Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3' UTRs and near stop codons
- PMID: 22608085
- PMCID: PMC3383396
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.003
Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3' UTRs and near stop codons
Abstract
Methylation of the N(6) position of adenosine (m(6)A) is a posttranscriptional modification of RNA with poorly understood prevalence and physiological relevance. The recent discovery that FTO, an obesity risk gene, encodes an m(6)A demethylase implicates m(6)A as an important regulator of physiological processes. Here, we present a method for transcriptome-wide m(6)A localization, which combines m(6)A-specific methylated RNA immunoprecipitation with next-generation sequencing (MeRIP-Seq). We use this method to identify mRNAs of 7,676 mammalian genes that contain m(6)A, indicating that m(6)A is a common base modification of mRNA. The m(6)A modification exhibits tissue-specific regulation and is markedly increased throughout brain development. We find that m(6)A sites are enriched near stop codons and in 3' UTRs, and we uncover an association between m(6)A residues and microRNA-binding sites within 3' UTRs. These findings provide a resource for identifying transcripts that are substrates for adenosine methylation and reveal insights into the epigenetic regulation of the mammalian transcriptome.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
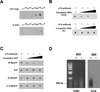

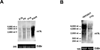

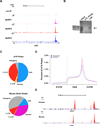
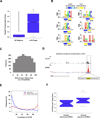
Comment in
-
Implications of widespread covalent modification of mRNA.Circ Res. 2012 Dec 7;111(12):1491-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.281071. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 23223930 No abstract available.
-
An epigenetics gold rush: new controls for gene expression.Nature. 2017 Feb 22;542(7642):406-408. doi: 10.1038/542406a. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28230146 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beemon K, Keith J. Localization of N6-methyladenosine in the Rous sarcoma virus genome. J Mol Biol. 1977;113:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Bringmann P, Luhrmann R. Antibodies specific for N6-methyladenosine react with intact snRNPs U2 and U4/U6. FEBS Lett. 1987;213:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Brockman JM, Singh P, Liu D, Quinlan S, Salisbury J, Graber JH. PACdb: PolyA Cleavage Site and 3'-UTR Database. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3691–3693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

