De novo assembly and characterization of bark transcriptome using Illumina sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.)
- PMID: 22607098
- PMCID: PMC3431226
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-192
De novo assembly and characterization of bark transcriptome using Illumina sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.)
Abstract
Background: In rubber tree, bark is one of important agricultural and biological organs. However, the molecular mechanism involved in the bark formation and development in rubber tree remains largely unknown, which is at least partially due to lack of bark transcriptomic and genomic information. Therefore, it is necessary to carried out high-throughput transcriptome sequencing of rubber tree bark to generate enormous transcript sequences for the functional characterization and molecular marker development.
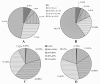
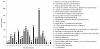
Results: In this study, more than 30 million sequencing reads were generated using Illumina paired-end sequencing technology. In total, 22,756 unigenes with an average length of 485 bp were obtained with de novo assembly. The similarity search indicated that 16,520 and 12,558 unigenes showed significant similarities to known proteins from NCBI non-redundant and Swissprot protein databases, respectively. Among these annotated unigenes, 6,867 and 5,559 unigenes were separately assigned to Gene Ontology (GO) and Clusters of Orthologous Group (COG). When 22,756 unigenes searched against the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Pathway (KEGG) database, 12,097 unigenes were assigned to 5 main categories including 123 KEGG pathways. Among the main KEGG categories, metabolism was the biggest category (9,043, 74.75%), suggesting the active metabolic processes in rubber tree bark. In addition, a total of 39,257 EST-SSRs were identified from 22,756 unigenes, and the characterizations of EST-SSRs were further analyzed in rubber tree. 110 potential marker sites were randomly selected to validate the assembly quality and develop EST-SSR markers. Among 13 Hevea germplasms, PCR success rate and polymorphism rate of 110 markers were separately 96.36% and 55.45% in this study.
Conclusion: By assembling and analyzing de novo transcriptome sequencing data, we reported the comprehensive functional characterization of rubber tree bark. This research generated a substantial fraction of rubber tree transcriptome sequences, which were very useful resources for gene annotation and discovery, molecular markers development, genome assembly and annotation, and microarrays development in rubber tree. The EST-SSR markers identified and developed in this study will facilitate marker-assisted selection breeding in rubber tree. Moreover, this study also supported that transcriptome analysis based on Illumina paired-end sequencing is a powerful tool for transcriptome characterization and molecular marker development in non-model species, especially those with large and complex genomes.
Figures

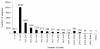
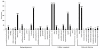

References
-
- Cataldo F. Guayule rubber: a new possible world scenario for the production of natural rubber. Prog Rubber Plastics Technology. 2000;16:31–59.
-
- Leitch AR, Lim KY, Leitch IJ, O’Neill M, Chye ML, Low FC. Molecular cytogenetic studies in rubber, Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg. (Euphorbiaceae) Genome. 1998;41:464–467.
-
- Venkatachalam P, Kumari JP, Sushmakumari S, Jayashree R, Rekha K, Sobha S, Priya P, Kala RG, Thulaseedharan A. Current Perspectives on Application of Biotechnology to Assist the Genetic Improvement of Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.): An Overview. Func Plant Sci Biotechnol. 2007;1(1):1–17.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

