The calcium: an early signal that initiates the formation of the nervous system during embryogenesis
- PMID: 22593733
- PMCID: PMC3351002
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00064
The calcium: an early signal that initiates the formation of the nervous system during embryogenesis
Abstract
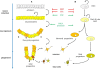
The calcium (Ca(2+)) signaling pathways have crucial roles in development from fertilization through differentiation to organogenesis. In the nervous system, Ca(2+) signals are important regulators for various neuronal functions, including formation and maturation of neuronal circuits and long-term memory. However, Ca(2+) signals are also involved in the earliest steps of neurogenesis including neural induction, differentiation of neural progenitors into neurons, and the neuro-glial switch. This review examines when and how Ca(2+) signals are generated during each of these steps with examples taken from in vivo studies in vertebrate embryos and from in vitro assays using embryonic and neural stem cells (NSCs). During the early phases of neurogenesis few investigations have been performed to study the downstream targets of Ca(2+) which posses EF-hand in their structure. This opens an entire field of research. We also discuss the highly specific nature of the Ca(2+) signaling pathway and its interaction with the other signaling pathways involved in early neural development.
Keywords: EF-hand; calcium signaling; early neural development; neural induction; neural progenitor; neuro-glial switch; stem cell.
Figures

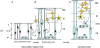
Similar articles
-
Early neural development in vertebrates is also a matter of calcium.Biochimie. 2011 Dec;93(12):2102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.06.032. Epub 2011 Jul 3. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21742011 Review.
-
Three calcium-sensitive genes, fus, brd3 and wdr5, are highly expressed in neural and renal territories during amphibian development.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jul;1833(7):1665-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.12.015. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23287019
-
Regulation of neurogenesis by calcium signaling.Cell Calcium. 2016 Mar;59(2-3):124-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.02.011. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Cell Calcium. 2016. PMID: 27020657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation of Neural Stem Cells and Progenitors: Neuronal Production and Grafting Applications.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2311:73-108. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1437-2_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34033079 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium and Neural Stem Cell Proliferation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 6;25(7):4073. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074073. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling human brain rhabdoid tumor by inactivating tumor suppressor genes in induced pluripotent stem cells.Bioact Mater. 2023 Aug 12;31:136-150. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.08.009. eCollection 2024 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 37637078 Free PMC article.
-
T-type Calcium Channel Regulation of Neural Tube Closure and EphrinA/EPHA Expression.Cell Rep. 2015 Oct 27;13(4):829-839. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.09.035. Epub 2015 Oct 17. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26489462 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs Regulate Ca2+ Homeostasis in Murine Embryonic Stem Cells.Cells. 2023 Jul 28;12(15):1957. doi: 10.3390/cells12151957. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37566036 Free PMC article.
-
Information Theory as an Experimental Tool for Integrating Disparate Biophysical Signaling Modules.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 24;23(17):9580. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179580. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36076979 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium Signaling of Lysophosphatidylethanolamine through LPA1 in Human SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2017 Mar 1;25(2):194-201. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.046. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2017. PMID: 27302965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Annaert W. G., Levesque L., Craessaerts K., Dierinck I., Snellings G., Westaway D., George-Hyslop P. S., Cordell B., Fraser P., De Strooper B. (1999). Presenilin 1 controls gamma-secretase processing of amyloid precursor protein in pre-golgi compartments of hippocampal neurons. J. Cell Biol. 147, 277–294 10.1083/jcb.147.2.277 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arcuri F., Papa S., Meini A., Carducci A., Romagnoli R., Bianchi L., Riparbelli M. G., Sanchez J. C., Palmi M., Tosi P., Cintorino M. (2005). The translationally controlled tumor protein is a novel calcium binding protein of the human placenta and regulates calcium handling in trophoblast cells. Biol. Reprod. 73, 745–751 10.1095/biolreprod.105.042077 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

