Renal denervation in moderate to severe CKD
- PMID: 22595301
- PMCID: PMC3380649
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011111062
Renal denervation in moderate to severe CKD
Abstract
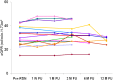
Sympathetic activation contributes to the progression of CKD and is associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes. Ablation of renal sympathetic nerves reduces sympathetic nerve activity and BP in patients with resistant hypertension and preserved renal function, but whether this approach is safe and effective in patients with an estimated GFR (eGFR) < 45 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) is unknown. We performed bilateral renal denervation in 15 patients with resistant hypertension and stage 3-4 CKD (mean eGFR, 31 ml/min per 1.73 m(2)). We used CO(2) angiography in six patients to minimize exposure to contrast agents. Estimated GFR remained unchanged after the procedure, irrespective of the use of CO(2) angiography. Mean baseline BP ± SD was 174 ± 22/91 ± 16 mmHg despite the use of 5.6 ± 1.3 antihypertensive drugs. Mean changes in office systolic and diastolic BP at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months were -34/-14, -25/-11, -32/-15, and -33/-19 mmHg, respectively. Night-time ambulatory BP significantly decreased (P<0.05), restoring a more physiologic dipping pattern. In conclusion, this study suggests a favorable short-term safety profile and beneficial BP effects of catheter-based renal nerve ablation in patients with stage 3-4 CKD and resistant hypertension.
Figures


Comment in
-
Renal nerves and CKD: is renal denervation the answer?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jul;23(7):1132-5. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012050513. Epub 2012 Jun 7. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22677558 No abstract available.
References
-
- Collins AJ, Li S, Ma JZ, Herzog C: Cardiovascular disease in end-stage renal disease patients. Am J Kidney Dis 38[Suppl 1]: S26–S29, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Anavekar NS, McMurray JJ, Velazquez EJ, Solomon SD, Kober L, Rouleau JL, White HD, Nordlander R, Maggioni A, Dickstein K, Zelenkofske S, Leimberger JD, Califf RM, Pfeffer MA: Relation between renal dysfunction and cardiovascular outcomes after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 351: 1285–1295, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Rahman M, Pressel S, Davis BR, Nwachuku C, Wright JT, Jr, Whelton PK, Barzilay J, Batuman V, Eckfeldt JH, Farber MA, Franklin S, Henriquez M, Kopyt N, Louis GT, Saklayen M, Stanford C, Walworth C, Ward H, Wiegmann T, ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group : Cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients stratified by baseline glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 144: 172–180, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Herzog CA: Cardiac arrest in dialysis patients: approaches to alter an abysmal outcome. Kidney Int Suppl S197–S200, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Multicentre, cross-sectional study of ventricular arrhythmias in chronically haemodialysed patients. Gruppo Emodialisi e Patologie Cardiovasculari. Lancet 2: 305–309, 1988 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

