Age and gender dependent bioavailability of R- and R,S-α-lipoic acid: a pilot study
- PMID: 22609537
- PMCID: PMC4084596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.05.002
Age and gender dependent bioavailability of R- and R,S-α-lipoic acid: a pilot study
Abstract
Lipoic acid (LA) shows promise as a beneficial micronutrient toward improving elder health. Studies using old rats show that (R)-α-LA (R-LA) significantly increases low molecular weight antioxidants that otherwise decline with age. Despite this rationale for benefiting human health, little is known about age-associated alterations in absorption characteristics of LA, or whether the commercially available racemic mixture of LA (R,S-LA) is equally as bioavailable as the naturally occurring R-enantiomer. To address these discrepancies, a pilot study was performed to establish which form of LA is most effectively absorbed in older subjects relative to young volunteers. Young adults (average age=32 years) and older adults (average age=79 years) each received 500 mg of either R- or R,S-LA. Blood samples were collected for 3h after supplementation. After a washout period they were given the other chiral form of LA not originally ingested. Results showed that 2 out of 6 elder males exhibited greater maximal plasma LA and area under the curve for the R-form of LA versus the racemic mixture. The elder subjects also demonstrated a reduced time to reach maximal plasma LA concentration following R-LA supplementation than for the racemic mixture. In contrast, young males had a tendency for increased bioavailability of R,S-LA. Overall, bioavailability for either LA isoform was much more variable between older subjects compared to young adults. Plasma glutathione levels were not altered during the sampling period. Thus subject age, and potential for varied response, should be considered when determining an LA supplementation regimen.
Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
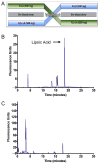
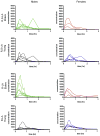
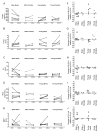
References
-
- Schmidt U, Grafen P, Goedde HW. Chemistry and biochemistry of alpha-lipoic acid. Angewandte Chemie (International ed in English) 1965;4:846–56. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara K, Okamura-Ikeda K, Motokawa Y. Lipoylation of acyltransferase components of alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:12932–6. - PubMed
-
- Teichert J, Kern J, Tritschler HJ, Ulrich H, Preiss R. Investigations on the pharmacokinetics of alpha-lipoic acid in healthy volunteers. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 1998;36:625–8. - PubMed
-
- Breithaupt-Grögler K, Niebch G, Schneider E, Erb K, Hermann R, Blume HH, et al. Dose-proportionality of oral thioctic acid – coincidence of assessments via pooled plasma and individual data. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 1999;8:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Smith AR, Shenvi SV, Widlansky M, Suh JH, Hagen TM. Lipoic acid as a potential therapy for chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 2004;11:1135–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

