Development of abbreviated nine-item forms of the Raven's standard progressive matrices test
- PMID: 22605785
- PMCID: PMC4410094
- DOI: 10.1177/1073191112446655
Development of abbreviated nine-item forms of the Raven's standard progressive matrices test
Abstract
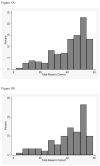
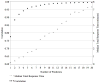
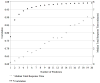
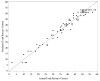
The Raven's standard progressive matrices (RSPM) is a 60-item test for measuring abstract reasoning, considered a nonverbal estimate of fluid intelligence, and often included in clinical assessment batteries and research on patients with cognitive deficits. The goal was to develop and apply a predictive model approach to reduce the number of items necessary to yield a score equivalent to that derived from the full scale. The approach is based on a Poisson predictive model. A parsimonious subset of items that accurately predicts the total score was sought, as was a second nonoverlapping alternate form for repeated administrations. A split sample was used for model fitting and validation, with cross-validation to verify results. Using nine RSPM items as predictors, correlations of .9836 and .9782 were achieved for the reduced forms and .9063 and .8978 for the validation data. Thus, a 9-item subset of RSPM predicts the total score for the 60-item scale with good accuracy. A comparison of psychometric properties between 9-item forms, a published 30-item form, and the 60-item set is presented. The two 9-item forms provide a 75% administration time savings compared with the 30-item form, while achieving similar item- and test-level characteristics and equal correlations to 60-item based scores.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV. 4. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press; 1994.
-
- Arthur W, Jr, Day DV. Development of a short form for the Raven Advanced Progressive Matrices Test. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 1994;54:394–403. doi: 10.1177/0013164494054002013. - DOI
-
- Bock RD. Estimating item parameters and latent ability when responses are scored in two or more nominal categories. Psychometrika. 1972;37:29–51. doi: 10.1007/BF02291411. - DOI
-
- Bors DA, Stokes TL. Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices: Norms for first-year university students and the development of a short form. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 1998;58:382–398. doi: 10.1177/0013164498058003002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

