Axillary lymph node dose with tangential whole breast radiation in the prone versus supine position: a dosimetric study
- PMID: 22607612
- PMCID: PMC3444918
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-72
Axillary lymph node dose with tangential whole breast radiation in the prone versus supine position: a dosimetric study
Abstract
Background: Prone breast positioning reduces skin reaction and heart and lung dose, but may also reduce radiation dose to axillary lymph nodes (ALNs).
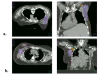
Methods: Women with early stage breast cancer treated with whole breast irradiation (WBI) in the prone position were identified. Patients treated in the supine position were matched for treating physician, laterality, and fractionation. Ipsilateral breast, tumor bed, and Level I, II, and III ALNs were contoured according to the RTOG breast atlas. Clips marking surgically removed sentinel lymph nodes (SLN)s were contoured. Treatment plans developed for each patient were retrospectively analyzed. V90% and V95% was calculated for each axillary level. When present, dose to axillary surgical clips was calculated.
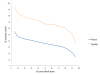
Results: Treatment plans for 46 women (23 prone and 23 supine) were reviewed. The mean V90% and V95% of ALN Level I was significantly lower for patients treated in the prone position (21% and 14%, respectively) than in the supine position (50% and 37%, respectively) (p < 0.0001 and p < 0.0001, respectively). Generally, Level II & III ALNs received little dose in either position. Sentinel node biopsy clips were all contained within axillary Level I. The mean V95% of SLN clips was 47% for patients treated in the supine position and 0% for patients treated in the prone position (p < 0.0001). Mean V90% to SLN clips was 96% for women treated in the supine position but only 13% for women treated in the prone position.
Conclusions: Standard tangential breast irradiation in the prone position results in substantially reduced dose to the Level I axilla as compared with treatment in the supine position. For women in whom axillary coverage is indicated such as those with positive sentinel lymph node biopsy who do not undergo completion axillary dissection, treatment in the prone position may be inappropriate.
Figures
References
-
- Giuliano AE, McCall L, Beitsch P. et al.Locoregional recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection with or without axillary dissection in patients with sentinel lymph node metastases: the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 randomized trial. Ann Surg. 2010;252:426–433. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aristei C, Chionne F, Marsella AR. et al.Evaluation of level I and II axillary nodes included in the standard breast tangential fields and calculation of the administered dose: Results of a prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51:69–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical