Loss of emerin alters myogenic signaling and miRNA expression in mouse myogenic progenitors
- PMID: 22606356
- PMCID: PMC3350500
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037262
Loss of emerin alters myogenic signaling and miRNA expression in mouse myogenic progenitors
Abstract
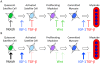
Emerin is an integral membrane protein of the inner nuclear membrane. Mutations in emerin cause X-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD), a disease characterized by skeletal muscle wasting and dilated cardiomyopathy. Current evidence suggests the muscle wasting phenotype of EDMD is caused by defective myogenic progenitor cell differentiation and impaired muscle regeneration. We obtained genome-wide expression data for both mRNA and micro-RNA (miRNA) in wildtype and emerin-null mouse myogenic progenitor cells. We report here that emerin-null myogenic progenitors exhibit differential expression of multiple signaling pathway components required for normal muscle development and regeneration. Components of the Wnt, IGF-1, TGF-β, and Notch signaling pathways are misexpressed in emerin-null myogenic progenitors at both the mRNA and protein levels. We also report significant perturbations in the expression and activation of p38/Mapk14 in emerin-null myogenic progenitors, showing that perturbed expression of Wnt, IGF-1, TGF-β, and Notch signaling components disrupts normal downstream myogenic signaling in these cells. Collectively, these data support the hypothesis that emerin is essential for proper myogenic signaling in myogenic progenitors, which is necessary for myogenic differentiation and muscle regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


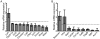
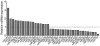
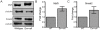

Similar articles
-
EDMD-Causing Emerin Mutant Myogenic Progenitors Exhibit Impaired Differentiation Using Similar Mechanisms.Cells. 2020 Jun 15;9(6):1463. doi: 10.3390/cells9061463. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32549231 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK signaling pathways and HDAC3 activity are disrupted during differentiation of emerin-null myogenic progenitor cells.Dis Model Mech. 2017 Apr 1;10(4):385-397. doi: 10.1242/dmm.028787. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Dis Model Mech. 2017. PMID: 28188262 Free PMC article.
-
The role of inner nuclear membrane protein emerin in myogenesis.FASEB J. 2025 Apr 15;39(7):e70514. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500323. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40178931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Emerin mRNA Lipid Nanoparticles to Rescue Myogenic Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 12;26(16):7774. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167774. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869095 Free PMC article.
-
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy at the nuclear envelope: 10 years on.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Dec;63(23):2702-9. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6247-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 17013557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant Caspase Activation in Laminin-α2-Deficient Human Myogenic Cells is Mediated by p53 and Sirtuin Activity.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2018;5(1):59-73. doi: 10.3233/JND-170262. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2018. PMID: 29278895 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila male and female germline stem cell niches require the nuclear lamina protein Otefin.Dev Biol. 2016 Jul 1;415(1):75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 May 10. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27174470 Free PMC article.
-
Emerin deficiency does not exacerbate cardiomyopathy in a murine model of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy caused by an LMNA gene mutation.J Physiol Sci. 2023 Nov 8;73(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12576-023-00886-0. J Physiol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37940872 Free PMC article.
-
EDMD-Causing Emerin Mutant Myogenic Progenitors Exhibit Impaired Differentiation Using Similar Mechanisms.Cells. 2020 Jun 15;9(6):1463. doi: 10.3390/cells9061463. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32549231 Free PMC article.
-
Diseases of the Nucleoskeleton.Compr Physiol. 2016 Sep 15;6(4):1655-1674. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150039. Compr Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27783855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vlcek S. Current opinion in cell biology; 2007. ScienceDirect - Current Opinion in Cell Biology : Lamins and lamin-associated proteins in aging and disease. - PubMed
-
- Bione S, Maestrini E, Rivella S, Mancini M, Regis S, et al. Identification of a novel X-linked gene responsible for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1994;8:323–327. - PubMed
-
- Manilal S, Nguyen TM, Sewry CA, Morris GE. The Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy protein, emerin, is a nuclear membrane protein. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:801–808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

