Identification of a third osmoprotectant transport system, the osmU system, in Salmonella enterica
- PMID: 22609924
- PMCID: PMC3416524
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00495-12
Identification of a third osmoprotectant transport system, the osmU system, in Salmonella enterica
Abstract
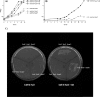
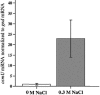
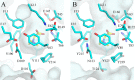
The growth of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium mutants lacking the ProP and ProU osmoprotectant transport systems is stimulated by glycine betaine in high-osmolarity media, suggesting that this organism has an additional osmoprotectant transport system. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that the genome of this organism contains a hitherto-unidentified operon, designated osmU, consisting of four genes whose products show high similarity to ABC-type transport systems for osmoprotectants in other bacteria. The osmU operon was inactivated by a site-directed deletion, which abolished the ability of glycine betaine to alleviate the inhibitory effect of high osmolarity and eliminated the accumulation of [(14)C]glycine betaine and [(14)C]choline-O-sulfate in high-osmolarity media in a strain lacking the ProP and ProU systems. Although the OsmU system can take up glycine betaine and choline-O-sulfate, these two osmoprotectants are recognized at low affinity by this transporter, suggesting that there might be more efficient substrates that are yet to be discovered. The transcription of osmU is induced 23-fold by osmotic stress (0.3 M NaCl). The osmU operon is present in the genomes of a number of Enterobacteriaceae, and orthologs of the OsmU system can be recognized in a wide variety of Bacteria and Archaea. The structure of the periplasmic binding protein component of this transporter, OsmX, was modeled on the crystallographic structure of the glycine betaine-binding protein ProX of Archaeoglobus fulgidus; the resultant model indicated that the amino acids that constitute substrate-binding site, including an "aromatic cage" made up of four tyrosines, are conserved between these two proteins.
Figures

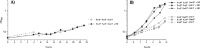


Similar articles
-
OusB, a broad-specificity ABC-type transporter from Erwinia chrysanthemi, mediates uptake of glycine betaine and choline with a high affinity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jul;71(7):3389-98. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.7.3389-3398.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16000740 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of YehZ, a putative osmoprotectant transporter, in tempering growth of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Nov 28;23(11):1560-8. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1308.08006. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23966021
-
Molecular characterization of the proU loci of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli encoding osmoregulated glycine betaine transport systems.Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1025-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00253.x. Mol Microbiol. 1989. PMID: 2691838
-
The osmoprotectant proline betaine is a major substrate for the binding-protein-dependent transport system ProU of Escherichia coli K-12.Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Mar 20;246(6):783-6. doi: 10.1007/BF00290728. Mol Gen Genet. 1995. PMID: 7898450
-
Adaptation of Escherichia coli to high osmolarity environments: osmoregulation of the high-affinity glycine betaine transport system proU.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994 May;14(1):3-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00067.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994. PMID: 8011357 Review.
Cited by
-
OpuF, a New Bacillus Compatible Solute ABC Transporter with a Substrate-Binding Protein Fused to the Transmembrane Domain.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Oct 1;84(20):e01728-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01728-18. Print 2018 Oct 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30097444 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Human Body Temperature on Stress Tolerance and Transcriptome of Cronobacter sakazakii.Pathogens. 2025 Mar 14;14(3):281. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14030281. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40137766 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and physiological adaptations of psychrophilic Pseudarthrobacter psychrotolerans YJ56 under temperature stress.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 11;13(1):14970. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42179-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37697016 Free PMC article.
-
ProP is required for the survival of desiccated Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium cells on a stainless steel surface.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Jul;79(14):4376-84. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00515-13. Epub 2013 May 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23666329 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of outer membrane vesicle-associated proteins in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2014 Oct;82(10):4001-10. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01416-13. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24935973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barron A, Jung JU, Villarejo M. 1987. Purification and characterization of a glycine betaine binding protein from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 262:11841–11846 - PubMed
-
- Biemans-Oldehinkel E, Doeven MK, Poolman B. 2006. ABC transporter architecture and regulatory roles of accessory domains. FEBS Lett. 580:1023–1035 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

