Idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying presenting in adults with post-prandial diarrhea and reactive hypoglycemia: a case series
- PMID: 22607835
- PMCID: PMC3407696
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-6-132
Idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying presenting in adults with post-prandial diarrhea and reactive hypoglycemia: a case series
Abstract
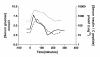
Introduction: We have previously reported the association of gastrointestinal and hypoglycemic symptoms, with idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying. We now report the first series of six similar cases.
Case presentations: Patient 1: A 24-year-old Caucasian man presented to our facility with a six-month history of post-prandial nausea, flatulence, bloating, abdominal discomfort and associated diarrhea. He had associated episodes of fatigue, sweating, anxiety, confusion and craving for sweet foods. Patient 2: A 52-year-old Caucasian woman presented to our facility with a 15-year history of post-prandial bloating, abdominal pain and diarrhea, often associated with nausea, severe sweating, and fatigue. Patient 3: An 18-year-old Caucasian woman presented to our facility with a nine-year history of post-prandial diarrhea, abdominal bloating and pain. There was associated nausea, tremor, lethargy, and craving for sweet foods. Patient 4: A 77-year-old Caucasian woman presented to our facility with a four-month history of epigastric distension, pain after eating and a change in bowel habit. She experienced intermittent severe diarrhea and marked fatigue, nausea and sweating. Patient 5: A 23-year-old Caucasian woman presented to our facility with a two-year history of early satiety, and diarrhea after eating. She also complained of feeling faint and weak between meals, when she became cold and clammy, and on several occasions lost consciousness during these episodes. Patient 6: A 64-year-old Caucasian woman presented to our facility with a 10-year history of nausea, early satiety and profound bloating followed by diarrhea. All symptoms predominantly occurred in the first three hours after eating, when she felt faint, lethargic, and had a craving for sweet foods. In all cases, symptoms were alleviated or resolved by taking sweet food or drink and response to treatment was 90% or greater in all cases.
Conclusions: This series extends our description of this new clinical syndrome. All patients responded well to treatment for accelerated gastric emptying. Clinicians in the disciplines of endocrinology, gastroenterology, neurology and general practice are likely to find this information useful as they will consult patients with some or all of these symptoms and in a proportion of these patients idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying may be present and provide a useful avenue for therapeutic intervention.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Post-prandial reactive hypoglycaemia and diarrhea caused by idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2011 May 13;5:177. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-177. J Med Case Rep. 2011. PMID: 21569503 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics associated with idiopathic rapid gastric emptying in patients referred for gastric emptying studies.J Dig Dis. 2021 Jun;22(6):329-333. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12990. Epub 2021 May 11. J Dig Dis. 2021. PMID: 33840163
-
Gastric electrical stimulation: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(16):1-79. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074486 Free PMC article.
-
Palliative Chemotherapy: Does It Only Provide False Hope? The Role of Palliative Care in a Young Patient With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Adenocarcinoma.J Adv Pract Oncol. 2017 May-Jun;8(4):382-386. Epub 2017 May 1. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2017. PMID: 30018843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current perspectives on the management of gastroparesis.J Postgrad Med. 2005 Jan-Mar;51(1):54-60. J Postgrad Med. 2005. PMID: 15793344 Review.
Cited by
-
International consensus on the diagnosis and management of dumping syndrome.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020 Aug;16(8):448-466. doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0357-5. Epub 2020 May 26. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32457534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor and α-Glucosidase Inhibitor Treatment in Postprandial Hypoglycemia.Clin Diabetes. 2022 Jan;40(1):116-119. doi: 10.2337/cd21-0042. Clin Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35221483 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rapid gastric emptying in diabetes mellitus: Pathophysiology and clinical importance.J Diabetes Complications. 2019 Nov;33(11):107414. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2019.107414. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Diabetes Complications. 2019. PMID: 31439470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Predictors of Rapid Gastric Emptying in Patients Presenting with Dyspeptic Symptoms.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct;64(10):2899-2909. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05620-8. Epub 2019 Apr 13. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30982211
-
Hypoglycemia Associated With Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.JCEM Case Rep. 2024 Nov 4;2(11):luae205. doi: 10.1210/jcemcr/luae205. eCollection 2024 Nov. JCEM Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39498469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leonetti F, Morviducci L, Giaccari A, Sbraccia P, Caiola S, Zorretta D, Lostia O, Tamburrano G. Idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia: a role for glucagon? J Endocrinol Invest. 1992;15:273–278. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

