G-protein-coupled receptors in adult neurogenesis
- PMID: 22611178
- PMCID: PMC3400834
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.111.004762
G-protein-coupled receptors in adult neurogenesis
Abstract
The importance of adult neurogenesis has only recently been accepted, resulting in a completely new field of investigation within stem cell biology. The regulation and functional significance of adult neurogenesis is currently an area of highly active research. G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have emerged as potential modulators of adult neurogenesis. GPCRs represent a class of proteins with significant clinical importance, because approximately 30% of all modern therapeutic treatments target these receptors. GPCRs bind to a large class of neurotransmitters and neuromodulators such as norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin. Besides their typical role in cellular communication, GPCRs are expressed on adult neural stem cells and their progenitors that relay specific signals to regulate the neurogenic process. This review summarizes the field of adult neurogenesis and its methods and specifies the roles of various GPCRs and their signal transduction pathways that are involved in the regulation of adult neural stem cells and their progenitors. Current evidence supporting adult neurogenesis as a model for self-repair in neuropathologic conditions, adult neural stem cell therapeutic strategies, and potential avenues for GPCR-based therapeutics are also discussed.
Figures
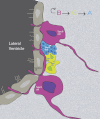
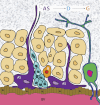
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoid hedgehog agonists in neurogenesis.Vitam Horm. 2011;87:207-15. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386015-6.00030-5. Vitam Horm. 2011. PMID: 22127244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell-based neuroprotective and neurorestorative strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 May 5;11(5):2039-55. doi: 10.3390/ijms11052039. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20559500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noggin rescues age-related stem cell loss in the brain of senescent mice with neurodegenerative pathology.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):11625-11630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1813205115. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30352848 Free PMC article.
-
Actions of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Glucocorticoid Stress in Neurogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 2;18(11):2312. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112312. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29099059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation, mitochondria, and the inhibition of adult neurogenesis.J Neurosci Res. 2011 Dec;89(12):1989-96. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22768. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Neurosci Res. 2011. PMID: 21910136 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Importance of GPCR-Mediated Microglial Activation in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Aug 21;12:258. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00258. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30186116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mice deficient for G-protein-coupled receptor 75 display altered presynaptic structural protein expression and disrupted fear conditioning recall.J Neurochem. 2023 Jun;165(6):827-841. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15818. Epub 2023 Apr 21. J Neurochem. 2023. PMID: 36978267 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Neurogenic Small Molecules as Innovative Treatments for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Molecules. 2016 Sep 1;21(9):1165. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091165. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27598108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin Promotes Development and Regeneration of Spinal Motor Neurons in Zebrafish.Cell Rep. 2015 Nov 3;13(5):924-32. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.09.050. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26565906 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive osseous heteroplasia: diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis.Appl Clin Genet. 2015 Jan 30;8:37-48. doi: 10.2147/TACG.S51064. eCollection 2015. Appl Clin Genet. 2015. PMID: 25674011 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L, Hansson E. (2006) Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:41–53 - PubMed
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Knight GE, Fumagalli M, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, et al. (2006) International Union of Pharmacology. LVIII: Update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol Rev 58:281–341 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdipranoto A, Wu S, Stayte S, Vissel B. (2008) The role of neurogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases and its implications for therapeutic development. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 7:187–210 - PubMed
-
- Agasse F, Bernardino L, Kristiansen H, Christiansen SH, Ferreira R, Silva B, Grade S, Woldbye DP, Malva JO. (2008) Neuropeptide Y promotes neurogenesis in murine subventricular zone. Stem Cells 26:1636–1645 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

