Peroxisome Proliferator-activated receptor γ activation by ligands and dephosphorylation induces proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 and low density lipoprotein receptor expression
- PMID: 22593575
- PMCID: PMC3390641
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.350181
Peroxisome Proliferator-activated receptor γ activation by ligands and dephosphorylation induces proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 and low density lipoprotein receptor expression
Abstract
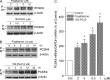
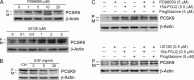
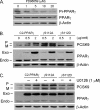
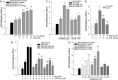
Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9) plays an important role in cholesterol homeostasis by enhancing the degradation of LDL receptor (LDLR) protein. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) has been shown to be atheroprotective. PPARγ can be activated by ligands and/or dephosphorylation with ERK1/2 inhibitors. The effect of PPARγ on PCSK9 and LDLR expression remains unknown. In this study, we investigated the effects of PPARγ on PCSK9 and LDLR expression. At the cellular levels, PPARγ ligands induced PCSK9 mRNA and protein expression in HepG2 cells. PCSK9 expression was induced by inhibition of ERK1/2 activity but inhibited by ERK1/2 activation. The mutagenic study and promoter activity assay suggested that the induction of PCSK9 expression by ERK1/2 inhibitors was tightly linked to PPARγ dephosphorylation. However, PPARγ activation by ligands or ERK1/2 inhibitors induced hepatic LDLR expression. The promoter assay indicated that the induction of LDLR expression by PPARγ was sterol regulatory element-dependent because PPARγ enhanced sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) processing. In vivo, administration of pioglitazone or U0126 alone increased PCSK9 expression in mouse liver but had little effect on PCSK9 secretion. However, the co-treatment of pioglitazone and U0126 enhanced both PCSK9 expression and secretion. Similar to in vitro, the increased PCSK9 expression by pioglitazone and/or U0126 did not result in decreased LDLR expression and function. In contrast, pioglitazone and/or U0126 increased LDLR protein expression and membrane translocation, SREBP2 processing, and CYP7A1 expression in the liver, which led to decreased total and LDL cholesterol levels in serum. Our results indicate that although PPARγ activation increased PCSK9 expression, PPARγ activation induced LDLR and CYP7A1 expression that enhanced LDL cholesterol metabolism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of Adiponectin Receptor Regulates Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Expression and Inhibits Lesions in ApoE-Deficient Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Jul;37(7):1290-1300. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309630. Epub 2017 May 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28546220
-
Hepatic overexpression of idol increases circulating protein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 in mice and hamsters via dual mechanisms: sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 and low-density lipoprotein receptor-dependent pathways.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Jun;34(6):1171-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302670. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24675665
-
MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, enhances LDL uptake in HepG2 cells in vitro by regulating LDLR and PCSK9 expression.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Aug;35(8):994-1004. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.52. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 25042549 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 for the treatment of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;62(16):1401-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.056. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23973703 Review.
-
On the function and homeostasis of PCSK9: reciprocal interaction with LDLR and additional lipid effects.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Feb;238(2):264-70. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.12.017. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 25544176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse Effects of Cilostazol on Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 between Obesity and Non-Obesity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;23(17):9768. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179768. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077166 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of liver X receptor induces macrophage interleukin-5 expression.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 21;287(52):43340-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.403394. Epub 2012 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23150660 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenol Effects on Cholesterol Metabolism via Bile Acid Biosynthesis, CYP7A1: A Review.Nutrients. 2019 Oct 28;11(11):2588. doi: 10.3390/nu11112588. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31661763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acaudina molpadioides mediates lipid uptake by suppressing PCSK9 transcription and increasing LDL receptor in human liver cells.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Dec;28(12):7105-7116. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.08.003. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34867013 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of liver X receptor inhibits the development of pulmonary carcinomas induced by 3-methylcholanthrene and butylated hydroxytoluene in BALB/c mice.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 2;6:27295. doi: 10.1038/srep27295. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27250582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nordestgaard B. G., Chapman M. J., Ray K., Borén J., Andreotti F., Watts G. F., Ginsberg H., Amarenco P., Catapano A., Descamps O. S., Fisher E., Kovanen P. T., Kuivenhoven J. A., Lesnik P., Masana L., Reiner Z., Taskinen M. R., Tokgözoglu L., Tybjærg-Hansen A., and European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel (2010) Lipoprotein(a) as a cardiovascular risk factor: current status. Eur. Heart J. 31, 2844–2853 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Defesche J. C. (2004) Low-density lipoprotein receptor. Its structure, function, and mutations. Semin. Vasc. Med. 4, 5–11 - PubMed
-
- van Aalst-Cohen E. S., Jansen A. C., de Jongh S., de Sauvage Nolting P. R., Kastelein J. J. (2004) Clinical, diagnostic, and therapeutic aspects of familial hypercholesterolemia. Semin. Vasc. Med. 4, 31–41 - PubMed
-
- Seidah N. G., Benjannet S., Wickham L., Marcinkiewicz J., Jasmin S. B., Stifani S., Basak A., Prat A., Chretien M. (2003) The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1). Liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 928–933 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

