As an independent unfavorable prognostic factor, IL-8 promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of AKT signaling
- PMID: 22610073
- PMCID: PMC3405654
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgs181
As an independent unfavorable prognostic factor, IL-8 promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of AKT signaling
Abstract
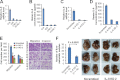
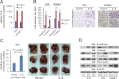
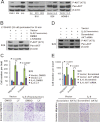
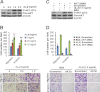
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) has the highest metastatic potential among head and neck cancers. Distant metastasis is the major cause of treatment failure. The role of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in NPC progression remains unknown. Our multivariate survival analyses of 255 patients with NPC revealed that higher IL-8 expression in primary NPC tissue was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival, disease-free survival, and distant metastasis-free survival of the patients. In vitro study revealed that IL-8 was highly expressed in the established high-metastasis NPC clone S18 relative to the low-metastasis cells. Suppression of IL-8 by short-hairpin RNA reduced the expression of IL-8 in S18 cells and subsequently inhibited migration, invasion, and hepatic metastasis of the cells without influencing cellular growth. Overexpression of IL-8 in S26 cells resulted in increased migration, invasion, and metastasis capabilities of the cells without affecting cellular growth. Exogenous IL-8 enhanced the migration and invasion of low-metastasis CNE-2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. An epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) could be induced by IL-8 in various NPC cell lines. The high level of phosphorylated AKT in S18 cells could be suppressed by knocking down IL-8 expression. Further, IL-8-promoted migration and invasion could be abolished by either the application of the phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 or the knock down of AKT expression by using small-interfering RNA. In summary, IL-8 serves as an independent prognostic indicator of overall survival, disease-free survival, and metastasis-free survival for patients with NPC. IL-8 promotes NPC metastasis via autocrine and paracrine means, involving activation of AKT signaling and inducing EMT in NPC cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
c-Src activation promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis by inducing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: a new and promising target for NPC.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):28340-55. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8634. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27078847 Free PMC article.
-
Hes1 triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like cellular marker alterations and promotes invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by activating the PTEN/AKT pathway.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 3;6(34):36713-30. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5457. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26452025 Free PMC article.
-
ADAM22 acts as a novel predictive biomarker for unfavorable prognosis and facilitates metastasis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Apr;256:155264. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155264. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38518731
-
Blocking PI3K/Akt signaling attenuates metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through induction of mesenchymal-epithelial reverting transition.Oncol Rep. 2014 Aug;32(2):559-66. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3220. Epub 2014 May 29. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24889918
-
HMGA2 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and is associated with tumor resistance and poor prognosis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 18;13:1271080. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1271080. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38304037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between serum inflammatory cytokines and lifestyle factors in gastric cancer.Mol Clin Oncol. 2019 Mar;10(3):401-414. doi: 10.3892/mco.2019.1804. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Mol Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30847182 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Chemokines in Thyroid Cancer Microenvironment: Is CXCL8 the Main Player?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Jun 21;9:314. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00314. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29977225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCL8 Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1302:25-39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-62658-7_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34286439 Review.
-
Cancer metastasis: issues and challenges.Chin J Cancer. 2017 Apr 3;36(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0206-7. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28372569 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-8 is a prognostic indicator in human hilar cholangiocarcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):8376-84. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26339407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wee, J.T.,, et al. Is nasopharyngeal cancer really a “Cantonese cancer”? Chin. J. Cancer, (2010);29,:517–526. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad, A.,, et al. Distant metastases of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a study of 256 male patients. J. Surg. Oncol., (1986);33,:194–197. - PubMed
-
- Geara, F.B.,, et al. Carcinoma of the nasopharynx treated by radiotherapy alone: determinants of distant metastasis and survival. Radiother Oncol, (1997);43,:53–61. - PubMed
-
- Lee, A.W.,, et al. Retrospective analysis of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during 1976–1985: survival after local recurrence. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys., (1993);26,:773–782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

