EEG-based Drowsiness Detection for Safe Driving Using Chaotic Features and Statistical Tests
- PMID: 22606668
- PMCID: PMC3342623
EEG-based Drowsiness Detection for Safe Driving Using Chaotic Features and Statistical Tests
Abstract
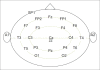
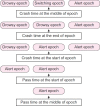
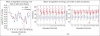
Electro encephalography (EEG) is one of the most reliable sources to detect sleep onset while driving. In this study, we have tried to demonstrate that sleepiness and alertness signals are separable with an appropriate margin by extracting suitable features. So, first of all, we have recorded EEG signals from 10 volunteers. They were obliged to avoid sleeping for about 20 hours before the test. We recorded the signals while subjects did a virtual driving game. They tried to pass some barriers that were shown on monitor. Process of recording was ended after 45 minutes. Then, after preprocessing of recorded signals, we labeled them by drowsiness and alertness by using times associated with pass times of the barriers or crash times to them. Then, we extracted some chaotic features (include Higuchi's fractal dimension and Petrosian's fractal dimension) and logarithm of energy of signal. By applying the two-tailed t-test, we have shown that these features can create 95% significance level of difference between drowsiness and alertness in each EEG channels. Ability of each feature has been evaluated by artificial neural network and accuracy of classification with all features was about 83.3% and this accuracy has been obtained without performing any optimization process on classifier.
Keywords: Alertness; drowsy driving; electro encephalography; fractal dimensions; two-tailed t-test.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kurt MB, Sezgin N, Akin M, Kirbas G, Bayram M. The ANN-based computing of drowsy level. Expert Syst Appl. 2009;36:2534–42.
-
- Ueno H, Kaneda M, Tsukino M. Development of drowsiness detection system. In Proc. of 1994 vehicle navigation and information systems Conference, Yokohama, Japan, IEEE. 1994:15–20.
-
- Boverie S, Leqellec JM, Hirl A. Intelligent systems for video monitoring of vehicle cockpit. In The 1998 international congress and exposition ITS: Advanced Controls and vehicle navigation systems. 1998:1–5. SAE international; SAE Technical Paper 980613 doi:10.4271/980613.
-
- Grace R. 2001. Drowsy driver monitor and warning system. In International driving symposium on human factors in driver assessment, training and vehicle design, Aspen, CO; pp. 201–208. citeseer.
-
- Vuckovic A, Radivojevic V, Chen AC, Popovic D. Automatic re cognition of alertness and drowsiness from EEG by an artificial neural network. Med Eng Phys. 2002;24:349–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
