Insights into the complex influence of 5-HT signaling on thalamocortical axonal system development
- PMID: 22607002
- PMCID: PMC3359868
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.8096.x
Insights into the complex influence of 5-HT signaling on thalamocortical axonal system development
Abstract
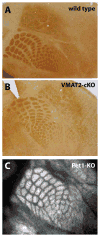
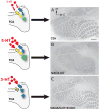
The topographic organization of the thalamocortical axons (TCAs) in the barrel field (BF) in the rodent primary somatosensory cortex results from a succession of temporally and spatially precise developmental events. Prenatally, growth and guidance mechanisms enable TCAs to navigate through the forebrain and reach the cortex. Postnatally, TCAs grow into the cortex, and the refinement of their terminal arborization pattern in layer IV creates barrel-like structures. The combined results of studies performed over the past 20 years clearly show that serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) signaling modulates these pre- and early postnatal developmental processes. In this context, 5-HT signaling can purposely be described as 'modulating' rather than 'controlling' because developmental alterations of 5-HT synthesis, uptake or degradation either have a dramatic, moderate or no effect at all on TCA pathway and BF formation. In this review we summarize and compare the outcomes of diverse pharmacological and genetic manipulations of 5-HT signaling on TCA pathway and BF formation, in an attempt to understand these discrepancies.
© 2012 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience © 2012 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interactions between TrkB signaling and serotonin excess in the developing murine somatosensory cortex: a role in tangential and radial organization of thalamocortical axons.J Neurosci. 2002 Jun 15;22(12):4987-5000. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-12-04987.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12077195 Free PMC article.
-
Refinement of thalamocortical arbors and emergence of barrel domains in the primary somatosensory cortex: a study of normal and monoamine oxidase a knock-out mice.J Neurosci. 2002 Oct 1;22(19):8541-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08541.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12351728 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of elevated serotonin levels on patterns of GAP-43 expression during barrel development in rat somatosensory cortex.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2002 Dec 15;139(2):167-74. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(02)00545-x. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12480131
-
Mechanisms controlling the guidance of thalamocortical axons through the embryonic forebrain.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 May;35(10):1573-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08119.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22607003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of cortical maps: perspectives from the barrel cortex.Neuroscientist. 2007 Feb;13(1):49-61. doi: 10.1177/1073858406296257. Neuroscientist. 2007. PMID: 17229975 Review.
Cited by
-
Perturbed Developmental Serotonin Signaling Affects Prefrontal Catecholaminergic Innervation and Cortical Integrity.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Feb;56(2):1405-1420. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1105-x. Epub 2018 Jun 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 29948943 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental changes in serotonin signaling: Implications for early brain function, behavior and adaptation.Neuroscience. 2017 Feb 7;342:212-231. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.037. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 26905950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible functional links among brain- and skull-related genes selected in modern humans.Front Psychol. 2015 Jun 16;6:794. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00794. eCollection 2015. Front Psychol. 2015. PMID: 26136701 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin functions as a bidirectional guidance molecule regulating growth cone motility.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(5):2247-2262. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03628-2. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32939562 Free PMC article.
-
A novel method for inducing nerve growth via modulation of host resting potential: gap junction-mediated and serotonergic signaling mechanisms.Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Jan;12(1):170-84. doi: 10.1007/s13311-014-0317-7. Neurotherapeutics. 2015. PMID: 25449797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alenina N, Kikic D, Todiras M, Mosienko V, Qadri F, Plehm R, Boye P, Vilianovitch L, Sohr R, Tenner K, Hortnagl H, Bader M. Growth retardation and altered autonomic control in mice lacking brain serotonin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106:10332–10337. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altamura C, Dell’Acqua ML, Moessner R, Murphy DL, Lesch KP, Persico AM. Altered neocortical cell density and layer thickness in serotonin transporter knockout mice: a quantitation study. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:1394–1401. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez C, Vitalis T, Fon EA, Hanoun N, Hamon M, Seif I, Edwards R, Gaspar P, Cases O. Effects of genetic depletion of monoamines on somatosensory cortical development. Neuroscience. 2002;115:753–764. - PubMed
-
- Balkovetz DF, Tiruppathi C, Leibach FH, Mahesh VB, Ganapathy V. Evidence for an imipramine-sensitive serotonin transporter in human placental brush-border membranes. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1989;264:2195–2198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

