Lower serum hepcidin and greater parenchymal iron in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients with C282Y HFE mutations
- PMID: 22611049
- PMCID: PMC3462887
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.25856
Lower serum hepcidin and greater parenchymal iron in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients with C282Y HFE mutations
Abstract
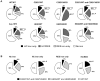
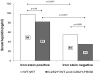
Hepcidin regulation is linked to both iron and inflammatory signals and may influence iron loading in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The aim of this study was to examine the relationships among HFE genotype, serum hepcidin level, hepatic iron deposition, and histology in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Single-nucleotide polymorphism genotyping for C282Y (rs1800562) and H63D (rs1799945) HFE mutations was performed in 786 adult subjects in the NASH Clinical Research Network (CRN). Clinical, histologic, and laboratory data were compared using nonparametric statistics and multivariate logistic regression. NAFLD patients with C282Y, but not H63D mutations, had lower median serum hepcidin levels (57 versus 65 ng/mL; P = 0.01) and higher mean hepatocellular (HC) iron grades (0.59 versus 0.28; P < 0.001), compared to wild-type (WT) subjects. Subjects with hepatic iron deposition had higher serum hepcidin levels than subjects without iron for all HFE genotypes (P < 0.0001). Hepcidin levels were highest among patients with mixed HC/reticuloendothelial system cell (RES) iron deposition. H63D mutations were associated with higher steatosis grades and NAFLD activity scores (odds ratio [OR], ≥1.4; 95% confidence interval [CI]: >1.0, ≤2.5; P ≤ 0.041), compared to WT, but not with either HC or RES iron. NAFLD patients with C282Y mutations had less ballooning or NASH (OR, ≤0.62; 95% CI: >0.39, <0.94; P ≤ 0.024), compared to WT subjects.
Conclusions: The presence of C282Y mutations in patients with NAFLD is associated with greater HC iron deposition and decreased serum hepcidin levels, and there is a positive relationship between hepatic iron stores and serum hepcidin level across all HFE genotypes. These data suggest that body iron stores are the major determinant of hepcidin regulation in NAFLD, regardless of HFE genotype. A potential role for H63D mutations in NAFLD pathogenesis is possible through iron-independent mechanisms.
Copyright © 2012 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bonkovsky HL, Lambrecht RW, Shan Y. Iron as a co-morbid factor in nonhemochromatotic liver disease. Alcohol. 2003;30:137–144. - PubMed
-
- Bonkovsky HL, Jawaid Q, Tortorelli K, et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and iron: increased prevalence of mutations of the HFE gene in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 1999;31:421–429. - PubMed
-
- George DK, Goldwurm S, MacDonald GA, et al. Increased hepatic iron concentration in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with increased fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Fargion S, Mattioli M, Fracanzani AL, et al. Hyperferritinemia, iron overload, and multiple metabolic alterations identify patients at risk for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:2448–2455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1RR02501401/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK002957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR020359/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK087696/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK087696/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR02413101/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK087696/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24DK002957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR020359/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
