Imaging lung perfusion
- PMID: 22604884
- PMCID: PMC3404706
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00320.2012
Imaging lung perfusion
Abstract
From the first measurements of the distribution of pulmonary blood flow using radioactive tracers by West and colleagues (J Clin Invest 40: 1-12, 1961) allowing gravitational differences in pulmonary blood flow to be described, the imaging of pulmonary blood flow has made considerable progress. The researcher employing modern imaging techniques now has the choice of several techniques, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computerized tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). These techniques differ in several important ways: the resolution of the measurement, the type of contrast or tag used to image flow, and the amount of ionizing radiation associated with each measurement. In addition, the techniques vary in what is actually measured, whether it is capillary perfusion such as with PET and SPECT, or larger vessel information in addition to capillary perfusion such as with MRI and CT. Combined, these issues affect quantification and interpretation of data as well as the type of experiments possible using different techniques. The goal of this review is to give an overview of the techniques most commonly in use for physiological experiments along with the issues unique to each technique.
Figures


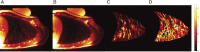
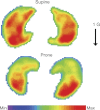
References
-
- Almquist H, Jonson B, Palmer J, Valind S, Wollmer P. Regional VA/Q ratios in man using 133Xe and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) corrected for attenuation. Clin Physiol 19: 475–481, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Almquist HM, Palmer J, Jonson B, Wollmer P. Pulmonary perfusion and density gradients in healthy volunteers. J Nucl Med 38: 962–966, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Altemeier WA, McKinney S, Glenny RW. Fractal nature of regional ventilation distribution. J Appl Physiol 88: 1551–1557, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Amundsen T, Torheim G, Kvistad KA, Waage A, Bjermer L, Nordlid KK, Johnsen H, Asberg A, Haraldseth O. Perfusion abnormalities in pulmonary embolism studied with perfusion MRI and ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy: an intra-modality and inter-modality agreement study. J Magn Reson Imaging 15: 386–394, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

