Insulin resistance improves metabolic and contractile efficiency in stressed rat heart
- PMID: 22611083
- PMCID: PMC3405268
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.12-208991
Insulin resistance improves metabolic and contractile efficiency in stressed rat heart
Abstract
Insulin resistance is a prominent feature in heart failure, while hyperglycemia impairs cardiac contraction. We propose that decreased insulin-mediated glucose uptake by the heart preserves cardiac function in response to metabolic and hemodynamic stress. To test this hypothesis, we fed rats a high-sucrose diet (HSD). Energy substrate metabolism and cardiac work were determined ex vivo in a sequential protocol simulating metabolic and hemodynamic stress. Compared to chow-fed, control rats, HSD impaired myocardial insulin responsiveness and induced profound metabolic changes in the heart, characterized by reduced rates of glucose uptake (7.91 ± 0.30 vs. 10.73 ± 0.67 μmol/min/g dry weight; P<0.001) but increased rates of glucose oxidation (2.38 ± 0.17 vs. 1.50 ± 0.15 μmol/min/g dry weight; P<0.001) and oleate oxidation (2.29 ± 0.11 vs. 1.96 ± 0.12 μmol/min/g dry weight; P<0.05). Tight coupling of glucose uptake and oxidation and improved cardiac efficiency were associated with a reduction in glucose 6-phosphate and oleoyl-CoA levels, as well as a reduction in the content of uncoupling protein 3. Our results suggest that insulin resistance lessens fuel toxicity in the stressed heart. This calls for a new exploration of the mechanisms regulating substrate uptake and oxidation in the insulin-resistant heart.
Figures

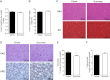

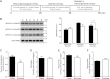
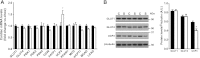

References
-
- Ingelsson E., Sundstrom J., Arnlov J., Zethelius B., Lind L. (2005) Insulin resistance and risk of congestive heart failure. JAMA 294, 334–341 - PubMed
-
- Garvey W. T., Hardin D., Juhaszova M., Dominguez J. H. (1993) Effects of diabetes on myocardial glucose transport system in rats: implications for diabetic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiol. 264, H837–H844 - PubMed
-
- Kannel W. B., Hjortland M., Castelli W. P. (1974) Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. Am. J. Cardiol. 34, 29–34 - PubMed
-
- Rossetti L. (2004) Glucose toxicity: effect of chronic hyperglycemia on insulin action. In Diabetes Mellitus: A Fundamental and Clinical Text (LeRoith D., Taylor S. I., Olefsky J. M., eds) pp. 939–951, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

