A regulatory potential of the Xist gene promoter in vole M. rossiaemeridionalis
- PMID: 22606223
- PMCID: PMC3350511
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033994
A regulatory potential of the Xist gene promoter in vole M. rossiaemeridionalis
Abstract
X chromosome inactivation takes place in the early development of female mammals and depends on the Xist gene expression. The mechanisms of Xist expression regulation have not been well understood so far. In this work, we compared Xist promoter region of vole Microtus rossiaemeridionalis and other mammalian species. We observed three conserved regions which were characterized by computational analysis, DNaseI in vitro footprinting, and reporter construct assay. Regulatory factors potentially involved in Xist activation and repression in voles were determined. The role of CpG methylation in vole Xist expression regulation was established. A CTCF binding site was found in the 5' flanking region of the Xist promoter on the active X chromosome in both males and females. We suggest that CTCF acts as an insulator which defines an inactive Xist domain on the active X chromosome in voles.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
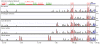
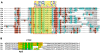
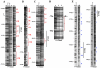
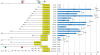
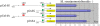
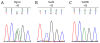

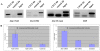
Comment in
-
Revisiting the past in view of the future.Evol Dev. 2013 Jan;15(1):1-2; discussion 3-4. doi: 10.1111/ede.12008. Evol Dev. 2013. PMID: 23331911 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
[Molecular genetic characterization of the regulatory region of the Xist gene in the common vole Microtus rossiaemeridionalis].Genetika. 2009 Oct;45(10):1341-52. Genetika. 2009. PMID: 19947545 Russian.
-
[Role of G(-43)A polymorphism in the promoter region of the Xist gene in non-random X-chromosome inactivation in intraspecific hybrid voles].Genetika. 2010 Oct;46(10):1397-400. Genetika. 2010. PMID: 21254564 Russian.
-
Familial cases of point mutations in the XIST promoter reveal a correlation between CTCF binding and pre-emptive choices of X chromosome inactivation.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Apr 1;14(7):953-65. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi089. Epub 2005 Feb 24. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 15731119
-
Xist regulation and function explored.Hum Genet. 2011 Aug;130(2):223-36. doi: 10.1007/s00439-011-1008-7. Epub 2011 May 28. Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21626138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xist and the order of silencing.EMBO Rep. 2007 Jan;8(1):34-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400871. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17203100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Xist RNA on chromatin modifications and transcriptional silencing maintenance at different stages of imprinted X chromosome inactivation in vole Microtus levis.Chromosoma. 2018 Mar;127(1):129-139. doi: 10.1007/s00412-017-0650-9. Epub 2017 Nov 18. Chromosoma. 2018. PMID: 29151149
-
Mapping of Replication Origins in the X Inactivation Center of Vole Microtus levis Reveals Extended Replication Initiation Zone.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 3;10(6):e0128497. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128497. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26038842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heard E. Recent advances in X-chromosome inactivation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:247–255. - PubMed
-
- Zakharova IS, Shevchenko AI, Zakian SM. Monoallelic gene expression in mammals. Chromosoma. 2009;118:279–290. - PubMed
-
- Tattermusch A, Brockdorff N. A scaffold for X chromosome inactivation. Human Genetics. 2011;130:247–253. - PubMed
-
- Xu N, Tsai CL, Lee JT. Transient homologous chromosome pairing marks the onset of X inactivation. Science. 2006;311:1149–1152. - PubMed
-
- Augui S, Filion GJ, Huart S, Nora E, Guggiari M, et al. Sensing X chromosome pairs before X inactivation via a novel X-pairing region of the Xic. Science. 2007;318:1632–1636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

