Targeting the lateral interactions of transmembrane domain 5 of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1
- PMID: 22609737
- PMCID: PMC3378808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.05.013
Targeting the lateral interactions of transmembrane domain 5 of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1
Abstract
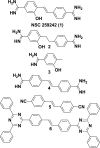
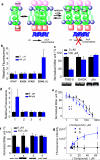
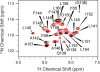
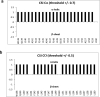
The lateral transmembrane protein-protein interaction has been regarded as "undruggable" despite its importance in many biological processes. The homo-trimerization of transmembrane domain 5 (TMD-5) of latent membrane protein 1 (LMP-1) is critical for the constitutive oncogenic activation of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Herein, we report a small molecule agent, NSC 259242 (compound 1), to be a TMD-5 self-association disruptor. Both the positively charged acetimidamide functional groups and the stilbene backbone of compound 1 are essential for its inhibitory activity. Furthermore, cell-based assays revealed that compound 1 inhibits full-length LMP-1 signaling in EBV infected B cells. These studies demonstrated a new strategy for identifying small molecule disruptors for investigating transmembrane protein-protein interactions.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Sackett DL, Sept D. Protein-protein interactions: making drug design second nature. Nat. Chem. 2009;1:596–597. - PubMed
-
- Arkin MR, Wells JA. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions: progressing towards the dream. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3:301–317. - PubMed
-
- Wilson AJ. Inhibition of protein-protein interactions using designed molecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009;38:3289–3300. - PubMed
-
- Yin H. Exogenous agents that target transmembrane domains of proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008;47:2744–2752. - PubMed
-
- Zhao TX, Martinko AJ, Le VH, Zhao J, Yin H. Development of agents that modulate protein-protein interactions in membranes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010;16:1055–1062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

