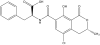
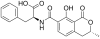Immunochemical methods for ochratoxin A detection: a review
- PMID: 22606375
- PMCID: PMC3347002
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins4040244
Immunochemical methods for ochratoxin A detection: a review
Abstract
The safety of food and feed depends to a great deal on quality control. Numerous compounds and organisms may contaminate food and feed commodities and thus pose a health risk for consumers. The compound of interest in this review is ochratoxin A (OTA), a secondary metabolite of the fungi Aspergillus and Penicillium. Due to its adverse health effects, detection and quantification are of utmost importance. Quality control of food and feed requires extraction and analysis, including TLC, HPLC, MS, and immunochemical methods. Each of these methods has its advantages and disadvantages. However, with regard to costs and rapidity, immunochemical methods have gained much interest in the last decade. In this review an introduction to immunochemistry and assay design will be given to elucidate the principles. Further, the application of the various formats to the detection and quantification of ochratoxin will be described, including the use of commercially available kits.
Keywords: detection; immunochemical methods; ochratoxin A (OTA); quantification.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aptamers: a promosing tool for ochratoxin A detection in food analysis.Toxins (Basel). 2013 Nov 5;5(11):1988-2008. doi: 10.3390/toxins5111988. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24196457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ochratoxin A detection in coffee by competitive inhibition assay using chitosan-based surface plasmon resonance compact system.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Feb 1;174:569-574. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.11.060. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 30502668
-
Determination of Ochratoxin A in apples contaminated with Aspergillus ochraceus by using a microfluidic competitive immunosensor with magnetic nanoparticles.Analyst. 2011 Jul 7;136(13):2756-62. doi: 10.1039/c1an15148g. Epub 2011 May 24. Analyst. 2011. PMID: 21611646
-
An immunoassay for ochratoxin A using tetramethylrhodamine-labeled ochratoxin A as a probe based on a binding-induced change in fluorescence intensity.Analyst. 2020 Jan 20;145(2):651-655. doi: 10.1039/c9an01879d. Analyst. 2020. PMID: 31793932
-
Ochratoxins in food and feed: Occurrence and its impact on human health and management strategies.Toxicon. 2020 Nov;187:151-162. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.08.031. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Toxicon. 2020. PMID: 32889024 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytic acid alleviates ochratoxin A-induced renal damage in chicks by modulating ferroptosis and the structure of the intestinal microbiota.Poult Sci. 2024 Sep;103(9):104027. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104027. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39024690 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Determination of Ochratoxin A in Grape and Its Commodities Based on a Label-Free Impedimetric Aptasensor Constructed by Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Jan 28;11(2):71. doi: 10.3390/toxins11020071. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30696025 Free PMC article.
-
Immunochemical assay with monoclonal antibodies for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin H.J Food Drug Anal. 2018 Apr;26(2):741-750. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.10.011. Epub 2017 Dec 2. J Food Drug Anal. 2018. PMID: 29567245 Free PMC article.
-
Ochratoxin A in Slaughtered Pigs and Pork Products.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jan 19;14(2):67. doi: 10.3390/toxins14020067. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35202095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamers: a promosing tool for ochratoxin A detection in food analysis.Toxins (Basel). 2013 Nov 5;5(11):1988-2008. doi: 10.3390/toxins5111988. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24196457 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Egmond H.P. Methods for determing ochratoxin A and other nephrotoxic mycotoxins. IARC Sci. Publ. 1991;115:57–70. - PubMed
-
- van Egmond H.P. Analytical methodology and regulations for ochratoxin A. Food Addit. Contam. 1996;13(Suppl.):11–13. - PubMed
-
- Crosby N.T. Determination of Veterinary Residues in Food. Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science; Cambridge, UK: 1984. p. 177.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical