Acute pancreatitis complicated with choledochal duct rupture
- PMID: 22606417
- PMCID: PMC3350291
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/413268
Acute pancreatitis complicated with choledochal duct rupture
Abstract
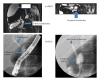
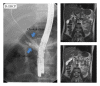
Recurrent acute pancreatitis is a rare clinical entity in childhood with unknown incidence (Rosendahl et al., 2007) and often occurring in a familial context. Genetic factors such as PRSS1 mutations (cationic trypsinogen gene) can be found in some patients. However, many remain idiopathic. The natural history remains poorly documented and the most frequent complications reported are pain, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, and pancreatic adenocarcinoma after long-standing hereditary pancreatitis. We describe a patient with hereditary pancreatitis in whom a mild pancreatitis episode was complicated by a perforation of the ductus choledochus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cationic trypsinogen mutations and pancreatitis.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2004 Dec;33(4):767-87. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2004.07.003. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15528017 Review.
-
Absence of PRSS1 mutations and association of SPINK1 trypsin inhibitor mutations in hereditary and non-hereditary chronic pancreatitis.Gut. 2004 May;53(5):723-8. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.026526. Gut. 2004. PMID: 15082592 Free PMC article.
-
The natural history of hereditary pancreatitis: a national series.Gut. 2009 Jan;58(1):97-103. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.149179. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Gut. 2009. PMID: 18755888
-
Cationic trypsinogen mutations and pancreatitis.Clin Lab Med. 2005 Mar;25(1):39-59. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2004.12.004. Clin Lab Med. 2005. PMID: 15749231 Review.
-
Hereditary chronic pancreatitis.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007 Jan 4;2:1. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-2-1. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007. PMID: 17204147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rebours V, Boutron-Ruault MC, Schnee M, et al. The natural history of hereditary pancreatitis: a national series. Gut. 2009;58(1):97–103. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Tu Y, Nakajima H, et al. Acute pancreatitis and a long common channel. Abdominal Imaging. 2007;32(3):365–369. - PubMed
-
- Kasat LS, Borwankar SS, Jain M, Naregal A. Spontaneous perforation of the extrahepatic bile duct in an infant. Pediatric Surgery International. 2001;17(5-6):463–464. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

