Rosuvastatin-induced pemphigoid
- PMID: 22605857
- PMCID: PMC3351646
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.11.2011.5180
Rosuvastatin-induced pemphigoid
Abstract
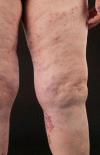
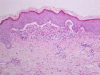
Statins are widely prescribed medications and very well tolerated. Rosuvastatin is another member of this drug used to treat dyslipidaemia. It is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Immunobullous disease is usually idiopathic but can be drug-induced. Both idiopathic and iatrogenic forms share common clinical and immunohistological features. The authors report a case of pemphigoid induced by rosuvastatin, a commonly prescribed medication. To our knowledge, there is limited report on rosuvastatin associated with pemphigoid in the literature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hodak E, Ben-Shetrit A, Ingber A, et al. Bullous pemphigoid–an adverse effect of ampicillin. Clin Exp Dermatol 1990;15:50–2 - PubMed
-
- Bean SF, Good RA, Windhorst DB. Bullous pemphigoid in an 11-year-old boy. Arch Dermatol 1970;102:205–8 - PubMed
-
- Kashihara M, Danno K, Miyachi Y, et al. Bullous pemphigoid-like lesions induced by phenacetin. Report of a case and an immunopathologic study. Arch Dermatol 1984;120:1196–9 - PubMed
-
- Ruocco V, Sacerdoti G. Pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid due to drugs. Int J Dermatol 1991;30:307–12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical