The clock gene, brain and muscle Arnt-like 1, regulates adipogenesis via Wnt signaling pathway
- PMID: 22611086
- PMCID: PMC6137895
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.12-205781
The clock gene, brain and muscle Arnt-like 1, regulates adipogenesis via Wnt signaling pathway
Abstract
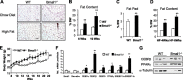
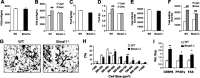
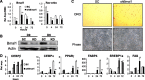
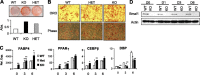
Circadian clocks in adipose tissue are known to regulate adipocyte biology. Although circadian dysregulation is associated with development of obesity, the underlying mechanism has not been established. Here we report that disruption of the clock gene, brain and muscle Arnt-like 1 (Bmal1), in mice led to increased adipogenesis, adipocyte hypertrophy, and obesity, compared to wild-type (WT) mice. This is due to its cell-autonomous effect, as Bmal1 deficiency in embryonic fibroblasts, as well as stable shRNA knockdown (KD) in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte and C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells, promoted adipogenic differentiation. We demonstrate that attenuation of Bmal1 function resulted in down-regulation of genes in the canonical Wnt pathway, known to suppress adipogenesis. Promoters of these genes (Wnt10a, β-catenin, Dishevelled2, TCF3) displayed Bmal1 occupancy, indicating direct circadian regulation by Bmal1. As a result, Wnt signaling activity was attenuated by Bmal1 KD and augmented by its overexpression. Furthermore, stabilizing β-catenin through Wnt ligand or GSK-3β inhibition achieved partial restoration of blunted Wnt activity and suppression of increased adipogenesis induced by Bmal1 KD. Taken together, our study demonstrates that Bmal1 is a critical negative regulator of adipocyte development through transcriptional control of components of the canonical Wnt signaling cascade, and provides a mechanistic link between circadian disruption and obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors thank The Methodist Hospital Research Institute (TMHRI) for funding support and the Center for Diabetes Research for technical assistance.
Figures



References
-
- Panda S., Antoch M. P., Miller B. H., Su A. I., Schook A. B., Straume M., Schultz P. G., Kay S. A., Takahashi J. S., Hogenesch J. B. (2002) Coordinated transcription of key pathways in the mouse by the circadian clock. Cell , 307–320 - PubMed
-
- Otway D. T., Frost G., Johnston J. D. (2009) Circadian rhythmicity in murine pre-adipocyte and adipocyte cells. Chronobiol. Int. , 1340–1354 - PubMed
-
- Wu X., Zvonic S., Floyd Z. E., Kilroy G., Goh B. C., Hernandez T. L., Eckel R. H., Mynatt R. L., Gimble J. M. (2007) Induction of circadian gene expression in human subcutaneous adipose-derived stem cells. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) , 2560–2570 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

