Notch-RBP-J signaling regulates the transcription factor IRF8 to promote inflammatory macrophage polarization
- PMID: 22610140
- PMCID: PMC3513378
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2304
Notch-RBP-J signaling regulates the transcription factor IRF8 to promote inflammatory macrophage polarization
Abstract
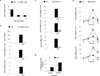
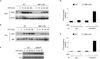
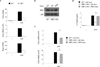
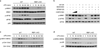
Emerging concepts suggest that the functional phenotype of macrophages is regulated by transcription factors that define alternative activation states. We found that RBP-J, the main nuclear transducer of signaling via Notch receptors, augmented Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-induced expression of key mediators of classically activated M1 macrophages and thus of innate immune responses to Listeria monocytogenes. Notch-RBP-J signaling controlled expression of the transcription factor IRF8 that induced downstream M1 macrophage-associated genes. RBP-J promoted the synthesis of IRF8 protein by selectively augmenting kinase IRAK2-dependent signaling via TLR4 to the kinase MNK1 and downstream translation-initiation control through eIF4E. Our results define a signaling network in which signaling via Notch-RBP-J and TLRs is integrated at the level of synthesis of IRF8 protein and identify a mechanism by which heterologous signaling pathways can regulate the TLR-induced inflammatory polarization of macrophages.
Figures



References
-
- Krausgruber T, et al. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2011;12:231–238. - PubMed
-
- Satoh T, et al. The Jmjd3-Irf4 axis regulates M2 macrophage polarization and host responses against helminth infection. Nat. Immunol. 2010;11:936–944. - PubMed
-
- Holtschke T, et al. Immunodeficiency and chronic myelogenous leukemia-like syndrome in mice with a targeted mutation of the ICSBP gene. Cell. 1996;87:307–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

