Levamisole receptors: a second awakening
- PMID: 22607692
- PMCID: PMC3378725
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2012.04.003
Levamisole receptors: a second awakening
Abstract
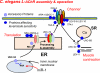
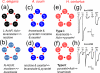
Levamisole and pyrantel are old (1965) but useful anthelmintics that selectively activate nematode acetylcholine ion channel receptors; they are used to treat roundworm infections in humans and animals. Interest in their actions has surged, giving rise to new knowledge and technical advances, including an ability to reconstitute receptors that reveal more details of modes of action/resistance. We now know that the receptors are plastic and may form diverse species-dependent subtypes of receptor with different sensitivities to individual cholinergic anthelmintics. Understanding the biology of the levamisole receptors is expected to inform other studies on anthelmintics (ivermectin and emodepside) that act on ion channels.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

