Exome sequencing generates high quality data in non-target regions
- PMID: 22607156
- PMCID: PMC3416685
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-194
Exome sequencing generates high quality data in non-target regions
Abstract
Background: Exome sequencing using next-generation sequencing technologies is a cost efficient approach to selectively sequencing coding regions of human genome for detection of disease variants. A significant amount of DNA fragments from the capture process fall outside target regions, and sequence data for positions outside target regions have been mostly ignored after alignment.
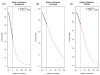
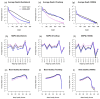
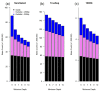
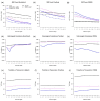
Result: We performed whole exome sequencing on 22 subjects using Agilent SureSelect capture reagent and 6 subjects using Illumina TrueSeq capture reagent. We also downloaded sequencing data for 6 subjects from the 1000 Genomes Project Pilot 3 study. Using these data, we examined the quality of SNPs detected outside target regions by computing consistency rate with genotypes obtained from SNP chips or the Hapmap database, transition-transversion (Ti/Tv) ratio, and percentage of SNPs inside dbSNP. For all three platforms, we obtained high-quality SNPs outside target regions, and some far from target regions. In our Agilent SureSelect data, we obtained 84,049 high-quality SNPs outside target regions compared to 65,231 SNPs inside target regions (a 129% increase). For our Illumina TrueSeq data, we obtained 222,171 high-quality SNPs outside target regions compared to 95,818 SNPs inside target regions (a 232% increase). For the data from the 1000 Genomes Project, we obtained 7,139 high-quality SNPs outside target regions compared to 1,548 SNPs inside target regions (a 461% increase).
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that a significant amount of high quality genotypes outside target regions can be obtained from exome sequencing data. These data should not be ignored in genetic epidemiology studies.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

