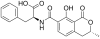Immunochemical methods for ochratoxin A detection: a review
- PMID: 22606375
- PMCID: PMC3347002
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins4040244
Immunochemical methods for ochratoxin A detection: a review
Abstract
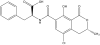
The safety of food and feed depends to a great deal on quality control. Numerous compounds and organisms may contaminate food and feed commodities and thus pose a health risk for consumers. The compound of interest in this review is ochratoxin A (OTA), a secondary metabolite of the fungi Aspergillus and Penicillium. Due to its adverse health effects, detection and quantification are of utmost importance. Quality control of food and feed requires extraction and analysis, including TLC, HPLC, MS, and immunochemical methods. Each of these methods has its advantages and disadvantages. However, with regard to costs and rapidity, immunochemical methods have gained much interest in the last decade. In this review an introduction to immunochemistry and assay design will be given to elucidate the principles. Further, the application of the various formats to the detection and quantification of ochratoxin will be described, including the use of commercially available kits.
Keywords: detection; immunochemical methods; ochratoxin A (OTA); quantification.
Figures
References
-
- van Egmond H.P. Methods for determing ochratoxin A and other nephrotoxic mycotoxins. IARC Sci. Publ. 1991;115:57–70. - PubMed
-
- van Egmond H.P. Analytical methodology and regulations for ochratoxin A. Food Addit. Contam. 1996;13(Suppl.):11–13. - PubMed
-
- Crosby N.T. Determination of Veterinary Residues in Food. Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science; Cambridge, UK: 1984. p. 177.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical