Novel tyrosine phosphorylation sites in rat skeletal muscle revealed by phosphopeptide enrichment and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS
- PMID: 22609512
- PMCID: PMC3398612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jprot.2012.05.009
Novel tyrosine phosphorylation sites in rat skeletal muscle revealed by phosphopeptide enrichment and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS
Abstract
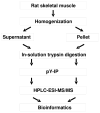
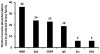
Tyrosine phosphorylation plays a fundamental role in many cellular processes including differentiation, growth and insulin signaling. In insulin resistant muscle, aberrant tyrosine phosphorylation of several proteins has been detected. However, due to the low abundance of tyrosine phosphorylation (<1% of total protein phosphorylation), only a few tyrosine phosphorylation sites have been identified in mammalian skeletal muscle to date. Here, we used immunoprecipitation of phosphotyrosine peptides prior to HPLC-ESI-MS/MS analysis to improve the discovery of tyrosine phosphorylation in relatively small skeletal muscle biopsies from rats. This resulted in the identification of 87 distinctly localized tyrosine phosphorylation sites in 46 muscle proteins. Among them, 31 appear to be novel. The tyrosine phosphorylated proteins included major enzymes in the glycolytic pathway and glycogen metabolism, sarcomeric proteins, and proteins involved in Ca(2+) homeostasis and phosphocreatine resynthesis. Among proteins regulated by insulin, we found tyrosine phosphorylation sites in glycogen synthase, and two of its inhibitors, GSK-3α and DYRK1A. Moreover, tyrosine phosphorylation sites were identified in several MAP kinases and a protein tyrosine phosphatase, SHPTP2. These results provide the largest catalogue of mammalian skeletal muscle tyrosine phosphorylation sites to date and provide novel targets for the investigation of human skeletal muscle phosphoproteins in various disease states.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
In vivo phosphoproteome of human skeletal muscle revealed by phosphopeptide enrichment and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS.J Proteome Res. 2009 Nov;8(11):4954-65. doi: 10.1021/pr9007267. J Proteome Res. 2009. PMID: 19764811 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin and exercise decrease glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity by different mechanisms in rat skeletal muscle.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 27;274(35):24896-900. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.35.24896. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10455163
-
Acute selective glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition enhances insulin signaling in prediabetic insulin-resistant rat skeletal muscle.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Jun;288(6):E1188-94. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00547.2004. Epub 2005 Jan 25. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 15671078
-
Participation of annexins in protein phosphorylation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1997 Jun;53(6):522-6. doi: 10.1007/s000180050066. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1997. PMID: 9230930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal processing by protein tyrosine phosphorylation in plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2011 Jul;6(7):942-51. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.7.15261. Plant Signal Behav. 2011. PMID: 21628997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Glioblastoma Phosphotyrosine-Containing Proteins with Two-Dimensional Western Blotting and Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:134050. doi: 10.1155/2015/134050. Epub 2015 May 18. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26090378 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

