubMed
Zheng EN {published data only}
-
- Zheng Q, Hu Q. The influence of enteral nutrition on gut barrier in the post‐operative patients with damaged hepatic function. Journal of Tongji Medical University 2001;21(4):323‐5. - PubMed
Zhuang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhuang W, Wu X, Lü R, Xu H, Cao J. Pre‐operation application of recombinant human growth hormone for liver cirrhosis with portal hypertension and hypoproteinemia. Sichuan da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban (Journal of Sichuan University. Medical science edition) 2003;34(1):109‐11. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Caballera Rovira 1987 {published data only}
-
- Caballeria Rovira E, Arago Lopez JV, Ubeda Masso RM, Vidal Clemente JL, Sanchis Closa A. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy with oral branched chain amino acids [Tratamiento de la encefalopatia hepatica con aminoacidos de cadena ramificada (BCAA) por via oral: I. Encefalopatia hepatica aguda]. Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas 1987;72(2):116‐22. - PubMed
Chen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chen Q. Effects of early enteral nutrition on acute inflammatory response syndrome after the operations for obstructive jaundice. Hepatology International 2011;5(1):415.
Fink 1978 {published data only}
-
- Fink M, Mader R, Brauer HTI. Controlled double‐blind study on the effectiveness and tolerability of a combination therapy in chronic alcoholic liver diseases [Kontrollierte Doppelblind‐Studie auf Effektivitat und Vertraglichkeit einer Kombinationstherapie bei chronischen alkoholischen Lebererkrankungen]. Fortschritte der Medizin 1978;96(28):1428‐32. - PubMed
Hartung 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hartung H‐D. Aminoacid prevents hepatic encephalopathy [Aminosauren verhindern hepatische Enzephalopathie]. Fortschritte der Medizin 1989;107:56. - PubMed
Khlynov 2009 {published data only}
-
- Khlynov IB, Chikunova MV, Lisovskaia TV. Effectiveness of nutritional support for the liver‐cell deficiency in the liver cirrhosis. Experimental and Clinical Gastroenterology 2009;2:39‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Korenaga 2011 {published data only}
-
- Korenaga M, Korenaga K, Nishina S, Tomiyama Y, Hino K. Oral branched‐chain amino acid supplementation reduces oxidative stress and interacts with iron metabolism in patients with hepatitis C virus‐related advanced liver fibrosis ‐ A pilot study (abstract). Hepatology 2011;54 Suppl 1:513A.
Leweling 1980 {published data only}
-
- Leweling H, Knauff HG, Nitschke J, Paquet KJ. Effect of parenteral amino acid administration on the brain function and the serum aminogram of patients with liver cirrhosis [Beeingflussung von zerebralem Funktionszustand und Serumaminogramm von Patienten mit Leberzirrhose durch parenterale Aminosaurenzufuhr]. Infusionstherapie und Klinische Ernahrung 1980;7:88‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schafer K, Winther MB, Ukida M, Leweling H, Reiter HJ, Bode JC. Influence of an orally administered protein mixture enriched in branched chain amino acids on the chronic hepatic encephalopathy (CHE) of patients with liver cirrhosis. Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie 1981;19(7):356‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Macias‐Rosales 2010 {published data only}
-
- Macias‐Rosales R, Larrosa‐Haro A. Efficacy of enteral vs. oral nutrition with a medium‐chain triglyceride formula to prevent malnutrition and growth impairment in infants with biliary atresia. Journal Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2011;51 Suppl 2:E22‐3. - PubMed
Zhu‐ming 2001 {published data only}
-
- Zhu‐ming J, Zhuo‐yun G, Fu‐lai C, Xiu‐rong W, Ze‐jian L, Yuan X, et al. The role of immune enhanced enteral nutrition on plasma amino acid, gut permeability and clinical outcome (A randomized, double blind, controlled, multi‐center clinical trial with 120 cases). Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae 2001;23(5):515‐8. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Mao {unpublished data only}
-
- Mao Y. A clinical study to evaluate the clinical outcomes of hepatectomy with nutritional risk after preoperative nutritional support. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01292330.
Pirlich {unpublished data only}
-
- Pirlich M. Enteral nutrition in liver cirrhosis. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00168961.
Seguin {unpublished data only}
-
- Seguin P, Boudjema K, Malledant Y, Bellissant E. Effect of a perioperative oral nutritional supplementation on patients undergoing hepatic surgery for liver cancer (IMPACT). ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00151671. - PubMed
Van Erpecum {unpublished data only}
-
- Erpecum KJ. Nutritional support during antiviral therapy for hepatitis C. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00841243.
Additional references
Alberino 2001
-
- Alberino F, Gatta A, Amodio P, Merkel C, Pascoli L, Boggo G, et al. Nutrition and survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2001;17:445‐50. - PubMed
Als‐Nielsen 2003
Alvares‐da‐Silva 2005
-
- Alvares‐da‐Silva MR, Reverbel da Silveira T. Comparison between handgrip strength, subjective global assessment, and prognostic nutritional index in assessing malnutrition and predicting clinical outcome in cirrhotic patients. Nutrition 2005;21:113‐7. - PubMed
Baker 1982
-
- Baker JP, Detsky AS, Wesson DE, Wolman SL, Stewart S, Whitewall J, et al. Nutritional assessment. A comparison of clinical judgment and objective measurements. New England Journal of Medicine 1982;306:969‐72. - PubMed
Brok 2008
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Gluud C, Wetterslev J. Trial sequential analysis reveals insufficient information size and potentially false positive results in many meta‐analyses. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(8):763‐9. - PubMed
Brok 2009
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta‐analyses may be inconclusive ‐ Trial sequential analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data in apparently conclusive neonatal meta‐analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):287‐98. - PubMed
Buzby 1980
-
- Buzby GP, Mullen JL, Matthews DC, Hobbs CL, Rosato EF. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery. American Journal of Surgery 1980;139:160‐7. - PubMed
DeMets 1987
-
- DeMets DL. Methods for combining randomized clinical trials: strengths and limitations. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6(3):341‐50. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Dudrick 1971
-
- Dudrick SJ, Ruberg RL. Principles and practices of parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology 1971;61:901‐10. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Fischer 1971
-
- Fischer JE, Baldessarini RJ. False neurotransmitters and hepatic failure. Lancet 1971;2:75‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gluud 2011
-
- Gluud C, Nikolova D, Klingenberg SL, Alexakis N, Als‐Nielsen B, Colli A, et al. Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group. About The Cochrane Collaboration (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)). 2011, Issue 11. Art. No.: LIVER.
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Colloboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
ICH‐GCP 1997
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation Expert Working Group. International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline. Guideline for good clinical practice1997 CFR & ICH Guidelines. Vol. 1, PA 19063‐2043, USA: Barnett International/PAREXEL, 1997.
Italian Multicentre Cooperative Project 1994
-
- Italian Multicentre Cooperative Project on Nutrition in Liver Cirrhosis. Nutritional status in cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology 1994;21:317‐25. - PubMed
Jensen 2010
-
- Jensen GL, Mirtallo J, Compher C, Dhaliwal R, Forbes A, Figueredo Grijalba R, et al. Adult starvation and disease‐related malnutrition. A proposal for etiology‐based diagnosis in the clinical practice setting from the International Consensus Guideline Committee. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2010; Vol. 34, issue 2:156‐9. - PubMed
Keys 1962
-
- Keys A. Caloric deficiency and starvation. In: Jolliffe N editor(s). Clinical Nutrition. 2nd Edition. New York: Harper and Brothers, 1962:122‐36.
Kjaergard 2001
-
- Kjaergard LL, Villumsen J, Gluud C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta‐analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;135:982‐9. - PubMed
Kondrup 1997
-
- Kondrup J, Muller MJ. Energy and protein requirements of patients with chronic liver disease. Journal of Hepatology 1997;27:239‐47. - PubMed
Koretz 2001
-
- Koretz RL, Lipman TO, Klein S. AGA technical review ‐ parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology 2001;121:970‐1001. - PubMed
Koretz 2005
-
- Koretz RL. Death, morbidity, and economics are the only end‐points for trials. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2005;64:277‐84. - PubMed
Koretz 2007
-
- Koretz RL, Avenell A, Lipman TO, Braunschweig C, Milne AC. Does enteral nutrition affect outcome: a systematic review of the randomized trials. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2007;102:412‐29. - PubMed
Langer 2009
Macaskill 2001
-
- Macaskill P, Walter SD, Irwig L. A comparison of methods to detect publication bias in meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(4):641‐54. - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352:609‐13. - PubMed
Morgan 1990
-
- Morgan MY. Branched chain amino acids in the management of chronic liver disease. Facts and fantasies. Journal of Hepatology 1990;11(2):133‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nielsen 1993
-
- Nielsen K, Kondrup J, Martinsen C, Stilling B, Wikman B. Nutritional assessment and adequacy of dietary intake in hospitalized patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. British Journal of Nutrition 1993;69:665‐79. - PubMed
Norman 2006
Reinhardt 1980
-
- Reinhardt GF, Myscofski JW, Wilkens DB, Dobrin PB, Mangan JE, Stannard RT. Incidence and mortality of hypoalbuminemic patients in hospitalized veterans. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1980;4:357‐9. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Rhoads 1981
-
- Rhoads JE, Vars HM, Dudrick SJ. The development of intravenous hyperalimentation. The Surgical Clinics of North America 1981;61:429‐35. - PubMed
Royle 2003
-
- Royle P, Milne R. Literature searching for randomized controlled trials used in Cochrane reviews: rapid versus exhaustive searches. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2003;19(4):591‐603. - PubMed
Sanchez 2006
-
- Sanchez AJ, Aranda‐Michel J. Nutrition for the liver transplant patient. Liver Transplantation 2006;12:1310‐6. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Studley 1936
-
- Studley HO. Percentage of weight loss. A basic indicator of surgical risk in patients with chronic peptic ulcer. JAMA 1936;106:458‐60. - PubMed
Tajika 2001
-
- Tajika M, Kato M, Mohri H, Miwa Y, Kato T, Ohnishi H, et al. Prognostic value of energy metabolism in patients with viral liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2002;18(3):229‐34. - PubMed
Thorlund 2009
-
- Thorlund K, Devereaux PJ, Wetterslev J, Gyuatt G, Ioannidis JPA, Thabane L, et al. Can trial sequential monitoring boundaries reduce spurious inferences from meta‐analyses?. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):276‐86. - PubMed
Wetterslev 2008
-
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61:64‐75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

