DOR activation inhibits anoxic/ischemic Na+ influx through Na+ channels via PKC mechanisms in the cortex
- PMID: 22609332
- PMCID: PMC3465681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.05.006
DOR activation inhibits anoxic/ischemic Na+ influx through Na+ channels via PKC mechanisms in the cortex
Abstract
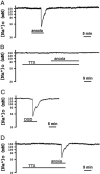
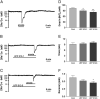
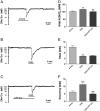
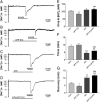
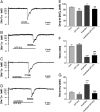
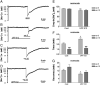
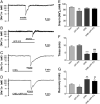
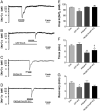
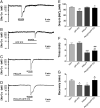
Activation of delta-opioid receptors (DOR) is neuroprotective against hypoxic/ischemic injury in the cortex, which is at least partially related to its action against hypoxic/ischemic disruption of ionic homeostasis that triggers neuronal injury. Na(+) influx through TTX-sensitive voltage-gated Na(+) channels may be a main mechanism for hypoxia-induced disruption of K(+) homeostasis, with DOR activation attenuating the disruption of ionic homeostasis by targeting voltage-gated Na(+) channels. In the present study we examined the role of DOR in the regulation of Na(+) influx in anoxia and simulated ischemia (oxygen-glucose deprivation) as well as the effect of DOR activation on the Na(+) influx induced by a Na(+) channel opener without anoxic/ischemic stress and explored a potential PKC mechanism underlying the DOR action. We directly measured extracellular Na(+) activity in mouse cortical slices with Na(+) selective electrodes and found that (1) anoxia-induced Na(+) influx occurred mainly through TTX-sensitive Na(+) channels; (2) DOR activation inhibited the anoxia/ischemia-induced Na(+) influx; (3) veratridine, a Na(+) channel opener, enhanced the anoxia-induced Na(+) influx; this could be attenuated by DOR activation; (4) DOR activation did not reduce the anoxia-induced Na(+) influx in the presence of chelerythrine, a broad-spectrum PKC blocker; and (5) DOR effects were blocked by PKCβII peptide inhibitor, and PKCθ pseudosubstrate inhibitor, respectively. We conclude that DOR activation inhibits anoxia-induced Na(+) influx through Na(+) channels via PKC (especially PKCβII and PKCθ isoforms) dependent mechanisms in the cortex.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of DOR attenuates anoxic K+ derangement via inhibition of Na+ entry in mouse cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2008 Sep;18(9):2217-27. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhm247. Epub 2008 Jan 17. Cereb Cortex. 2008. PMID: 18203692 Free PMC article.
-
delta-, but not mu-, opioid receptor stabilizes K(+) homeostasis by reducing Ca(2+) influx in the cortex during acute hypoxia.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Jul;212(1):60-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21000. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17373650
-
Cortical delta-opioid receptors potentiate K+ homeostasis during anoxia and oxygen-glucose deprivation.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007 Feb;27(2):356-68. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600352. Epub 2006 Jun 14. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007. PMID: 16773140
-
Ionic storm in hypoxic/ischemic stress: can opioid receptors subside it?Prog Neurobiol. 2010 Apr;90(4):439-70. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.12.007. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Prog Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20036308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of voltage-gated Na+ channels in hypoxia-induced neuronal injuries.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000 Aug;27(8):569-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2000.03309.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10901384 Review.
Cited by
-
δ-opioid receptor activation and microRNA expression of the rat cortex in hypoxia.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051524. Epub 2012 Dec 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23272113 Free PMC article.
-
δ-Opioid receptor activation modified microRNA expression in the rat kidney under prolonged hypoxia.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 15;8(4):e61080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061080. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23596515 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection against hypoxia/ischemia: δ-opioid receptor-mediated cellular/molecular events.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jul;70(13):2291-303. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1167-2. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23014992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
δ-Opioid Receptors, microRNAs, and Neuroinflammation in Cerebral Ischemia/Hypoxia.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 25;11:421. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00421. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32269564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
δ-Opioid receptors up-regulate excitatory amino acid transporters in mouse astrocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;171(23):5417-30. doi: 10.1111/bph.12857. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25052197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ammon-Treiber S, Stolze D, Schröder H, Loh H, Höllt V. Effects of opioid antagonists and morphine in a hippocampal hypoxia/hypoglycemia model. Neuropharmacology. 2005;49:1160–1169. - PubMed
-
- Ayata C, Ropper AH. Ischaemic brain aedema. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2002;9:113–124. - PubMed
-
- Balboni G, Salvadori S, Guerrini R, Negri L, Giannini E, Jinsmaa Y, Bryant SD, Lazarus LH. Potent δ-opioid receptor agonists containing the Dmt-Tic pharmacophore. J. Med. Chem. 2002;45:5556–5563. - PubMed
-
- Banasiak KJ, Burenkova O, Haddad GG. Activation of voltage-sensitive sodium channels during oxygen deprivation leads to apoptotic neuronal death. Neuroscience. 2004;126:31–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

