Correction of anophthalmic enophthalmos with a three-staged procedure: two case reports
- PMID: 22606592
- PMCID: PMC3350191
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/731259
Correction of anophthalmic enophthalmos with a three-staged procedure: two case reports
Abstract
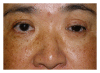
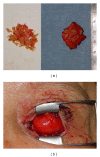
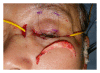
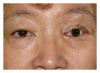
Surgical correction of an anophthalmic enophthalmos secondary to inappropriate repair of the eye socket involves several difficult aesthetic issues associated with long-term use of a poorly fitting prosthetic eye. In this paper, we present two cases of anophthalmic enophthalmos. During the treatment of the first patient, unsatisfactory cosmetic problems including lower eyelid retraction, hypoglobus, and severe upper eyelid ptosis were revealed. Accordingly, a three-staged procedure was performed on the second patient, including autologous augmentation of the eye socket, correction of lower eyelid retraction with a cartilage graft, and a frontalis sling procedure to correct upper eyelid ptosis.
Figures




References
-
- Hashikawa K, Terashi H, Tahara S. Therapeutic strategy for the triad of acquired anophthalmic orbit. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2007;119(7):2182–2188. - PubMed
-
- Minagawa T, Maeda T, Yamao T, Hayashi T. Diced cartilage ball graft wrapped in fascia for autologous augmentation of an eye socket. Journal of Japan Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2010;30(9):491–494.
-
- Carraway JH, Mellow CG, Mustarde JC. Use of cartilage graft for an orbital socket implant. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 1990;24(2):139–148. - PubMed
-
- Ashworth JL, Rhatigan M, Brammar R, Sunderland S, Leatherbarrow B. A clinical study of the hydroxyapatite orbital implant. European Journal of Ophthalmology. 1997;7(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Yanaga H, Mori S. Eyelids and eye socket reconstruction using the expanded forehead flap and scapha composite grafting. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2001;108(1):8–16. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

