Global health-a circumpolar perspective
- PMID: 22594729
- PMCID: PMC3478014
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300584
Global health-a circumpolar perspective
Abstract
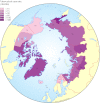
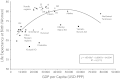
Global health should encompass circumpolar health if it is to transcend the traditional approach of the "rich North" assisting the "poor South." Although the eight Arctic states are among the world's most highly developed countries, considerable health disparities exist among regions across the Arctic, as well as between northern and southern regions and between indigenous and nonindigenous populations within some of these states. While sharing commonalities such as a sparse population, geographical remoteness, harsh physical environment, and underdeveloped human resources, circumpolar regions in the northern hemisphere have developed different health systems, strategies, and practices, some of which are relevant to middle and lower income countries. As the Arctic gains prominence as a sentinel of global issues such as climate change, the health of circumpolar populations should be part of the global health discourse and policy development.
Figures
References
-
- Banta JE. From international to global health. J Community Health. 2001;26:73–76 - PubMed
-
- Rajaratnam JK, Marcus JR, Flaxman ADet al.Neonatal, postneonatal, childhood, and under-5 mortality for 187 countries, 1970-2010: a systematic analysis of progress towards the Millennium Development Goal 4. Lancet. 2010;375:1988–2008 - PubMed
-
- Bjerregaard P, Stensgaard P. Greenland. : Young TK, Bjerregaard P, Health Transitions in Arctic Populations. Toronto: University of Toronto Press; 2008:23–38
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

